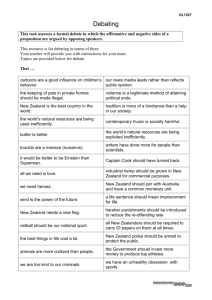
Preliminary list of references
advertisement

Understanding and addressing the impact of invasive non-native species in the UK Overseas Territories in the South Atlantic: A review of the potential for biocontrol DEFRA ref: CR 0492 CABI ref: TR10086 Preliminary list of references Norbert Maczey, Rob Tanner and Richard Shaw March 2012 1 Contents Norbert Maczey Senior Ecologist/Entomologist CABI Bakeham Lane Egham, Surrey TW20 9TY UK T: +44 (0) 1491 829029 E: n.maczey@cabi.org 2 Project introduction Recent reviews of invasive non-native species (INNS) on the South Atlantic UKOTs, revealed that there is a considerable on-going threat by these species to the endemic biodiversity on these islands. Management plans and capacity building efforts to combat invasive plants have already been developed, or are in the process of being developed, by various conservation bodies and other research institutions. However, to-date, there are few plans to include classical biological control in these new schemes despite this management practise having a long history of successful use on islands in the past. We understand that many species including rare, endangered and/or iconic species are negatively impacted upon by introduced invasive plants or invertebrate species and that the reduction of their impact through biological control could bring tangible benefits to biodiversity in these fragile habitats. At present there is little known about the potential of this tool in South Atlantic UKOTs and therefore this feasibility study focuses on the future potential usage of this method. A major component of this study is a desk-based review assessing the impact of non-native plant and invertebrate species in the South Atlantic UKOTs. We rank the need and suitability for biological control of individual invasive species, from high to low, using a recently-developed weed biocontrol prioritisation tool, developed initially for Australia, but already proving to be very useful on the islands in the South Pacific. Priority species are selected on the basis of population dynamics, reported impact on biodiversity, impact on livelihoods, costs for on-going control measures other than biological control and others. In addition, two detailed case studies will evaluate the potential of implementing a biological control programme against priority species for the Falklands and South Georgia more closely. These detailed assessments will combine all current information about the target pest species including information on their native range, areas of introduction and recorded natural enemies in their areas of origin. Ranked in order of priority, and associated costs of available control options, we will include a catalogue of recommended strategies for each priority target species aimed to halt the biodiversity loss through invasive plant and invertebrate species more effectively. References Records of IAS on SAUKOT Andrews, F.G. (1995) The Genus Aridius Motschulsky in the Falkland and South Georgia Islands (Coleoptera: Lathridiidae). - The Coleopterists’ Bulletin, 49: 29-34. Ashmole, N.P. & Ashmole, M.J. (1997) The Land Fauna of Ascension Island: New Data from Caves and Lava Flows, and a Reconstruction of the Prehistoric Ecosystem. - Journal of Biogeography, 24, (5): 549-589. Ashmole, P. & Ashmole, M. (2000) St Helena and Ascension Island: A natural history. - Published by Anthony Nelson, Oswestry, Shropshire, UK: 475 pp. Ashmole, P. & Ashmole, M. (2004) The invertebrates of Prosperous Bay Plain, St Helena. - Report to the St Helena National Trust: 80 pp. Basilewsky, P. (ed.) (1970, 1972, 1976, 1977) La faune terrestre de l'île de Sainte- Hélène, parts 1, 2, 3, 4. Annales Musée Royal de l’Afrique Centrale, Série in-80 - Sciences zoologiques: 181, 192, 215, 220. Blakemore, R.J. (2006) Review of Southern Ocean, South Atlantic and Subantarctic Island earthworms updated from Lee (1994). COE Soil Ecology Group Yokohama National University. Japan, 16pp., http://bioeco.eis.ynu.ac.jp/eng/database/earthworm/Subantarctic/Subantarctic%20Species.pdf (accessed February 2012). Bonner, W.N. & Honey, M.R. (1987) Agrotis ipsilon (Lepidoptera) at South Georgia. - British Antarctic Survey Bulletin, 77: 157–161. Bourgeois, T. le, Blanfort, V., Baret, S., Lavergne, C., Soubeyran, Y., Meyer, J.Y. (2008) Opportunities for classical biological control of weeds in European overseas territories. – In: Julien, M.H., Sforza, R., Bon, M.C., Evans, H.C., Hatcher, P.E., Hinz, H.L., Rector, B.G: Proceedings of the XII International 3 Symposium on Biological Control of Weeds, La Grande Motte, France, 22-27 April, 2007, CAB International, Wallingford,UK: 476-483. Brooke, M. (1998) Conservation challenges in the smaller Overseas Territories. - Ecos, 19: 31-35. Cheesman, O.D. & Clubbe, C. (2007) Dealing with Alien Invasive Species – Introduction, Overview and Conclusions. pp 193-200 in Biodiversity That Matters: a conference on conservation in UK Overseas Territories and other small island communities, Jersey 6th to 12th October 2006 (ed. M. Pienkowski). UK Overseas Territories Conservation Forum, www.ukotcf.org. Chown, S.L. & Block, W. (1997) Comparative nutritional ecology of grass-feeding in a sub-Antarctic beetle: the impact of introduced species on Hydromedion sparsutum from South Georgia. –Oecologia, 111: 216224. Chown, S.L. & Language, K. (1994) Recently established Diptera and Lepidoptera on sub-Antarctic Marion Island. African Entomology, 2 (1): 57-60. Convey P., Key R.S., Key R.J.D., Belcher, M., & Waller C.L. (2011) Recent range expansions in non-native predatory beetles on sub-Antarctic South Georgia. - Polar Biology, 34 597–602. Convey P., Key, R. S. & KEY, R.J.D. (2010) The establishment of a new trophic guild of pollinating insects on sub-Antarctic South Georgia. - Antarctic Science, 22: 508-512. Convey, P. (2005) Recent lepidopteran records from sub-Antarctic South Georgia. - Polar Biol., 28: 108–110. Convey, P. (2008) Adding a new trophic level to natural ecosystems: recent range expansions of alien predatory carabid beetles on Sub-Antarctic islands. Poster abstract. pp 18-19 in:- DST-NRF Centre of Excellence for Invasion Biology. 2008. Proceedings of symposium “Fifty years of invasion ecology – the legacy of Charles Elton”. 12-14 November 2008. Stellenbosch University, South Africa: 55pp. Convey, P., Lewis-Smith, R.I., Hodgson, D.A. & Peat, H.J. (2000) The flora of the South Sandwich Islands, with particular reference to the influence of geothermal heating. - Journal of Biogeography, 27: 1279-1295. Crafford, J.E. & Chown, S.L. (1987) Plutella xylostella L. (Lepidoptera: Pluttellidae) on Marion Island. Journal of Entomological Society of South Africa, 15: 259-260. Cronk, Q.C.B (1980) Extinction and survival in the endemic vascular flora of Ascension Island. - Biological Conservation 17: 207-219. Cronk, Q.C.B. (1986) The decline of the St Helena gumwood, Commidendrum robustum. - Biological Conservation, 35: 173-186. Cronk, Q.C.B. (1989) The past and present vegetation of Saint Helena. - Journal of Biogeography, 16: 47-64. Dahl, C. (1970) Diptera: Trichoceridae of South Georgia. pp 271-273 in: Gressitt, J.L. (ed) 1970. Subantarctic entomology, particularly of South Georgia and Heard Island. Pacific Insects Monograph 23. Bishop Museum, Hawaii. 383pp. Darlington, P.J. Jr. (1970) Coleoptera: Carabidae of South Georgia. p 234 in: Gressitt, J.L. (ed) 1970. Subantarctic entomology, particularly of South Georgia and Heard Island. Pacific Insects Monograph 23. Bishop Museum, Hawaii. 383pp. Darlow, A. (2008) Have you seen this insect? Public education poster about common wasps. - Public education poster about common wasps on St. Helena. Duffey, E. (1964) The Terrestrial Ecology of Ascension Island. - The Journal of Applied Ecology, 1 (2): 219-251. Ernsting, C., (1993) Observations on life cycle and feeding ecology of two recently introduced predatory beetle species at South Georgia, sub-Antarctic. - Polar Biol., 13: 423-428. Ernsting, G., Block, W., MacAlister, H & Todd, C. (1995) The invasion of the carnivorous carabid beetle Trechisibus antarcticus on South Georgia (sub-Antarctic) and its effect on the endemic herbivorous beetle Hydromedion sparsutum. – Oecologia, 103: 34-42. Frenot, Y., Chown, S.L, Whinam, J., Selkirk, P.M., Convey, P., Skotnicki, M. & Bergstrom, D.M. (2005) Biological invasions in the Antarctic: extent, impacts and implications. - Biological Review, 80: 45-72. Frenot, Y., Convey, P., Lebouvier, M., Chown, S.L., Whinam, J., Selkirk, P.M., Skotnicki, M. & Bergstrom, D.M. (2007) Antarctic biological invasions: sources, extents, impacts and implications. - Non-native Species in the Antarctic: Proceedings (Ed. Finnemore), Gateway Antarctica, Christchurch, pp. 53-96. 