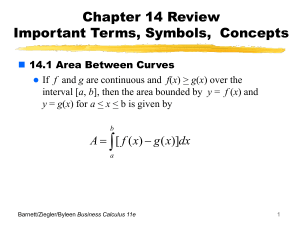
Calculus 4.3 power point lesson
advertisement

Chapter 4 Additional Derivative Topics Section 3 Derivatives of Products and Quotients Objectives for Section 4.3 Derivatives of Products and Quotients The student will be able to calculate: ■ the derivative of a product of two functions, and ■ the derivative of a quotient of two functions. Barnett/Ziegler/Byleen Business Calculus 12e 2 Review Exponential & Log Derivatives Find the derivative of each function: 𝑦 = 𝑒𝑥 𝑦′ = 𝑒 𝑥 𝑦 = ln 𝑥 1 𝑦′ = 𝑥 𝑦 = 𝑏𝑥 𝑦′ = 𝑏 𝑥 ln 𝑏 𝑦 = log 𝑏 𝑥 1 𝑦′ = 𝑥 ln 𝑏 Barnett/Ziegler/Byleen Business Calculus 12e 3 Example 1 Derivative of a Product Sometimes the derivative of a product can be found by first using the distributive property. Find the derivative of y = 5x2(x3 + 2). 𝑦 = 5𝑥 5 + 10𝑥 2 𝑦 ′ = 25𝑥 4 + 20𝑥 But what about a product like this one? 𝑦 = 5𝑥 8 𝑒 𝑥 You MUST use the Product Rule… Barnett/Ziegler/Byleen Business Calculus 12e 4 Derivatives of Products Theorem 1 (Product Rule) If f (x) = L(x) R(x), and if L(x) and R(x) exist, then f (x) = L(x) R(x) + R(x) L(x) Mnemonic: Left D Right + Right D Left 𝐿𝑅′ + 𝑅𝐿′ Barnett/Ziegler/Byleen Business Calculus 12e 5 Example 2 𝑓 𝑥 = 5𝑥 8 𝑒 𝑥 Find 𝑓′(𝑥) 𝐿 𝑥 = 5𝑥 8 𝑅 𝑥 = 𝑒𝑥 𝐿′ 𝑥 = 40𝑥 7 𝑅′ 𝑥 = 𝑒 𝑥 𝑓 ′ (𝑥) = 𝐿 𝑥 ∙ 𝑅′ 𝑥 + 𝑅(𝑥) ∙ 𝐿′(𝑥) 𝑓 ′ (𝑥) = 5𝑥 8 ∙ 𝑒 𝑥 + 𝑒 𝑥 ∙ 40𝑥 7 𝑓 ′ (𝑥) = 5𝑥 7 𝑒 𝑥 (𝑥 + 8) Barnett/Ziegler/Byleen Business Calculus 12e 6 Example 3 𝑦 = 𝑥 + 2 3𝑥 Find y′ 𝐿 𝑥 =𝑥+2 𝑅 𝑥 = 3𝑥 𝐿′ 𝑥 = 1 𝑅′ 𝑥 = 3𝑥 ln 3 𝑦 ′ = 𝐿 𝑥 ∙ 𝑅′ 𝑥 + 𝑅(𝑥) ∙ 𝐿′(𝑥) 𝑦 ′ = 𝑥 + 2 (3𝑥 ln 3) + 3𝑥 ∙ 1 𝑦 ′ = 𝑥 + 2 (3𝑥 ln 3) + 3𝑥 𝑦 ′ = 3𝑥 [ 𝑥 + 2 ln 3 + 1] Barnett/Ziegler/Byleen Business Calculus 12e 7 Derivatives of Quotients Some derivatives of quotients can be found by rewriting the function: 4𝑥 3 − 8𝑥 2 𝑓 ′ 𝑥 = 4𝑥 − 4 𝑓 𝑥 = 2𝑥 = 2𝑥 2 − 4𝑥 You can’t do that with functions like this: 𝑡 3 − 3𝑡 𝑦= 2 𝑡 −4 Barnett/Ziegler/Byleen Business Calculus 12e 8 