Notes: Part 1
advertisement
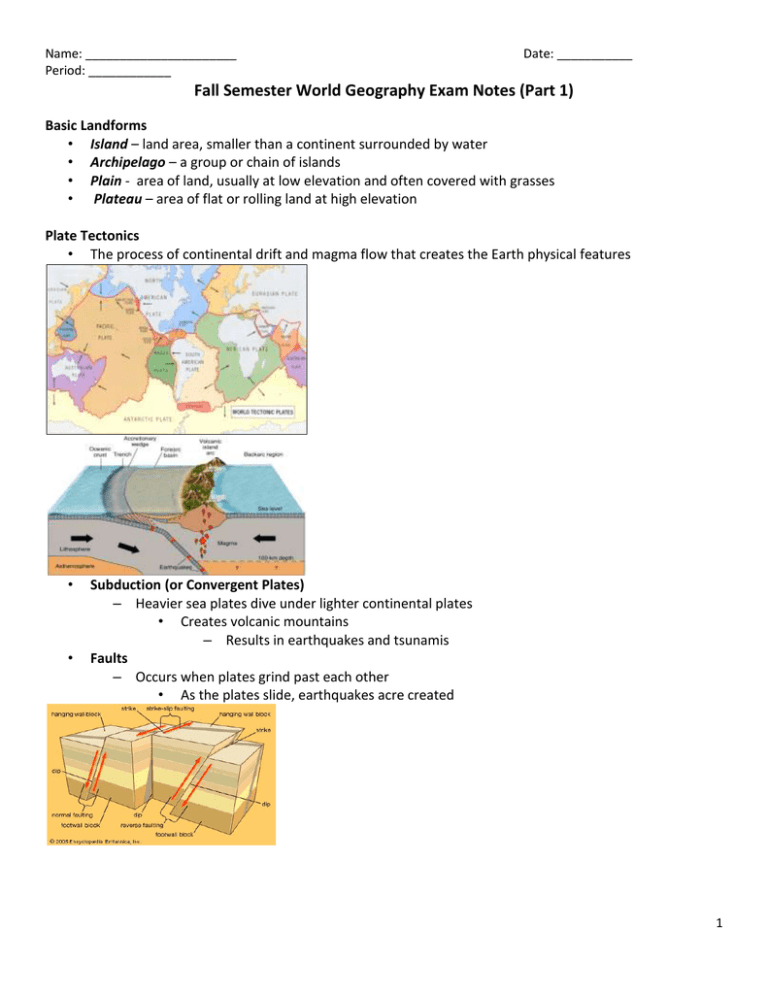
Name: ______________________ Period: ____________ Date: ___________ Fall Semester World Geography Exam Notes (Part 1) Basic Landforms • Island – land area, smaller than a continent surrounded by water • Archipelago – a group or chain of islands • Plain - area of land, usually at low elevation and often covered with grasses • Plateau – area of flat or rolling land at high elevation Plate Tectonics • The process of continental drift and magma flow that creates the Earth physical features • • Subduction (or Convergent Plates) – Heavier sea plates dive under lighter continental plates • Creates volcanic mountains – Results in earthquakes and tsunamis Faults – Occurs when plates grind past each other • As the plates slide, earthquakes acre created 1 Name: ______________________ Period: ____________ Date: ___________ “Ring of Fire” The Pacific ”Ring of Fire” (or just The Ring of Fire) is an area where large numbers of earthquakes and volcanic eruptions occur in the basin of the Pacific Ocean (responsible for creating places such as the Hawaiian islands). Mountain Ranges of North America The Rocky Mountains stretch from Texas up to Canada. The Appalachian Mountains are mostly In the United States (the northern portion extends into Canada). The Appalachian Mountains are older than the Rocky Mountains. Ural Mountains • The Ural Mountain range separates Europe from Asia. Orographic (Rain Shadow Effect) The higher the elevation, the temperature gets cooler. Rising air cools and condenses and creates precipitation. Landforms • Delta: A delta is an area of land in which a river divides into smaller rivers and empties into a larger body of water. 2 Name: ______________________ Period: ____________ • Date: ___________ A tropical hurricane is caused by the very rapid evaporation of warm ocean water in the late summer months. Eight Factors That Affect Climate (LAMECOWS) L - Latitude A - Air Pressure M - Mountain Barriers E - Elevation C - Continental location O - Ocean Currents W - Wind Currents S - Storms Climate Factors • In the map below, the major influencing climatic factor are mountain barriers (i.e., coastal ranges, Sierra Nevada mountains). Remember, mountain barriers is one of the factors in LAMECOWS. The Seasons The seasons occur because of the tilt of the earth and our revolution around the sun. Due to tilt of earth, not all places receive same amount of light at one time. Definition: Axial tilt is the inclination angle of a planet's rotational axis in relation to its orbital plane What would happen If the earth’s tilt changed? Answer: The seasons would change Tilt 3 Name: ______________________ Period: ____________ Date: ___________ Population Pyramids Remember, countries with pyramid shapes, such as the Philippines, are less developed, whereas, countries with “honey-combed” shapes are more developed. Less Developed More Developed X and Y Axis of Human Pyramid In the population pyramids below, you can see that in 1950 Japan had a high birth rate and high death rate (i.e. developing country); in the 2007 population pyramid, Japan’s pyramid looks like a honey comb, which signifies a developed country with lower birth rates and lower death rates. In 2050, Japan is projected to have an even lower birth rate and high life expectancies for the elder populations…i.e. Japan will be a country of mostly old people, and few young people. 