4 Gaston, K.J., Chown, S.L. & Bradley. P. (2002) Invertebrate diversity and endemism at Gough Island and threats from introduced species. – Final project report, Project Ref. 162/8/253, Darwin Initiative for the Survival of Species, 7th Round, 31pp. Gaston, K.J., Jones, A.G., Hanel, C. & Chown, S.L. (2003) Rates of species introduction to a remote oceanic island. - Proceedings of the Royal Society, London (B) 270: 1091-1098. George, T. & White, R. (2003) Ascension - focus on dealing with invasive species. pp 155-160 In A sense of direction: a conference on conservation in UK Overseas Territories and other small island communities (ed. M. Pienkowski). - UK Overseas Territories Conservation Forum, www.ukotcf.org. Gray, A., Pelembe, T. & Stroud, S. (2005) The conservation of the endemic vascular flora of Ascension Island and threats from alien species. – Oryx, 39 (4): 449-453. Gressitt, J.L. & Clagg, H, (1970) Introduction to South Georgia. pp 1-15 in Gressitt, J.L. (ed) 1970. Subantarctic entomology, particularly of South Georgia and Heard Island. - Pacific Insects Monograph 23. Bishop Museum, Hawaii, 383pp. Gressitt, J.L. (1970b) Subantarctic entomology and biogeography. pp 295-374 in Gressitt, J.L. (ed) 1970. Subantarctic entomology, particularly of South Georgia and Heard Island. - Pacific Insects Monograph 23. Bishop Museum, Hawaii, 383pp. Gressitt, J.L. (1970c) Coleoptera: Dytiscidae and Lathridiidae of South Georgia. pp 235-239 in Gressitt, J.L. (ed) 1970. Subantarctic entomology, particularly of South Georgia and Heard Island. - Pacific Insects Monograph 23. Bishop Museum, Hawaii, 383pp. Gressitt, J.L. (ed) (1970a) Subantarctic entomology, particularly of South Georgia and Heard Island. - Pacific Insects Monograph 23. Bishop Museum, Hawaii. 383pp. Hall, J.R., Woods, R.W., Brooke, M. de L. & Hilton, G.M. (2002) Factors affecting the distribution of landbirds on the Falkland Islands. - Bird Conservation International, 12: 151-167. Hänel, C. & Disney, R.H.L. (2006) Phoridae (Dipt) from Nightingale Island, South Atlantic. - Entomologists Monthly Magazine, 142: 127-128. Hänel, C. & Heloises, H. (2008) Ticks of the Tristan da Cunha Archipelago (Acarina: Ixodidae: Argasidae). Beitraege zur Entomologie, 58 (1): 121-134. Hänel, C. & Palma, R. (2007) The lice of the Tristan da Cunha Archipelago (Insecta: Phthiraptera). - Beitraege zur Entomologie, 57 (1): 105-133. Hänel, C. & Palma, R.L. (2007) The lice of the Tristan da Cunha Archipelago (Insecta: Phthiraptera) - Beitr. Ent. 57 (1): 105–133. Hänel, C. & Pont, A. (2008) Houseflies of the Tristan da Cunha Islands: new records, including the first for Fannia albitarsis STEIN, 1911 (Diptera: Fanniidae, Muscidae). - Beitraege zur Entomologie, 58 (1): 211222. Hänel, C. (2006) Tristan da Cunha Invertebrate Project Report. - Unpublished report to RSPB, funded by the Darwin Initiative Hänel, C. (2008) Things of note. Re: Ichneumonid wasps at the Tristan Archipelago, with reference to the recent identifications from the 2005 invertebrate collection. - Unpublished report to RSPB. Hänel, C., Chown, S.L., & Davies, L. (1998) Records of Alien Insects from sub-Antarctic Marion and South Georgia Islands. - African Entomology, 6: 366-369. Henry, P.W.T. (1974) List of tree and shrub species known to have been planted on St Helena. - Appendix 4 of Land Resource Report Number LRR2: 186-194. Holdgate, M.W. (1960) The Fauna of the Mid-Atlantic Islands (pp. 550-567). Proceedings of the Royal Society of London. Series B, Biological Sciences, Vol. 152, No. 949, A Discussion on the Biology of the Southern Cold Temperate Zone Published by: The Royal Society. Holdgate, M.W. (1965) The Fauna of the Tristan Da Cunha Islands Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London. Series B, Biological Sciences, Vol. 249, No. 759 (Oct. 7, 1965): 361-402. Horstmann, K. (2008) Two species of Ichneumonidae from Tristan da Cunha and Nightingale Islands, South Atlantic (Hymenoptera). - Mitteilungen der Munchener Entomologischen Gesellschaft, 98: 31-35. Jackson, E.L. (1905) St. Helena: the historic island from its discovery to the present date (1905). - New York, Thomas Whittaker: 5 http://www.archive.org/stream/sthelenahistoric00jackrich/sthelenahistoric00jackrich_djvu.txt February 2012) (accessed Jones, A.G., Chown, S.L., Ryan, P.G., Gremmen, N.J.M. & Gaston, K.J. (2003) A review of conservation threats on Gough Island: a case study for terrestrial conservation in the Southern Oceans. - Biological Conservation, 113: 75-87. Jones, A.G., Chown, S.L., Webb, T.J. & Gaston, K.J. (2003) The free-living pterygote insects of Gough Island, South Atlantic Ocean. - Systematics and Biodiversity, 1(2): 213-273. Karisch, T. (2001) Zur Schmetterlingsfauna von St. Helena. 1. Teil: Großschmetterlinge (Insecta: Lepidoptera). Linzer biologische Beiträge, 33: 407-434. Karisch, T. (2003) Zur Schmetterlingsfauna von St. Helena. 2. Teil: Kleinschmetterlinge (1) (Insecta: Lepidoptera: Tortricidae, Glyphipterigidae, Cosmopterigidae, Plutellidae, Pterophoridae). - Linzer biologische Beiträge, 35: 1081-1085. Karisch, T. (2007) Zur Schmetterlingsfauna von St. Helena 3. Teil: Kleinschmetterlinge (2) (Insecta: Lepidoptera: Pyraloidea). - Linzer biologische Beiträge, 39: 405-414. Kendle, A.D. & Rose, J.E. (2001) Invasive plants on land recovering from desertification on Saint Helena island In: G. Brundu, J. Brock, I. Camarda, L. Child and M. Wade (Eds) Plant Invasions: Species Ecology and Ecosystem Management. - Backhuys, Leiden, The Netherlands: 311-318. Lavery, A. (2004) Falkland Island Spiders - a preliminary report. - Unpublished report to the RSPB. Lavery, A. (2009) Introduced spiders on the Falkland Islands. - A preliminary report. Lavery, A. (2004) The Spiders of South Georgia - A Preliminary Handbook. Version 1., unpublished. Lewis-Smith, R.I. (1996) Introduced plants in Antarctica: potential impacts and conservation issues. - Biological Conservation, 76: 135-146. Maunder, M., Upson, T., Spooner, B. & Kendle, T. (1995) Saint Helena: Sustainable development and conservation of a highly degraded island ecosystem. - In: Vitousek, P., Loope, L.L. & Adersen, H. (Eds) Islands: Ecological Studies, Vol 115, Berlin, Springer Verlag: pp 205-217. McCulloch, N. & Norris, K. (in prep) Potential threats to the survival of the wirebird. - Chapter 2 in: A Review of the Status and Ecology of the St Helena Wirebird, with recommendations for its conservation. University of Reading. McCulloch, N. & Norris, K. (in prep) Status of wirebird habitat. - Chapter 4 in: A Review of the Status and Ecology of the St Helena Wirebird, with recommendations for its conservation. - University of Reading. McDowall, R.M., Allibone, R.M. & Chadderton, W.L. (2001) Issues for the conservation and management of Falklands Islands freshwater fishes. - Aquatic Conservation: Marine and freshwater ecosystems, 11: 473-486. Mendel,H., Ashmole, P. & Ashmole, M. (2008) Invertebrates of the Central Peaks and Peak Dale, St Helena. – Report to the St Helena National Trust: 122pp. Osborne, J., Borosova, R., Briggs, M. & Cable, S. (2009) Survey for baseline information on introduced vascular plants and invertebrates: South Georgia: Introduced Vascular Plants. - report 159 pp, http://www.kew.org/gis/downloads/South%20Georgia%20Introduces%20Vascular%20Plants%202009.p df (accessed February 2012). Pugh, P.J.A. (2004) Biogeography of spiders (Araneae: Arachnida) on the islands of the Southern Ocean. Journal of Natural History, 38: 1461–1487. Reynolds, J.W. & Hänel, C. (2005) The Earthworms (Oligochaeta: Lumbricidae) of Gough Island, South Atlantic Ocean. - Megadrilogica, 10 (7): 47-56. Reynolds, J.W., Jones, A.G., Gaston, K.J. & Chown, S.L. (2002) The earthworms (Oligochaeta: Lumbricidae) of Gough Island, South Atlantic Ocean. – Megadrilogica, 9 (2): 5-15. Ringuelet, R.A. (1955) Ubicación zoogeográfica de las Islas Malvinas. - Extracto de la Revista del Museo de la Universidad de la Plata (nueva serie), Tomo VI, Sección Zoología: 419-464. RSPB (2007) Costing Biodiversity Priorities in the UK Overseas Territories. – report, 105pp, https://www.rspb.org.uk/Images/Costing_biodiversity_in_UKOTs_tcm9-273309.pdf (accessed February 2012). 