FORMS of GOVERNMENT

FORMS of GOVERNMENT
SS6CG4: The student will compare and contrast various forms of government.
FORMS of GOVERNMENT
• SS6CG4: a. Describe the ways government systems distribute power : unitary, confederation, and federal
ESSENTIAL QUESTION
How is power distributed in different forms of government (unitary, confederation, and federal)?
Social Studies Theme:
GOVERNANCE
• The student will understand that as society increases in complexity and interacts with other societies, the complexity of the government increases.
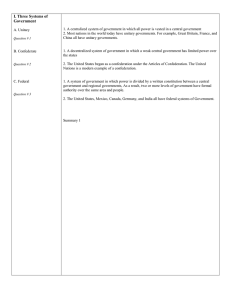
Types of Distribution
• There are three (3) basic types of ways in which power is distributed, or spread throughout a government: to spread power throughout government
• Unitary
• Confederation
• Federal
These terms are just words to describe WHO has the power in the government, WHO is the decision maker.
Types of Distribution
• UNITARY: a form of government in which power is held by one central authority
Examples of Unitary governments:
Dictatorship, absolute monarchy
Countries with Unitary governments:
Iran, Cuba, North Korea
Types of Distribution
• Confederation voluntary associations of independent states that, to secure some common purpose, agree to certain limitations on their freedom of action and establish some joint machinery of consultation or deliberation.
In simpler terms, it means that groups get together to voluntarily work together for each other’s benefit. It is not required that they work together.
Each group may choose to leave the confederation at any time.
Types of Distribution
• Confederation (continued)
• Usually created by a treaty, in today’s world, confederations are mostly created for common action towards other states
Types of Leaders:
Secretary-General (UN) United Nations
Example:
European Union, United Nations
Types of Distribution
• Federal:
A form of government in which power is divided between one central and several regional authorities
• Types of leaders:
Presidents, Prime Ministers
Examples of Federal governments:
United States, Canada, Australia, Russia, Belgium, India,
Malaysia