questionnaire: the five kingdoms

QUESTIONNAIRE: THE FIVE KINGDOMS
MONERA KINGDOM
1.
Which of the following characteristics apply to bacteria? a.
They are present everywhere. b.
They are multicellular. c.
They reproduce through binary fission. d.
Some have chlorophyll. e.
They have nucleus.
2.
Bacteria reproduce extremely quickly through binary fission. Under optimal conditions, they can grow and divide every half hour. a.
Based on the data of the diagram, how many bacteria would there be after one hour? b.
And after an hour and a half? c.
Is it possible to continue this reproduction rate indefinitely? Why?
3.
Draw a bacteria and label it.
4.
Do you think that all bacteria are harmful for humans? Give examples.
PROTISTA KINGDOM
5.
Which of the following characteristics refer to protozoa? a.
They have prokaryotic cells. b.
They consist of a single cell.
c.
They form spores. d.
They have chloroplasts. e.
They are heterotrophs. f.
They live attached to a substrate.
6.
How are algae and plants alike? Why are not algae included in the Plant kingdom?
7.
Indicate through a schema the different groups we can find in both protozoa and algae.
8.
A group of scientists has collected data on the amount of oxygen released by algae in a pond. Data was collected for two days. The results are shown in the following graph:
Analyse the results and explain the reason for the amount of oxygen released over the two days.
FUNGI KINGDOM
9.
Why do you think fungi are not include in the Plant kingdom?
10.
What do fungi and animals have in common?
11.
What is the name of the chemical substances fungi produce to stop the growth of competitors such as bacteria?
12.
Label the parts of a fungus.
13.
Indicate through a schema the different groups of fungi we can find.
PLANT KINGDOM
14.
Indicate if the following sentences are true or false: a.
Stomata are located on the upper side of the leaves. b.
Most flowers have stamens and a pistils. c.
During pollination, pollen grains travel from the anther to the stigma. d.
A fertilized ovule develops into a fruit. e.
All flowering plants produce fruits. f.
Gymnosperms don’t have flowers. g.
Spores and seeds have the same function. h.
Ferns and mosses are heterotrophs and produce spores.
15.
Label the following diagram of a flower.
16.
How are ferns and mosses alike and how are they different?
17.
The following picture show different moments in the life cycle of an angiosperm. a.
Label the numbered part of the plant. b.
Order the pictures and explain what they show.
18.
Indicate through a schema the different groups of plants we can find.
ANIMAL KINGDOM
INVERTEBRATES
19.
Indicate if the following sentences are true or false: a.
Polyps and jellyfish use tentacles to catch their prey. b.
Annelids have bilateral symmetry. c.
Most molluscs are terrestrial. d.
Echinoderms have an exoskeleton made of plates. e.
Arthropods moult periodically until they reach adult size. f.
Invertebrates are present in terrestrial and aquatic environments.
20.
The following pictures show a polyp and a sponges.
Which one is the polyp and which one the sponges. How do you know?
A B
21.
The number of limbs that arthropods have helps to identify the different groups of arthropods. Classify the arthropods from the picture into arachnids (4 pairs), crustaceans (5 pairs), myriapods (many pairs) or insects (3 pairs).
Centipede
Moth
22.
Match each invertebrate with its group.
Oyster
Earthworm
Jellyfish
Ant
Sponge
Starfish
VERTEBRATES
23.
Indicate if the following sentences are true or false. a.
Animals can be heterotrophs or autotrophs. b.
The body of all vertebrates is divided into three segments. c.
Fish have scales, fins and gills. d.
Reptiles can breathe through their skin. e.
Reptiles and birds are oviparous and incubate their eggs.
f.
Mammals are vertebrates that live in a terrestrial or an aquatic environment. g.
Amphibians and mammals have gland in their skin. h.
Reptiles and mammals can keep their body temperature constant.
24.
Reptiles are cold blooded vertebrates. However, by adapting their behavior, some keep their body temperature lower or higher than their environment.
The following picture shows a lizard from the desert at different hours of the day. a.
What do we mean when we say an animal is coldblooded? b.
Describe the behavior of the lizard at the different times of the day and explain the effect this behavior has on its body temperature.
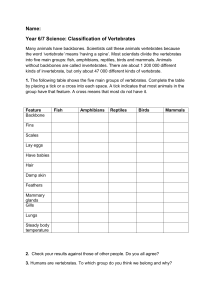
25.
Complete the following table in your notebook with the characteristics of the different types of vertebrates:
VERTEBRATES TYPE OF LIMBS BODY
TEMPERATURE
BREATHING
ORGAN
TYPE OF
REPRODUCTION
Fish
Gills
Amphibians
Cold-blooded
Reptiles
Lungs Oviparous
Birds
Wings Oviparous
Mammals
Warm-blooded
26.
The following graph represents the number of known species from the different groups of vertebrates. a.
Which is the group of vertebrates with the most diversity of species?
And with the least? b.
What is the totals number of known species of vertebrates? c.
What percentage of the total number of species is warmblooded?