6 RSPB (2011) Action to reduce the impacts of invasive species on the South Atlantic United Kingdom Overseas Territories. - http://www.rspb.org.uk/Images/Invasivesleaflet_tcm9-208866.pdf (accessed February 2012). Schiner, J.R. (1868): Diptera. - in Wüllerstorf-Urbair, B. von (ed.) Reise der österreichischen Fregatte Novara. Zool., 2, Abt. 1,B: 1-388. Schmelz, R.M., & Hänel, C. (2007) On a collection of Enchytraeidae and Naididae (Oligochaeta) from the Tristan da Cunha Islands, South Atlantic Ocean. - Folia Fac. Sci. Nat. Univ. Masaryk. Brun. Biol., 110: 193-202. Slabber, S. & S. L. Chown (2002) The first record of a terrestrial crustacean, Porcellio scaber (Isopoda, Porcellionidae), from sub-Antarctic Marion Island. - Polar Biol., 25: 855–858. Varnham, K. (2005) Database of non-native species occurring in UK Overseas Territories. Annex 4 to JNCC Report 372: Non-native species in UK Overseas Territories: A review. Peterborough, UK, http://jncc.defra.gov.uk/page-3660 (accessed February 2012). Varnham, K. (2006) Non-native species in UK Overseas Territories: a review. - JNCC Report, No. 372, 39pp. http://jncc.defra.gov.uk/pdf/jncc372_web.pdf (accessed February 2012). Vogel, M. (1985) The distribution and ecology of epigeic invertebrates on the Subantarctic island of South Georgia. - Spixiana, 8:153-163. Wilson, T.H. & Stannard, L.J. (1970) Thysanoptera of South Georgia. pp 221-226 in Gressitt, J.L. (ed.) 1970. Subantarctic entomology, particularly of South Georgia and Heard Island. - Pacific Insects, Monograph 23. - Bishop Museum, Hawaii: 383pp. Wise, K.A.J., (1970) Collembola of South Georgia. pp 183-208 in: Gressitt, J.L. (ed.) 1970. Subantarctic entomology, particularly of South Georgia and Heard Island. - Pacific Insects Monograph 23. Bishop Museum, Hawaii: 383pp. Worland, R., Block, W. & Rothery, P. (1992) Survival of sub-zero temperatures by two South Georgian beetles (Coleoptera, Perimylopidae). - Polar Biology, 11: 607-613. BAPs regarding IAS on SAUKOT Cairns-Wicks, R. (2008) Protected Area Plan for the Central Peaks 2007-2010. - Developed with funding from OTEP. Cooper, J. & Glass, J. (2006) Eradicating invasive species in the United Kingdom Overseas Territory of Tristan da Cunha. - Aliens 23: 1-4. Cooper, J. & Ryan, P.G. (1994) Management Plan for the Gough Island Wildlife Reserve Published by the Government of Tristan da Cunha, Edinvurgh, Tristan da Cunha. Forbes, A., Derry, J. & Warren, N. (2010) Review of the Darwin Initiative’s Support to Overseas Territories: with the Falklands Islands as a case study. – A Publication in the Darwin Initiative’s Thematic Review Series,71 pp. Glass, S., Glass, J., Sanders, S (2006) Tristan Biodiversity Action Plan (2006 – 2010), Tristan Island Government, 109 pp. Hartikainen, M. (2009) South Atlantic Invasive Species Project, Risk Assessment. – Report of the Royal Society for the Protection of Birds, 23 pp. Jenner, N. (2009) Falkland Island invasive species projects. - Summary of invasive species actions on the Falkland Islands produced as part of an ongoing RSPB project. Kew Gardens (2010a): St. Helena and dependencies: http://dps.plants.ox.ac.uk/bol/helena Kew Gardens (2010b): Ascension database: http://dps.plants.ox.ac.uk/bol/ascension Kew Gardens (2010c): Falklands database: http://dps.plants.ox.ac.uk/bol/falklands Kew Gardens (2010d): South Georgia database: http://dps.plants.ox.ac.uk/bol/southgeorgia Kew Gardens (2010e): Tristan da Cunha: http://dps.plants.ox.ac.uk/bol/tristan (accessed February 2012). McIntosh, E. & Walton, D.W.H. (2000) Environmental Management Plan for South Georgia. - Published by the British Antarctic Survey on behalf of the Government of South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands. 7 Miller, C. (2007) Tristan da Cunha – Invasive Species Awareness surveys. - Report of EU/ RSPB South Atlantic Invasive Species Project. Pickup, A.R. (1999) Ascension Island Management Plan. - Published by The Royal Society for the Protection of Birds, Sandy, Beds, UK. RSPB (2010): Action to reduce the impacts of invasive species on the South Atlantic United Kingdom Overseas Territories (2010): http://www.rspb.org.uk/Images/Invasivesleaflet_tcm9-208866.pdf Ryan, P.G. & Glass, J.P. (2001) Inaccessible Island Nature Reserve Management Plan. - Published by the Government of Tristan da Cunha, Edinburgh, Tristan da Cunha. Shine, C. & Stringer, C. (2010) South Atlantic Invasive Species Strategy and Action Plan. - Based on the contributions by participants to a Regional Meeting, Ascension Island, 14-19 May 2009, 39 pp. Smith, D. (1997) The progress and problems of the ‘Endemic Section’ of St Helena Island. – Oryx, 31 (3): 218224. Stringer, C. (2010) Increasing regional capacity to reduce the impacts of invasive species on the South Atlantic United Kingdom Overseas Territories. – Final report to the European Commission of Project N° 9 PTO REG 5/1; PTR 003/05/EDF IX. 46 pp. +29 annexes. Whitehead, J. (2008) Priorities for Control: A Risk Assessment of Introduced Species on the Falkland Islands, South Atlantic Invasive Species Project. – RSBP report, 36 pp. Wolfaardt A.C, Glass, J. & Glass, T. (2009) Tristan da Cunha implementation plan for the Agreement on the Conservation of Albatrosses and Petrels (ACAP): review of current work and a prioritised work programme for the future. Tristan da Cunha Government. Tristan da Cunha, 51pp. Wolfaardt, A.C. & Christie, D. (2010) Guidelines for the implementation of the Agreement on the Conservation of Albatrosses and Petrels (ACAP) at South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands. Government of South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands, Stanley, Falkland Islands. 55 pp. Wolfaardt, A.C., Rendell, N.& Brickle, P. (2010) Falkland Islands implementation plan for the Agreement on the Conservation of Albatrosses and Petrels (ACAP): review of current work and a prioritised work programme for the future. Falkland Islands Government. Stanley, Falkland, 62pp. BC of IAS on SAUKOT Belton, T. (2008) Mexican Thorn (Prosopis juliflora) on Ascension Island. - An assessment of this species, and recommendations for management. RSPB, SAIS project report, 18pp. Booth, R.G., Cross, A.E., Fowler, S.V. & Shaw, R.H. (2001) Biological control of an insect to save an endemic tree on St Helena. - Case Study 5.24 In: Invasive Alien Species: A toolkit of best prevention and management practices (Eds. Wittenberg, R. & Cock, M.J.W.). - CAB International, Wallingford, UK. Booth, R.G., Cross, A.E., Fowler, S.V., & Shaw, R.H. (1995): The biology and taxonomy of Hyperaspis pantherina (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae) and the classical biological control of its prey, Orthezia insignis (Homoptera: Ortheziidae). - Bulletin of Entomological Research 8 (5): 307-314. Fowler, S.V. (1996): Saving the Gumwoods in St Helena. - in Aliens (4): 9. Fowler, S.V. (1998) Report on the invasion, impact and control of 'Mexican thorn', Prosopis juliflora, on Ascension Island. - Ascot, UK: CABI Bioscience. Fowler, S.V. (2004) Biological control of an exotic scale, Orthezia insignis Browne (Homoptera: Ortheziidae), saves the endemic gumwood tree, Commidendrum robustum (Roxb.) DC. (Asteraceae) on the island of St. Helena. - Biological Control, 29 (3): 367-374. Fowler, S.V. (2011) Weed bio control on Ascension Island. - Ascension Conservation Quarterly, 36: 16-21. Fowler, S.V., Syrett, P. and Hill, R.L. (2000) Success and safety in the biological control of environmental weeds in New Zealand; Thematic issue: Environmental weeds. Papers from a symposium at the first joint conference of the Ecological Society of Australia and the New Zealand Ecological Society, Dunedin, New Zealand, November 1998, Austral Ecology 25 (5): pp.553-562. Gray, A., Pelembe, T. & Stroud, S. (2005) The conservation of the endemic vascular flora of Ascension Island and threats from alien species. – Oryx, 39 (4): 449-453. 8 Greathead, D.J. (1971) A review of biological control in the Ethiopian Region. - Commonwealth Institute of Biological Control, Technical Communication no.5: 162 pp. Jewsbury, N. (2001) Assessing the effectiveness of the biological control of ‘Mexican thorn’, Prosopis juliflora, via the introductions of two seed feeding bruchids, on Ascension Island. - BSc Joint Honours Degree, Unpublished report, Kingston University. Summers, B. (2008) Report on bittercress control: South Georgia 25-31 March 2008. - Report to EU/ RSPB South Atlantic Invasive Species Project. White, L.F. (2009) Survey of Biocontrol Agents of Mexican Thorn (Prosopis juliflora) on Ascension Island. University of Exeter, Environmental Studies Dissertation Module: Level 3, 75pp. Methods and Regulations Callaham, Mac A., Gonzalez, G., Hale, C.M., Heneghan, L., Lachnicht, S.L. & Zou, X. (2006) Policy and management responses to earthworm invasions in North America. - Biol. Invasions, 8:1317–1329. de Villiers, Marienne S., John Cooper, Noel Carmichael, James P. Glass, Gordon M. Liddle, Ewan McIvor, Thierry Micol and Andy Roberts., 2006. Conservation Management at Southern Ocean Islands: towards the Development of Best-Practice Guidelines. - Polarforschung 75 (2–3), 113 – 131, 2005 (erschienen 2006), http://epic.awi.de/Publications/Polarforsch2005_2-3_6.pdf (accessed February 2012). Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (1997): Code of Conduct for the Import and Release of Exotic Biological Control Agents. – Biocontrol News and Information, 18 (4): 119–124. Ehlers, R.U. (ed.) (2011) Regulation of Biological Control Agents. - Springer: 417pp. Hulme, P.E., Brundu, G., Camarda, I., Dalias, P., Lambdon, P., Lloret, F., Medail, F., Moragues, E., Suehs, C., Traveset, A., Troumbis, A. & Vilà, M. (2008) Assessing the risks to Mediterranean islands ecosystems from alien plant introductions. – In: Plant invasions: human perception, ecological impacts and management, Backhuys Publishers, Leiden, Netherlands: 39-56. International Plant Protection Convention (1996): Code of Conduct for the Import and Release of Biological Control Agents. International Plant Protection Convention, Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations, Rome, 19 pp. Moller, H. (1996) Lessons for invasion theory from social insects. - Biological Conservation, 78: 125–142. Paynter, Q. (2010) Priorisatation of targets for biological control of weeds on Pacific Island. – Landcare Research, New Zealand, 69 pp., http://www.issg.org/cii/Electronic%20references/pii/references/pacific_weed_biocontrol_prioritisation_rep ort.pdf. Paynter, Q., Hill, R., Bellgard, S. & Dawson, M. (2009) Improving Targeting of Weed Biological Control Projects in Australia.- Land & Water Australia, 123 pp. Pemberton, R.W. (2000) Predictable risk to native plants in weed biological control, Oecologia 125 (4): pp.489494. Way, M.J., Conlong, D.E. & Rutherford, R.S. (2011) Biosecurity against invasive alien insect pests: a case study of Chilo sacchariphagus (Lepidoptera: Crambidae) in the Southern African region. - Proceedings of the Annual Congress - South African Sugar Technologists' Association, 84: 84-91. Wittenberg, R., Cock, M.J.W. (eds.) (2001): Invasive Alien Species: A Toolkit of Best Prevention and Management Practices. - CAB International, Wallingford, Oxon, UK, xvii - 228. Invasivness & impact of IAS in other geographical regions Anthony, C.D., Hickerson, C.A.M. & Venesky, M.D. (2007) Responses of juvenile terrestrial salamanders to introduced (Lithobius forficatus) and native centipedes (Scolopocryptops sexspinosus). - Journal of Zoology, 271 (1): 54-62. Archibald, R.D. & Maddison, P.A. (1988) A summary of stored product Coleoptera in New Zealand and neighbouring Pacific countries. - New Zealand entomologist, 11: 1-6. 9 Arndt, E. (2006) Niche Occupation by Invasive Ground-Dwelling Predator Species in Canarian Laurel Forests. Biological Invasions, 8 (4): 893-902. Barlow, N.D., Beggs, J.R. & Barron, M.C. (2002) Dynamics of common wasps in New Zealand beech forests: a model with density dependence and weather. - Journal of Animal Ecology, 71: 663-671. Barr, K., Moller, H., Christmas, E., Lyver, P. & Beggs, J. (1996) Impacts of introduced common wasps (Vespula vulgaris) on experimentally placed mealworms in a New Zealand beech forest. – Oecologia, 105: 266– 270. Barrion, A.T., Litsinger, J.A. (1987) Herpetogramma licarsisalis (Walker) (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae): a new pest of lowland rice in the Philippines. - Philippine Entomologist, 7 (1): 67-84. Beggs, J., & Harris, R. (2002) The status of Vespula vulgaris as a conservation pest in Australasia. In: Proceedings 14th Congress of the International Union for the Study of Social Insects, 27 July - 3 August 2002, Hokkaido University, Sapporo, Japan: 95. Beggs, J.R. & Rees, J.S. (1999) Restructuring of Lepidoptera communities by introduced Vespula wasps in a New Zealand beech forest. – Oecologia, 119: 565–571. Beggs, J.R. & Wilson, P.R. (1991) The kaka, Nestor meridionalis, a New Zealand parrot endangered by introduced wasps and mammals. - Biological Conservation, 56: 23–38. Beggs, J.R. (1991) Altitudinal variation in abundance of common wasps (Vespula vulgaris). New Zealand Journal of Zoology 18: 155–158. Beggs, J.R. (1999) The ecological impact and control of introduced wasps (Vespula spp) in Nothofagus forest. Unpubl. PhD thesis, University of Otago, Dunedin, New Zealand: 197 pp. Beggs, J.R. (2000) Impact and control of introduced Vespula wasps in New Zealand. - In: Austin, A.D. & Dowton, M. (eds.) Hymenoptera: Evolution, Biodiversity and Biological Control. - CSIRO publishing, 468 pp. Beggs, J.R. (2001) The ecological consequences of social wasps (Vespula spp.) invading an ecosystem that has an abundant carbohydrate resource. - Biological Conservation, 99: 17-28. Bell, W.J. & Adiyodi, K.G. (1981). The American Cockroach. - London: Chapman and Hall. Bieler, R. & Slapcinsky, J. (2000) A case study for development of an island fauna: recent terrestrial mollusks of Bermuda. – Nemouria, 44:1-99. Biernbaum, C.K. (1980) Occurrence of the 'tramp' terrestrial amphipods Talitroides alluaudi and T. topitotum (Burt) (Amphipoda: Talitridae) in South Carolina. – Brimleyana, 3: 107-111. Bishopp, F.C. & Laake, E.W. (1915) A Preliminary Statement regarding Wool Maggots of Sheep in the United States. - Journal of Economic Entomology, 8 (5): 466-474. Bolger, D.T., Suarez, A.V., Crooks, K.R. Morrison, S.A. & Case, T.J. (2000) Arthropods in urban habitat fragments in Southern California: area, age, and edge effects. - Ecological Applications, 10 (4): 12301248. Braack, L.E.O., Maggs, K.A.R., Zeller, D.A. & Horak, I.G (1995) Exotic arthropods in the Kruger National Park, South Africa: modes of entry and population status. - African Entomology, 3 (1): 39-48. British Arachnological society (2011) Checklist of British spiders. http://wiki.britishspiders.org.uk/index.php5?title=The_Checklist_of_British_Spiders (accessed February 2012). Brunel, E. (1973) Some problems presented by Diptera in maize crops in the west. - Sciences Agronomiques Rennes: 205-207. Buckle, D.G. & Hormiga, G. (2000) A catalog of the linyphid spiders of South America, Central America, Mexico and the West Indies (Araneae, Linyphiidae) http://www.gwu.edu/~clade/spiders/SA-LIN.3.htm Burke, J.L., Maerz, J.C., Milanovich, J.R., Fisk, M.C., Gandhi, K.J.K. (2011) Invasion by exotic earthworms alters biodiversity and communities of litter- and soil-dwelling oribatid mites. - Diversity, 3 (1): 155-175. CABI (1968) Distribution Maps of Plant Pests. – Adoretus versutus, Map 247. http://www.cabi.org/dmpp/?loadmodule=review&page=4049&reviewid=12861&site=164 (accessed February 2012). 10 CABI (2003): see Kairo, M. & Ali, www.issg.org/database/species/reference_files/Kairo%20et%20al,%202003.pdf 2012). B. (accessed (2003) February CABI (2011) Plantwise datasheet Adoretus versutus. http://www.plantwise.org/?dsid=3283&loadmodule=plantwisedatasheet&page=4270&site=234 (accessed February 2012). Callaham, Mac A., Gonzalez, G., Hale, C.M., Heneghan, L., Lachnicht, S.L. & Zou, X. (2006) Policy and management responses to earthworm invasions in North America. - Biol. Invasions, 8:1317–1329. Cameron, E.K., Bayne, E.M. & Clapperton, M.J. (2007) Human-facilitated invasion of exotic earthworms into northern boreal forests. – Ecoscience, 14 (4): 482-490. Carpintero, S., Reyes-López, J. & Arias de Reyna, L. (2005) Impact of Argentine ants (Linepithema humile) on an arboreal ant community in Doñana National Park, Spain. - Biodiversity and Conservation, 14(1):151163. Center for Invasive Species Research info on the Brown http://cisr.ucr.edu/brown_widow_spider.html (accessed February 2012). Widow Spider (2011) Chhotani, O.B. (1970) Taxonomy, zoogeography and phylogeny of the genus Cryptotermes (Isoptera: Kalotermitidae) from the Oriental region. - Memoirs of the Zoological Survey of India, 15: 1-81. Clapperton, B.K. & Dymock, J.J. (1997) Growth and survival of colonies of the Asian paper wasp, Polistes chinensis antennalis (Hymenoptera:Vespidae), in New Zealand. - New Zealand journal of zoology, 24: 9–15. Clapperton, B.K. & Lo, P.L. (2000) Nesting biology of Asian paper wasps Polistes chinensis antennalis Perez, and Australian paper wasps P-humilis (Fab.) (Hymenoptera : Vespidae) in northern New Zealand. - New Zealand Journal of Zoology, 27 (3): 189–195. Clapperton, B.K.(1999) Abundance of wasps and prey consumption of paper wasps (Hymenoptera, Vespidae: Polistinae) in Northland, New Zealand. - New Zealand Journal of Ecology, 23 (1): 11–19. Clapperton, B.K., Alspach, P.A., Moller, H. & Matheson, A.G. (1989) The impact of common and German wasps (Hymenoptera:Vespidae) on the New Zealand beekeeping industry. - New Zealand Journal of Zoology, 16: 325-332. Clapperton, B.K., Lo, P.L., Moller, H. & Sandlant, G.R. (1989) Variation in colour markings of German wasps Vespula germanica (F.) and common wasps Vespula vulgaris (L.) (Hymenoptera:Vespidae) in New Zealand. - New Zealand journal of zoology, 16: 303–313. Clapperton, B.K., Moller, H. & Sandlant, G. (1989) Distribution of social wasps (Hymenoptera:Vespidae) in New Zealand in 1987. - New Zealand journal of zoology, 16: 315–323. Clapperton, B.K., Tilley, J.A.V. & Pierce, R.J. (1996) Distribution and abundance of Asian paper wasps Polistes chinensis antennalis Perez and Australian paper wasps P. humilis (Fab.) (Hymenoptera:Vespidae) in various habitats in New Zealand. - New Zealand journal of zoology, 23: 19–25. Clapperton, B.K., Tilley, J.A.V., Beggs, J.R. & Moller, H. (1994) Changes in the distribution and proportions of Vespula vulgaris (L.) and Vespula germanica (Fab.) (Hymenoptera:Vespidae) between 1987 and 1990 in New Zealand. - New Zealand journal of zoology, 21: 295–303. Clarke, J. & Gates, F. (1986): Pyralidae and Microlepidoptera of the Marquesas Archipelago. -Smithsonian Contributions to Zoology 416: 1-485. Clausen, C.P. (1978) Dermaptera -- Forficulidae -- European Earwig. In: Clausen, C.P. (ed.) Introduced Parasites and Predators of Arthropod Pests and Weeds: A World Review, Handbook No. 480, United States Department of Agriculture, Washington, DC: 15-18. Collingwood, C.A., Tigar, B.J., Agosti, D. (1997) Introduced ants in the United Arab Emirates. - Journal of Arid Environments, i37 (3): 505-512. Couilloud, R. (1988) Cryptophlebia (=Argyroploce) leucotreta (Meyrick) (Lepidoptera, Tortricidae, Olethreutinae). – Coton et Fibres Tropicales, 63 (4): 319-351. CSIRO (Commonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research Organisation) (2004) "Periplaneta australasiae (Fabricius)". http://www.ces.csiro.au/aicn/system/c_481.htm (accessed Dec. 2011). 