Derivatives of Quotients Theorem 2 (Quotient Rule) 𝐻(𝑥) If f (x) = , and if H(x) and L(x) exist, then 𝐿(𝑥) ′ 𝑥 − 𝐻(𝑥) ∙ 𝐿′(𝑥) 𝐿 𝑥 ∙ 𝐻 𝑓′ 𝑥 = 𝐿(𝑥)2 Mnemonic: 𝐿𝑜𝑤 𝐷 𝐻𝑖𝑔ℎ−𝐻𝑖𝑔ℎ 𝐷 𝐿𝑜𝑤 𝐿𝑜𝑤 2 𝐿𝐻 ′ − 𝐻𝐿′ 𝐿2 Barnett/Ziegler/Byleen Business Calculus 12e 9 Example 4 𝑡 3 − 3𝑡 Find the derivative of: 𝑦 = 2 𝑡 −4 𝐻 𝑡 = 𝑡 3 − 3𝑡 𝐿 𝑡 = 𝑡2 − 4 𝐻 ′ 𝑡 = 3𝑡 2 − 3 𝐿′ 𝑡 = 2𝑡 ′ 𝑡 − 𝐻(𝑡) ∙ 𝐿′(𝑡) 𝐿 𝑡 ∙ 𝐻 𝑦′ = 𝐿(𝑡)2 𝑦′ 𝑡 2 − 4 3𝑡 2 − 3 − 𝑡 3 − 3𝑡 2𝑡 = 𝑡2 − 4 2 4 − 3𝑡 2 − 12𝑡 2 + 12 − 2𝑡 4 − 6𝑡 2 3𝑡 𝑦′ = 𝑡2 − 4 2 Barnett/Ziegler/Byleen Business Calculus 12e 4 − 9𝑡 2 + 12 𝑡 𝑦′ = 𝑡2 − 4 2 10 Example 5 Find the derivative of 𝑦 = 𝐻 𝑥 = ln 𝑥 1 ′ 𝐻 𝑥 = 𝑥 𝐿 𝑥 ∙ 𝐿 𝑥 = 2𝑥 + 5 𝐿′ 𝑥 = 2 𝐻′ 𝑥 − 𝐻(𝑥) ∙ 𝐿′(𝑥) = 𝐿(𝑥)2 1 2𝑥 + 5 ∙ − (ln 𝑥) ∙ 2 𝑥 𝑦′ = 2𝑥 + 5 2 𝑦′ ln 𝑥 2𝑥+5 2𝑥 + 5 − 2𝑥 ln 𝑥 𝑥 𝑦′ = 2𝑥 + 5 2 2𝑥 + 5 − 2𝑥ln 𝑥 𝑦 = 𝑥 2𝑥 + 5 2 ′ 2𝑥 + 5 − 2 ln 𝑥 𝑥 ′ 𝑦 = 2𝑥 + 5 2 Barnett/Ziegler/Byleen Business Calculus 12e 11 Homework Barnett/Ziegler/Byleen Business Calculus 12e 12 Objectives for Section 4.3 Day 2 The student will be able to : ■ Review derivatives of products and quotients 𝐿𝐻′ − 𝐻𝐿′ 𝑦′ = 𝐿2 ■ Find the equations of tangent lines ■ Solve applications Barnett/Ziegler/Byleen Business Calculus 12e 13 Review What is the mnemonic for finding the derivative of a product 𝑦 = 𝐿𝑅 ? 𝑦 ′ = 𝐿𝑅′ + 𝑅𝐿′ What is the mnemonic for finding the derivative of a 𝐻 quotient 𝑦 = ? 𝐿 ′ 𝑦 = 𝐿𝐻 ′ −𝐻𝐿′ 𝐿2 Barnett/Ziegler/Byleen Business Calculus 12e 14 Example 1 Find ℎ′ 𝑥 , where f(x) is an unspecified differentiable function. ℎ 𝑥 = 2𝑥 4 𝑓(𝑥) ℎ′ 𝑥 = 𝐿𝑅′ + 𝑅𝐿′ ℎ′ 𝑥 = 2𝑥 4 ∙ 𝑓 ′ 𝑥 + 𝑓(𝑥) ∙ 8𝑥 3 ℎ′ 𝑥 = 2𝑥 3 𝑥𝑓 ′ 𝑥 + 4𝑓(𝑥) Barnett/Ziegler/Byleen Business Calculus 12e Factor 2𝑥 3 from each term. 15 Example 2 Find ℎ′ 𝑥 , where f(x) is an unspecified differentiable function. ′ 𝐿𝐻 − 𝐻𝐿′ ′ 𝑓(𝑥) ℎ 𝑥 = 2 ℎ 𝑥 = 3 𝐿 𝑥 3 𝑓′(𝑥) − 𝑓(𝑥)3𝑥 2 𝑥 ℎ′ 𝑥 = 𝑥3 2 Divide each term by 𝑥 2 . 