4 Name: ______________________ Period: ____________ Date: ___________ North Africa (See below) As everyone can see, population density are in clusters, since this is North Africa, located in the Sahara desert, settlements are found in areas with reliable sources of water. Also, since the northern area of Africa receives less than 10 inches of annual rainfall, this area would be defined as a Desert. Region Characteristics • In the South American country of Brazil, the official language is Portuguese, which comes from Portugal. This thematic map would be most useful to a — • For these kinds of questions, use your common sense. For example, since the thematic map above shows the average amount of rain in California, it can be inferred that a farmer would find this information more useful. Urban Buildup With the rise of the Industrial Revolution (i.e. factories, industrial facilities, etc.) an increased labor force in urban areas was needed in order to operate the factories/industry. This increase in human population in the cities has created what is now known as “urban sprawl.” Economics High tech industry, service and manufacturing industries are an example of Market oriented economy The European Union (EU) consists of countries that are physically located in Europe. Subsistence Farming: Farmers grow just enough food crops to feed their own families. Commercial Farming: Farmers grow food crops in order to sell and make a profit. 5 Name: ______________________ Period: ____________ Subsistence Agriculture Small Scale Family produced Low Level of technology Both Date: ___________ Commercial Agriculture Type of Agriculture Depends on supply and demand; Common in developed countries; Farmers raise goods that give the most profit •As In a market economy, supply and demand determines the prices of goods and services. Traditional Economy Early form, very primitive and basic Economic decisions based on customs and beliefs Passed from one generation to the next by family, etc. Economic system where people produce what they need to survive Often centered around hunting and gathering, subsistence farming, or herding Example: A primitive tribe Communism A system of government in which the state plans and controls the economy and citizens, claiming to make progress toward a higher social order in which all goods are equally shared by the people A major goal of communism is to have a classless society Three types of Regions Formal, Functional, and Perceptual Formal (uniform) – defined by a common characteristics such as a product produced there or climate experienced there The Corn Belt – Iowa-Illinois area in the US o Common Characteristic? Islamic World – Middle East o Common Characteristic? Functional - a central place and the surrounding area linked to it – Group of places that help each other function Examples: • Regional airport of Dallas/Fort Worth • Trade area of city Perceptual - defined by popular feelings and images rather than by objective data • “Heartland” • It’s what YOU think an area is • Hollywood! 6 Name: ______________________ Period: ____________ Date: ___________ Part II 7