11 Diba, H., Jamont, M., Sauphanor, B. & Capowiez, Y. (2011) Predation potency and intraguild interactions between generalist (Forficula auricularia) and specialist (Episyrphus balteatus) predators of the rosy apple aphid (Dysaphis plantaginea). - Biological Control, 59 (2): 90-97. Donovan, B.J. (1984) Occurrence of the common wasp, Vespula vulgaris (L.) (Hymenoptera:Vespidae) in New Zealand. - New Zealand journal of zoology, 11: 417–427. Donovan, B.J. (1991) Nest initiation by German and common wasp queens (Hymenoptera:Vespidae) and nest fate at Christchurch, New Zealand. - New Zealand journal of zoology, 18: 95–99. Donovan, B.J., Howie, A.M.E., Schroeder, N.C., Wallace, A.R. & Read, P.E.C. (1992) Comparative characteristics of nests of Vespula germanica (F.) and Vespula vulgaris (L.) (Hymenoptera:Vespinae). New Zealand journal of zoology, 19: 61–71. Dorow, W.H.O. (1996) Review and bibliography of the ants of the Seychelles (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Journal of African Zoology, 110 (2): 73-96. Eldridge, B.F. & Edman, J.D. (eds.) (2003) Medical Entomology: A Textbook on Public Health and Veterinary Problems Caused by Arthropods. - New York: Springer Publishing Company: 672 pp. Emmanuel, N., Sujatha, A. & Gautam, B. (2010) Record of Leaf Chafer Beetles Adoretus versutus Harold and Apogonia blanchardi Ritsema on Cocoa (Theobroma cacao L.) in Andhra Pradesh. - Insect Environment, 16 (1): 23. EPPO (2011) Data sheets on quarantine pests Heteronychus http://www.eppo.org/QUARANTINE/insects/Heteronychus_arator/HETRAR_ds.pdf arator. - European and Mediterranean Plant Protection Organization (EPPO) (2005) Maconellicoccus hirsutus OEPP/EPPO Bulletin, 35: 413–415. http://www.eppo.org/QUARANTINE/insects/Maconellicoccus_hirsutus/DS_Maconellicoccus_hirsutus.pdf (accessed February 2012) Evans, T.A. (2011) Invasive Termites. In: Bignell, David Edward; Roisin, Yves; Lo, Nathan (Eds.): Biology of Termites: a Modern Synthesis. - Springer: 519-562. Fordham, R.A. (1991) Vespulid wasps at the upper forest margin in Tongariro National Park - a threat to the native biota? - New Zealand Journal of Zoology, 18: 151–153. Fordham, R.A., Craven, A.J. & Minot, E.O. (1991) Phenology and population structure of annual nests of the German wasp Vespula germanica (Fab.) in Manawatu, New Zealand, with particular reference to late summer and autumn. - New Zealand journal of zoology, 18: 127–137. Forster, R.R. & Forster, L.M. (1973) New Zealand Spiders: An Introduction. - Collins, Auckland. Fowler, H.G., Bueno, O.C., Sadatsune, T. & Montelli, A.C. (1993) Ants as potential vectors of pathogens in hospitals in the state of Sao Paulo, Brazil. - Insect Science and its Application, 14 (3): 367-370. Glare, T. R.; Richards, N. K.; Nelson, T. L. & Toft, R. J. (2004) Preliminary analysis of Vespula speciation in New Zealand using DNA sequencing. In: Entomological Society of New Zealand 53rd Annual Conference, NMIT, Nelson, 13-16 April 2004: 39. Gómez, C. & Oliveras, J. (2003) Can the Argentine ant (Linepithema humile Mayr) replace native ants in myrmecochory? - Acta Oecologica, 24 (1): 47-53. Gómez, K. & Espadaler, X. (2005) La Hormiga Argentina (Linepithema humile) en las Islas Baleares. Listado Preliminar de las Hormigas de las Islas Baleares. - Documentos Técnicos de Conservación, II, época, 13. Conselleria de Medi Ambient.: 68pp. Haines, C.P. & Rees, D.P. (1989). "Necrobia rufipes". A field guide to the types of insects and mites infesting cured fish. - Food and Agriculture Organization. Harris, A.C. (1979) Occurrence and nesting of the yellow Oriental paper wasp, Polistes olivaceus (Hymenoptera: Vespidae), in New Zealand. - New Zealand Entomologist, 7: 41–44. Harris, R. J. & Beggs, J. R. (1995) Variation in the quality of Vespula vulgaris (L.) queens (Hymenoptera:Vespidae) and its significance in wasp population dynamics. - New Zealand journal of zoology, 22: 131–142. Harris, R. J. (1991) Diet of the wasps Vespula vulgaris and V. germanica in honeydew beech forest of the South Island, New Zealand. - New Zealand Journal of Zoology, 18: 159–170. 12 Harris, R.J. & Oliver, E.H. (1993) Prey diets and population densities of the wasps Vespula vulgaris and V. germanica in scrubland-pasture. - New Zealand journal of ecology, 17: 5–12. Harris, R.J. (1989) An entrance trap to sample foods of social wasps (Hymenoptera: Vespidae). - New Zealand journal of zoology, 16: 369–371. Harris, R.J. (1995) Effect of starvation of larvae of Vespula vulgaris (L.) (Hymenoptera: Vespidae) on subsequent survival and adult size. - New Zealand journal of zoology, 22: 33–38. Harris, R.J. (1996) Frequency of over wintered Vespula germanica (Hymenoptera: Vespidae) colonies in scrubland- pasture habitat and their impact on prey. - New Zealand journal of zoology, 23: 11–17. Harris, R.J., Moller, H. & Tilley, J.A.V. (1991) Weather-related differences in attractiveness of protein foods to Vespula wasps. - New Zealand journal of ecology, 15: 167–170. Harris, R.J., Moller, H. & Winterbourn, M.J. (1994) Competition for honeydew between two social wasps in South Island beech forests, New Zealand. - Insectes Sociaux, 41: 379–394. Harris, R.J., Thomas, C.D. & Moller, H. (1991) The influence of habitat use and foraging on the replacement of one introduced wasp species by another in New Zealand. - Ecological Entomology, 16: 441–448. Heath, A.C.G. & Bishop, D.M. (1995) Flystrike in New Zealand. – Surveillance, 22 (2): 12-13. Hendrix, F.P. (ed.) (2006) Biological invasions belowground earthworms as invasive species. - SpringerLink Dordrecht, Netherlands: Springer. Hoare, R.J.B. (2001) Adventive species of Lepidoptera recorded for the first time in New Zealand since 1988. New Zealand Entomologist, 24: 23-47. Jacobs, S.B. (2006) House cenripede, Scutigera coleoptrata, Centipedes, Class Chilopoda. - The Pennsylvania State University: http://ento.psu.edu/extension/factsheets/pdf/HouseCentipedes2.pdf (accessed February 2012). Janssens, F. (2011) Checklist of the Collembola.- http://www.collembola.org/taxa/collembo.htm (accessed February 2012). Johnson, D.M, & Stiling, D.S. (1998) Distribution and dispersal of Cactoblastis cactorum (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae), and exotic opuntia-feeding moth. - Florida Entomologist 81 (1): 12-21. Johnston, T.H. (1921) The Sheep Maggot Fly Problem in Queensland. - Queensland Agricultural Journal, 6: 244248. Kairo, M. & Ali, B. (2003) Invasive Species Threats in the Caribbean Region. – Report to the Nature Conservancy, 134pp, www.issg.org/database/species/reference_files/Kairo%20et%20al,%202003.pdf (accessed February 2012). Keller, R.P., Cox, A.N., Van Loon, C., Lodge, D.M., Herborg, L.-M. & Rothlisberger, J. (2007) From bait shops to the forest floor: Earthworm use and disposal by anglers. - American Midland Naturalist, 158 (2): 321328. Klotz, J.H., Mangold, J.R., Vail, K.M., Davis, L. R. & Patterson, R.S. (1995) A survey of the urban pest ants (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) of peninsular Florida. - Florida Entomologist, 78 (1): 109-118. Kucerova, Z. (2002) Weight losses of wheat grains caused by psocid infestation (Liposcelis bostrychophila: Liposcelididae: Psocoptera). - Plant Protection Science 38: 103-107. Leathwick, D.M. & Godfrey, P.L. (1996) Overwintering colonies of the common wasp (Vespula vulgaris) in Palmerston North, New Zealand. - New Zealand journal of zoology, 23: 355–358. Leathwick, D.M. (1997) Growth and development of queen colonies of Vespula germanica and V. vulgaris. - New Zealand journal of zoology, 24: 17–23. Leathwick, D.M., Godfrey, P.L., Fordham, R.A. & Potter, M.A. (1999) Comparative growth and seasonality of Vespula germanica and V. vulgaris (Hymenoptera: Vespidae) colonies in the Manawatu region of New Zealand. - New Zealand journal of zoology, 26: 27–38. Malham, J.P., Rees, J.S., Alspach, P.A., Beggs, J.R. & Moller, H. (1991) Traffic rate as an index of colony size in Vespula wasps. - New Zealand journal of zoology, 18: 105–109. Markwell, T.J., Kelly D. & Duncan K.W. (1993) Competition between honey bees (Apis mellifera) and wasps (Vespula spp) in honeydew beech (Nothofagus solandri var solandri) forest. - New Zealand Journal of Ecology, 17 (2): 85–93. 