3 𝑓′(𝑥) − 𝑓(𝑥)3𝑥 2 𝑥 ℎ′ 𝑥 = 𝑥6 ℎ′ 𝑥𝑓′(𝑥) − 3𝑓 𝑥 𝑥 = 𝑥4 Barnett/Ziegler/Byleen Business Calculus 12e 16 Example 3 Let f (x) = (x2 + 6)(ln x). Find the equation of the line tangent to the graph of f (x) at x = 1. 1 𝑓 𝑥 = 𝑥 + 6 + ln 𝑥 2𝑥 𝑥 1 ′ 𝑓 1 = 1 + 6 + ln 1 2(1) 1 𝑓′ 1 = 7 + 0 ∙ 2 = 7 𝑦 − 𝑦1 = 𝑚(𝑥 − 𝑥1 ) 𝑓 1 = (7)(ln 1) = 7 ∙ 0 = 0 𝑦 − 0 = 7(𝑥 − 1) ′ 2 𝑚=7 (1,0) 𝑦 = 7𝑥 − 7 Barnett/Ziegler/Byleen Business Calculus 12e 17 Example 4 3𝑥 . 2𝑥−1 Let f (x) = Find the equation of the line tangent to the graph of f (x) at x = 2. 𝑓′ 2𝑥 − 1 3 − 3𝑥(2) 𝑥 = (2𝑥 − 1)2 𝑓′ −3 6𝑥 − 3 − 6𝑥 = 𝑥 = (2𝑥 − 1)2 (2𝑥 − 1)2 −3 −1 𝑓 2 = = 9 3 ′ 2, 𝑓 2 = (2,2) 𝑦 − 𝑦1 = 𝑚(𝑥 − 𝑥1 ) −1 𝑦−2= (𝑥 − 2) 3 −1 8 𝑦= 𝑥+ 3 3 Barnett/Ziegler/Byleen Business Calculus 12e 18 Application 1 The total sales (in thousands of games) of Call of Duty x months after the game is introduced is given by: 150𝑥 𝑇 𝑥 = 𝑥+3 A) Find 𝑇 ′ 𝑥 B) Find 𝑇 12 and 𝑇 ′ 12 and interpret the results. C) Use the results from (B) to estimate the total sales after 13 months. Barnett/Ziegler/Byleen Business Calculus 12e 19 150𝑥 𝑇 𝑥 = 𝑥+3 Application 1 (continued) A) Find 𝑇 ′ 𝑥 ′ − 𝐻𝐿′ 𝐿𝐻 𝑇′ 𝑥 = 𝐿2 𝑇′ 𝑥 + 3 150 − 150𝑥(1) 𝑥 = (𝑥 + 3)2 𝑇′ 150𝑥 + 450 − 150𝑥 𝑥 = (𝑥 + 3)2 𝑇′ 450 𝑥 = (𝑥 + 3)2 Barnett/Ziegler/Byleen Business Calculus 12e 20 Application 1 (continued) B) Find 𝑇 12 and 𝑇 ′ 12 and interpret the results 150𝑥 𝑇 𝑥 = 𝑥+3 𝑇 12 = 150(12) 12 + 3 𝑇′ 450 𝑥 = (𝑥 + 3)2 𝑇 ′ 12 = 450 (12 + 3)2 1800 𝑇 12 = 15 450 𝑇 12 = 225 𝑇 12 = 120 𝑇 ′ 12 = 2 ′ After 12 months, the total sales are 120,000 games and sales are increasing at a rate of 2,000 games per month. Barnett/Ziegler/Byleen Business Calculus 12e 21 Application 1 (continued) C) Use the results from (B) to estimate the total sales after 13 months. 𝑇 12 + 𝑇′(12) 120 + 2 = 122 After 13 months, the total sales will be 122,000 games. Barnett/Ziegler/Byleen Business Calculus 12e 22 Homework #4-3B: Pg 231 31, 35, 39, 43, 49, 51, 81, 83, 87 Barnett/Ziegler/Byleen Business Calculus 12e 23