13 Marquez, J.G., Cummings, M.A. & Krafsur, E.S. (2007) Phylogeography of stable fly (Diptera: Muscidae) estimated by diversity at ribosomal 16S and cytochrome oxidase I mitochondrial genes. - Journal of Medical Entomology, 44 (6): 998-1008. Martinez, M.J. (1992) A new ant introduction for North America: Pheidole teneriffana (Forel) (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). - Pan-Pacific Entomologist, 68 (2): 153-154. Moller, H. & Tilley, J.A.V. (1989) Beech honeydew: seasonal variation and use by wasps, honeybees and other insects. - New Zealand Journal of Zoology, 16: 289–302. Moller, H. (1990) Wasps kill nestling birds. – Notornis, 37: 76–77. Moller, H., Clapperton, B. K., Alspach, P. A. & Tilley, J. A. V. (1991) Comparative seasonality of Vespula germanica (F.) and Vespula vulgaris (L.) colonies (Hymenoptera:Vespidae) in urban Nelson, New Zealand. - New Zealand journal of zoology, 18: 111–120. Moller, H., Tilley, J.A.V., Plunkett, G. M. & Clapperton, B.K. (1991) Nest sites of common and German wasps (Hymenoptera:Vespidae). - New Zealand journal of zoology, 18: 121–125. Moller, H., Tilley, J.A.V., Thomas, B.W. & Gaze, P.D. (1991) Effect of introduced social wasps on the standing crop of honeydew in New Zealand beech forests. - New Zealand Journal of Zoology 18: 171–179. Morrison, L. W. (1997) Polynesian ant (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) species richness and distribution: a regional survey. - Acta Oecologica, 18 (6): 685-695. Mound, L.A. & Marullo, R. (1996) The thrips of Central and South America: an introduction (Insecta: Thysanoptera). - Memoirs on Entomology, International 6: 1-487. Mound, L.A. & Walker, A.K. (1982) Terebrantia (Insecta: Thysanoptera). - Fauna of New Zealand 1: 1-113. Mound, L.A. (1996) Thysanoptera. pp. 249-332, 333-337 (App. I-III), 397-414 (index) in Wells, A. (ed.) Zoological Catalogue of Australia. Vol. 26. Psocoptera, Phthiraptera, Thysanoptera. - Melbourne: CSIRO Publishing, Australia. Murdoch, C.L., Tashiro, H., Tavares, J.W. & Mitchell, W.C. (1990) Economic damage and host preference of lepidopterous pests of major warm season turfgrasses of Hawaii. - Proceedings of the Hawaiian Entomological Society, 30: 63-70. Ness, J.H. & Bronstein J.L. (2004) The effects of invasive ants on prospective ant mutualists. -Biological Invasions, 6: 445-461. Norden, A.W. (2008). "The terrestrial isopods (Crustacea: Isopoda: Oniscidea) of Plummers Island, Maryland". Bulletin of the Biological Society of Washington 15 (1): 41–43. Olsen, K.M. (1995) Cordioniscus stebbingi (Patience, 1907) and Trichorhina tomentosa (Budde-Lund, 1893), two greenhouse woodlice (Isopoda, Oniscidea) new to Norway. - Fauna Norvegica. Serie B, Norwegian Journal of Entomology, 42 (1): 67-69. Ori, M., Shinkai, E. & Ikeda, H. (1996) Introduction of widow spiders into Japan. - Medical Entomology and Zoology, 47 (2): 111-119. Palmer, J.M. (1975) The grass-living genus Aptinothrips Haliday (Thysanoptera: Thripidae). - Journal of Entomology (B) 44: 175-188. Peck, S. B., Roth, L. M. (1992) Cockroaches of the Galápagos Islands, Ecuador, with descriptions of three new species (Insecta: Blattodea). - Canadian Journal of Zoology, 70 (11): 2202-2217. Platnick, N.I. (2010) Linyphiidae World Spider Catalog. - American Museum of Natural History. Plunkett, G.M., Moller, H., Hamilton, C. & Thomas, C.D. (1989) Overwintering colonies of German (Vespula germanica) and common wasps (Vespula vulgaris) (Hymenoptera:Vespidae) in New Zealand. - New Zealand journal of zoology, 16: 343–353. Rees, D.P. & Walker, A.J. (1990) The effect of temperature and relative humidity on population growth of three Liposcelis species infesting stored products in tropical countries. - Bulletin of Entomological Research 80: 353-358. Rentz, D.C.F. (1988) The orthopteroid insects of Norfolk Island, with descriptions and records of some related species from Lord Howe Island, South Pacific. - Invertebrate Taxonomy, 2 (8): 1013-1077. Richardson, A.M.M. (1992) Altitudinal distribution of native and alien landhoppers (Amphipoda: Talitridae) in the Ko'olau Range, O'ahu, Hawaiian Islands. - Journal of Natural History, 26 (2): 339-352. 14 Roth, L. M. (1994) New Queensland cockroaches of Macrocerca Hanitsch and Periplaneta Burmeister (Blattidae). - Memoirs of the Queensland Museum, 35 (1): 225-233. Roth, L. M. (1996) Cockroaches from the Seychelles Islands (Dictyoptera: Blattaria). - Journal of African Zoology, 110 (2): 97-128. Sandlant, G.R. & Moller, H. (1989) Abundance of common and German wasps (Hymenoptera: Vespidae) in the honeydew beech forests of New Zealand. - New Zealand journal of zoology, 16: 333–343. Santini, L. & Caroli, L. (1992) Damage to fruit crops by European earwig (Forficula auricularia L.). -InformatoreFitopatologico, 42: 35–38. Schmidt, E.R. & New, T.R. (2008): The Psocoptera (Insecta) of Tasmania, Australia. - Memoirs of Museum Victoria, 65: 71–152. Shelley, R.M. (2004) Occurrences of the centipedes, Scolopendra morsitans L. and S. subspinipes Leach, on Pacific Islands (Chilopoda: Scolopendromorpha: Scolopendridae). - Entomological News 115: 78-83. Silverman, J. & Liang, D. (2001) Colony disassociation following diet partitioning in a unicolonial ant. Naturwissenschaften, 88 (2): 73-77. Smit, B. (1929) The Sheep Blow-flies of South Africa. - Bull. Dept. Agrie. S. Africa, 47: 27 pp. Suarez, A.V., Tsutsui, N.D., Holway, D.A. & Case, T.J. (1999) Behavioral and genetic differentiation between native and introduced populations of the Argentine ant. - Biological Invasions, 1 (1): 43-53. Taiti, S., Howarth, F.G. (1996) Terrestrial isopods from the Hawaiian Islands (Isopoda: Oniscidea). - Bishop Museum Occasional Papers, 45: 59-71. Teulon, D.A.J., Drayton, G M. & Scott, I.A.W. (2009) Exotic introductions of primary parasitoids of aphids in New Zealand: the good and the bad. - Proceedings of the 3rd International Symposium on Biological Control of Arthropods, Christchurch, New Zealand, 8-13 February, 2009: 421-430. Thomas, C.D., Moller, H., Plunkett, G.M. & Harris, R.J. (1990) The prevalence of introduced Vespula vulgaris wasps in a New Zealand beech forest community. - New Zealand Journal of Ecology, 13: 63-72. Thompson, F.C. & Rogers, T. (1992) Sylvicola cinctus (Fabricius), the Hawaiian Wood Gnat, with Notes on the Family (Diptera: Anisopodidae). - Proceedings, Hawaiian Entomological Society, 31: 47-57. Toft, R.J. & Beggs, J.R. (1995) Seasonality of crane flies (Diptera:Tipulidae) in South Island beech forest in relation to the abundance of Vespula wasps (Hymenoptera: Vespidae). - New Zealand entomologist, 18: 37–43. Toft, R.J., Rees, J.S. (1998) Reducing predation of orb-web spiders (Araneidae) by controlling common wasps (Vespula vulgaris) in a New Zealand beech forest. Ecological Entomology, 23: 90–95. Tomalak, M. (2008) Major problems in protection of oyster mushroom (Pleurotus spp.) cultures against pests. Progress in Plant Protection, 48 (3): 978-987. Tryon G.W. (1885) Manual of Conchology. Second series: Pulmonata Volume 1. Testacellidae, Oleacinidae, Streptaxidae, Helicoidea, Vitrinidae, Limacidae, Arionidae: 364 pp. University of California (2008) Thrips of California. http://keys.lucidcentral.org/keys/v3/thrips_of_california/data/key/thysanoptera/Media/Html/overview/intro duced_thrips.html (accessed February 2012). Vila, M., Espinar, J.L., Hejda, M., Hulme, P.E., Jarosik, V., Maron, J.L., Pergl, J., Schaffner, U., Sun, Y. & Pysek, P. (2011) Ecological impacts of invasive alien plants: a meta-analysis of their effects on species, communities and ecosystems. - Ecology Letters, 14: 702–708. Wall, R. & Shearer, D. (1997) Arthropod ectoparasites of veterinary importance. – In: Veterinary Entomology: Chapman & Hall, London: 439 pp. (references to impact of Protophormia terraenovae). Ward, D., Honan, P. & Lefoe, G. (2002) Colony structure and nest characteristics of European wasps Vespula germanica (F.) (Hymenoptera: Vespidae) in Victoria, Australia. - Australian Journal of Entomology, 31 (4): 306-309. Watt, J.C. (1975) Some Coleoptera from the Kermadec Islands. - New Zealand entomologist, 6: 50-55. Wetterer, J. K. (1998) Nonindigenous ants associated with geothermal and human disturbance in Hawaii Volcanoes National Park. - Pacific Science, 52 (1): 40-50. 15 Wetterer, J.K., Espadaler, X., Wetterer, A.L., Aguin-Pombo, D., Franquinho-Aguiar, A.M. (2007b) Ants (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) of the Madeiran archipelago. – Sociobiology, 49 (3): 265-298. Wilson, P.R., Karl, B.J., Toft, R.J., Beggs, J.R. & Taylor, R.H. (1998) The role of introduced predators and competitors in the decline of kaka (Nestor meridionalis) populations in New Zealand. -Biological Conservation, 83: 175–185. Wittmer, W. & Peck, S.B. (1993) Cantharidae and Malachiidae of the Galapagos Islands, Ecuador. - The Coleopterists Bulletin, 47 (1): 77-81. Wu, Y., Chen, B. & Ou, G.(2011) Damage of Coffee Bean weevil (Araecerus fasciculatus, De Geer) on its new host Jatropha curcas L. – Plant Diseases and Pests, 2 (2): 22-24. Yao, M.C. & Lo, K.C. (1992) Insect species and population densities in stored japonica rice in Taiwan. - Chinese Journal of Entomology, 12 (3): 161-169. Zimmerman, E.C. (1978) Insects of Hawaii. A manual of the insects of the Hawaiian Islands, including an enumeration of the species and notes on their origin, distribution, hosts, parasites, etc. Volume 9. Microlepidoptera. Part I. Monotrysia, Tineoidea, Tortricoidea, Gracillarioidea, Yponomeutoidea, and Alucitoidea. - University Press of Hawaii., Honolulu, Hawaii, USA: 1-882. Zur Strassen, R. (2006) Checklist of the Thysanoptera (Insecta) of southern Africa. - African Entomology 14: 6368. BC and other control efforts of weeds Andres, L.A. (1980) The biological control of Canada thistle (Cirsium arvense (L.) Scop.) in the United States. Canada Thistle Symposium. Agric. Canada, Regina Research Station: 112-127. Andres, L.A., Hawkes, R.B. & Rizza, A. (1967) Apion seed weevil introduced for biological control of Scotch broom. - California Agriculture, 21: 13. Ang, B.N., Kok, L.T., Holtzman, G.I. & Wolf, D.D. (1995) Canada thistle (Cirsium arvense (L.) Scop.) response to density of Cassida rubiginosa Mnller (Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae) and plant competition. - Biological Control, 5 (1): 31-38. Bacher, S., Friedli, J. & SchSr, I. (2002) Developing in diseased host plants increases survival and fecundity in a stem-boring weevil. - Entomologia Experimentalis et Applicata, 103 (2): 191-195. Bentley, S. & Whittaker, J.B. (1979) Effects of grazing by a Chrysomelid beetle, Gastrophysa viridula, on competition between Rumex obtusifolius and Rumex crispus. - Journal of Ecology, 67 (1): 79-90. Bentley, S., Whittaker, J.B. 7 Malloch, A.J.C. (1980) Field experiments on the effects of grazing by a chrysomelid beetle (Gastrophysa viridula) on seed production and quality in Rumex obtusifolius and Rumex crispus. Journal of Ecology, 68 (2): 671-674. Binggeli, P. (1997) Casuarina equisetifolia L. (Casuarinaceae), - Woody Plant Ecology. Bond, W. & Turner, R.J. (2003) The biology and non-chemical control of creeping thistle (Cirsium arvense), spear thistle (Cirsium vulgare) and perennial sowthistle (Sonchus arvensis). - HDRA Organic Weed Management, Conventry, UK. World Wide Web page at http://www.hdra.org.uk/organicweeds/downloads/thistle_review.pdf (accessed February 2012). Bourdot, G.W. & Harvey, I.C. (1994) A review of recent research on the microbial control of Californian thistle and other pasture weeds using the fungus Sclerotinia sclerotiorum as a biological herbicide. Proceedings of the New Zealand Grassland Association, 56: 43-48. Bourdôt, G.W. & Harvey, I.C. (1996) The potential of the fungus Sclerotinia sclerotiorum as a biological herbicide for controlling thistles in pasture. - Plant Protection Quarterly, 11 (SUP2): 259-262. Bourdot, G.W., Hurrell, G.A., Saville, D.J. & de Jong, M.D. (2001) Risk analysis of Sclerotinia sclerotiorum for biological control of Cirsium arvense in pasture: ascospore dispersal. - Biocontrol Science and Technology, 11: 119-139. Brière, S.C., Watson, A.K. & Paulitz, T.C. (1992) Evaluation of granular sodium alginate formulations of Sclerotinia minor as potential biological control agent of turf grass weed species. - Phytopathology, 82: 1081. 16 Brosten, B.S. & Sands, D.C. (1986) Field trials of Sclerotinia sclerotiorum to control Canada thistle (Cirsium arvense). - Weed Science, 34 (3): 377-380. Brown, R.E. (1990) Biological control of tansy ragwort (Senecio jacobaea) in western Oregon, USA, 1975-87. Proceedings of the VII International Symposium on Biological Control of Weeds Rome, Italy; Istituto Sperimentale per la Patologia Vegetale, Ministero dell'Agricoltura e delle Foreste: 299-305. Bruun, H.H. (2005) Biological Flora of the British Isles. No. 239. Rosa rugosa Thunb. ex Murray. - Journal of Ecology, 93 (2): 441-470. http://www3.interscience.wiley.com/cgi-bin/fulltext/118645540/PDFSTART (accessed February 2012). Bruun, H.H. (2006) Prospects for biocontrol of invasive Rosa rugosa. - BioControl, 51 (2): 141-181. Burpee, L.L. (1992) A method for assessing the efficacy of a biocontrol agent on dandelion (Taraxacum officinale). - Weed Technology, 6 (2): 401-403. Campobasso, G. & Murano, F. (1988) Laboratory and field biology of Lixomorphus ocularis (Fabricius) (Coleoptera, Curculionidae). - Fragmenta Entomologica, 10 (2): 309-316. Charles J.G. (1993) A survey of mealybugs and their natural enemies in horticultural crops in North Island, New Zealand, with implications for biological control. - Biocontrol Science and Technology, 3 (4): 405-418. Cilliers, C.J. & Neser, S. (1991) Biological control of Lantana camara (Verbenaceae) in South Africa. Agriculture, Ecosystems and Environment, 37 (1-3): 57-75. Ciotola, M., Wymore, L.A. & Watson, A.K. (1991) Sclerotinia, a potential mycoherbicide for lawns. - Weed Science Society of America, Abstracts: 81. Clay, D.V., Boatman, N.D., Goodman, A., Marrs, R.H., Marshall, E.J.P., Newman, J.R., Putwain, P.D. & Pywell, R.F. (2000) Spread and control of common ragwort Senecio jacobaea in England. - Aspects of Applied Biology, 58: 63-70. Cowley, J.M. (1983) Life cycle of Apion ulicis (Coleoptera: Apionidae), and gorse seed attack around Auckland, New Zealand. - New Zealand Journal of Zoology, 10 (1): 83-86. Crawley, M.J. & Pattrasudhi, R. (1988) Interspecific competition between insect herbivores: asymmetric competition between cinnabar moth and the ragwort seed-head fly. - Ecological Entomology, 13 (3): 243249. CSIRO (1999) Weed Management report of research 1997-1999. - CSIRO www.ento.csiro.au/research/weedmgmt/pdf/ror_weeds.pdf (accessed February 2012). Entomology. CSIRO. (2007) Management and control of sowthistles in Australia. - Commonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research Organisation: http://www.csiro.au/science/SowthistleControl.html (accessed February 2012) Davis, C.J., Yoshioka. E. & Kageler, D. (1992) Biological control of lantana, prickly pear, and Hamakua pamakani in Hawaii: a review and update. - In: Stone, C.P., Smith, C.W., Tunison, J.T. (eds.) Alien Plant Invasions in Native Ecosystems of Hawaii: Management and Research. - Honolulu, Hawaii, USA: University of Hawaii Press: 411-431. Day, M.D., Wiley, C.J., Playford, J. & Zalucki, M.P. (2003) Lantana: current management status and future prospects. Australia. - ACIAR Monograph, 102. Dempster, J.P. (1982) The population ecology of the cinnabar moth, Tyria jacobaeae L. (Lepidoptera, Arctiidae). - Oecologia, 7: 26-67. Denton, G.R.W., Muniappan, R. & Marutani, M. (1991) Status and natural enemies of the weed, Lantana camara, in Micronesia. - Tropical Pest Management, 37 (4): 338-344. Dodd, A.P. (1940) The biological campaign against prickly pear. - Commonwealth Prickly Pear Board Bulletin, Brisbane, Australia: 1-177. Drlik, T., Woo, I., Swiadon, L. & Quarles, W. (2000) Integrated management of Canada thistle. - IPM Practitioner, 22 (9): 1-9. Elfers, S.C. (1988) Element Stewardship Abstract for Casuarina equisetifolia. - The Nature Conservancy. Evans, H.C. & Fleureau, L. (1993) Studies on the rust, Maravalia cryptostegiae, a potential biological control agent of rubber-vine weed, Cryptostegia grandiflora (Asclepiadaceae: Periplocoideae), in Australia, II: infection. - Mycopathologia, 124 (3): 175-184. 17 Evans, H.C. & Tomley, A.J. (1994) Studies on the rust, Maravalia cryptostegiae, a potential biological control agent of rubber-vine weed, Cryptostegia grandiflora (Asclepaidaceae: Periplocoideae), in Australia, III: host range. - Mycopathologia, 126 (2): 93-108. Evans, H.C. (1993) Studies on the rust Maravalia cryptostegiae, a potential biological control agent of rubbervine weed (Cryptostegia grandiflora, Asclepiadaceae: Periplocoideae) in Australia, I: life-cycle. Mycopathologia, 124 (3): 164-174. Evans, H.C. (2002) Biological control of weeds. - In: Kempken, F. (ed.) The Mycota XI: Agricultural Applications. - Berlin, Germany, Springer-Verlag: 135-152. Field, R.P. (1990) Progress towards biological control of ragwort in Australia. - Proceedings of the VII International Symposium on Biological Control of Weeds: 315-322. Fisher, K. (1992) Clearwing moths are key to dock control. - Journal of Agriculture, Western Australia, 33 (4): 152-155. Flores, A. (2008) ARS Researchers Search for Casuarina Biological Control Agents. - USDA-ARS (United States Department of Agriculture Agricultural Research Service): http://www.ars.usda.gov/is/pr/2008/080902.htm (accessed February 2012) Forcella, F. & Randall, J.M. (1994) Biology of bull thistle, Cirsium vulgare (Savi) Tenore. - Reviews of Weed Science, 6: 29-50. Forsyth, S.F. & Watson, A.K. (1985) Predispersal seed predation of Canada thistle. - Canadian Entomologist, 117 (9): 1075-1081. Frank, P.A. (1973) A biological control agent for Rumex crispus. - Proceedings of the 2nd International Symposium on Biological Control of Weeds, Rome, 1971: 121-126. Frank, P.A. (1973) A biological control agent for Rumex crispus. - Proceedings of the 2nd International Symposium on Biological Control of Weeds, Rome, 1971. Commonwealth Agricultural Bureaux. Slough UK: 121-126. Frick, K.E. (1970) Ragwort flea beetle established for biological control of tansy ragwort in Northern California. California Agriculture, 24: 12-13. Friedli, J. & Bacher, S. (2001) Direct and indirect effects of a shoot-base boring weevil and plant competition on the performance of creeping thistle, Cirsium arvense. - Biological Control, 22 (3): 219-226. Fröhlich, J. & Gianotti, A. (2000) Development of a bioherbicide to control gorse and broom in New Zealand: research update. - New Zealand Journal of Forestry, 45 (3): 38-40. Fröhlich, J. & Gianotti, A. (2000) Development of a bioherbicide to control gorse and broom in New Zealand: research update, 45: 38-40. Garcia-Baudin, J.M. & Santiago-Alvarez, C. (1978) Biological control of Rumex obtusifolius L. I. Preliminary considerations on the species Gastroidea (=Gastrophysa) unicolor Marsham (Coleoptera Chrysomelidae). - Anales del Instituto Nacional de Investigaciones Agrarias. Serie: Proteccion Vegetal, 1976, recd. 1978, 6: 127-139. Green, S., Mortensen, K. & Bailey, K.L. (2001) Host range, temperature response, survival, and overwintering of Alternaria cirsinoxia. - Biological Control, 20 (1): 57-64. Gronwald, J.W., Plaisance, K.L., Ide, D.A. & Wyse, D.L. (2002) Assessment of Pseudomonas syringae pv. tagetis as a biocontrol agent for Canada thistle. - Weed Science, 50 (3): 397-404. Grosskopf, G., Butler, S., Recher, H. & Schneider, H. (2001) Biological control of hawkweeds, Hieracium spp. Unpublished Annual Report 2001. Delémont, Switzerland: CABI Bioscience Switzerland Centre. Grosskopf, G., Chevillat, V., Klymenko, S., Lovis, L. & Wang, J. (2003) Biological control of hawkweeds, Hieracium spp. - Unpublished Annual Report 2002. Delémont, Switzerland: CABI Bioscience Switzerland Centre. Grosskopf, G., Smith, L.A. & Syrett, P. (2002) Host range of Cheilosia urbana (Meigen) and Cheilosia psilophthalma (Becker) (Diptera: Syrphidae), candidates for the biological control of invasive alien hawkweeds (Hieracium spp., Asteraceae) in New Zealand. - Biological Control, 24 (1): 7-19. Grossrieder, M. & Keary, I.P. (2004) The potential for the biological control of Rumex obtusifolius and Rumex crispus using insects in organic farming, with particular reference to Switzerland. -. Biocontrol News and Information, 25 (3): 65–79. 18 Harris, P. & Wilkinson, A.T.S. (1984) Cirsium vulgare (Savi) Ten., bull thistle (Compositae). - In: Kelleher, J.S. & Hulme, M.A. (eds.) Biological control programmes against insects and weeds in Canada 1969-1980. Farnham Royal, Slough, UK: Commonwealth Agricultural Bureaux: 147-153. Harris, P., Wilkinson, A.T.S., Myers, J.H., Kelleher, J.S.& Hulme, M.A. (1981) Senecio jacobaea L., tansy ragwort (Compositae). - Biological control programmes against insects and weeds in Canada 19691980. - Slough; UK: Commonwealth Agricultural Bureaux: 195-201. Harris, P., Wilkinson, A.T.S., Thompson LS, Neary M, Freeman TE,1979. Interaction between the cinnabar moth, Tyria jacobaeae L. (Lep.: Arctiidae) and ragwort, Senecio jacobaea L. (Compositae) in Canada. Proceedings of the IV International Symposium on Biological Control of Weeds. Gainesville, Florida; USA: Center for Environmental Programs, Institute of Food and Agricultural Sciences, Florida University, 174-180. Hatcher, P.E. & Paul, N.D. (2000) Beetle grazing reduces natural infection of Rumex obtusifolius by fungal pathogens. - New Phytologist, 146 (2): 325-333. Hatcher, P.E., Brandsaeter, L.O., Davies, G., Lüscher, A., Hinz,, H.L., Eschen, R. & Schaffner, U. (2008) Biological control of Rumex species in Europe: opportunities and constraints. - XII International Symposium on Biological Control of Weeds: 470-475. Hawkes, R.B. & Johnson, G.R. (1978) Longitarsus jacobaeae aids moth in the biological control of tansy ragwort. - Proceedings of the 4th International Symposium on Biological Control of Weeds, Gainesville, 1976: 193-196. Hawkes, R.B. (1981) Biological control of tansy ragwort in the state of Oregon, USA. - Proceedings of the 5th International Symposium on Biological Control of Weeds. - Commonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research Organization. Australia: 623-626. Heimann, B. & Cussans, G.W. (1996) The importance of seeds and sexual reproduction in the population biology of Cirsium arvense - a literature review. - Weed Research (Oxford), 36 (6): 493-503. Henderson, L. (2001) Alien Weeds and Invasive Plants. Plant Protection Research Institute Handbook No. 12. Cape Town, South Africa: Paarl Printers. Hill, R.L. & Gourlay, A.H. (2002) Host-range testing, introduction, and establishment of Cydia succedana (Lepidoptera: Tortricidae) for biological control of gorse, Ulex europaeus L., in New Zealand. - Biological Control, 25 (2): 173-186. Hill, R.L., Gourlay, A.H. & Fowler, S.V. (2000) The biological control programme against gorse in New Zealand. In: Spencer, N.R. (ed.) Proceedings of the X International Symposium on Biological Control of Weeds, 414 July 1999. Bozeman, Montana, USA: Montana State University: 909-917. Hill, R.L., Markin, G.P., Gourlay, A.H., Fowler, S.V. & Yoshioka, E. (2001) Host range, release, and establishment of Sericothrips staphylinus Haliday, (Thysanoptera: Thripidae) as a biological control agent for gorse, Ulex europaeus L. (Fabaceae), in New Zealand and Hawaii. - Biological Control, 21 (1): 63-74. Hill, R.L., O'Donnell, D.J., Gourlay, A.H. & Speed, C.B. (1995) Suitability of Agonopterix ulicetella (Lepidoptera: Oecophoridae) as a control for Ulex europaeus (Fabaceae: Genisteae) in New Zealand. - Biocontrol Science and Technology, 5 (1): 3-10. Hill. R.L., Gourlay, A.H. & Winks, C.J. (1993) Choosing gorse spider mite strains to improve establishment in different climates. In: Prestidge, R.A. (ed.) Proceedings, 6th Australasian Grasslands Invertebrate Ecology Conference 17-19 February 1993, Hamilton New Zealand: 377-383. Hodkinson, I.D. (1991) New World legume-feeding psyllids of the genus Aphalaroida Crawford (Insecta: Homoptera: Psylloidea). - Journal of Natural History, 25 (5): 1281-1296. Hodson, J.L., Hoffmann, J.H. & Zimmermann, H.G. (2003) Biological control of spear thistle, Cirsium vulgare (Asteraceae), in South Africa: a modest start for Rhinocyllus conicus (Coleoptera: Curculionidae). African Entomology, 11: 15-20. Hoeft, E.V., Jordan, N., Zhang, J.H. & Wyse, D.L. (2001) Integrated cultural and biological control of Canada thistle in conservation tillage soybean. - Weed Science, 49 (5): 642-646. Hoffmann, J.H. (1995) Biological control of weeds: the way forward, a South African perspective, pp.77-89 in: Weeds in a Changing World. Proceedings of a Symposium, Brighton, UK, 20 November 1995. 19 Holloway, J.K. & Huffaker, C.B. (1957) Establishment of the seed weevil Apion ulicis for suppression of gorse in California. - Journal of Economic Entomology, 50: 498-499. Holm, L.G., Plucknett, D.L., Pancho, J.V. & Herberger, J.P. (1977) The World's Worst Weeds. Distribution and Biology. - Honolulu, Hawaii, USA: University Press of Hawaii. Hosking, J.R., Sullivan, P.R. & Welsby, S.M. (1994) Biological control of Opuntia stricta (Haw.) Haw. var. stricta using Dactylopius opuntiae (Cockerell) in an area of New South Wales, Australia, where Cactoblastis cactorum (Berg) is not a successful biological control agent. - Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment, 48 (3): 241-255. Huber-Meinicke, G., Defago, G. & Sedlar, L. (1989) Ramularia rubella (Bon.) Nannf. as a potential mycoherbicide against Rumex weeds. - Botanica Helvetica, 99 (1): 81-89. Hughes, C.N.G., West, J.S. & Fox, R.T.V. (1996) Control of broad-leaved docks by Armillaria mellea. Proceedings of the 9th international symposium on biological control of weeds, Stellenbosch, South Africa, 19-26 January 1996: 531-534. Inman, R.E. (1971) A preliminary evaluation of Rumex rust as a biological control agent for Curly Dock. Phytopathology, 61 (1): 102-107. Ireson, J.E., Gourlay, A.H., Kwong, R.M., Holloway, R.J. & Chatterton, W.S. (2003) Host specificity, release, and establishment of the gorse spider mite, Tetranychus lintearius Dufour (Acarina: Tetranychidae), for the biological control of gorse, Ulex europaeus L. (Fabaceae), in Australia. - Biological Control, 26: 117-127. Ireson, J.E., Leighton, S.M., Holloway, R.J. & Chatterton, W.S. (2000) Establishment and redistribution of Longitarsus flavicornis (Stephens) (Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae) for the biological control of ragwort (Senecio jacobaea) in Tasmania. - Australian Journal of Entomology, 39 (1): 42-46. Ivens, G.W. (1979) Weeds of note: ragwort. - New Zealand Journal of Agriculture, 139 (3): 48-49. James, R.R., McEvoy, P.B. & Cox, C.S. (1992) Combining the cinnabar moth (Tyria jacobaeae) and the ragwort flea beetle (Longitarsus jacobaeae) for control of ragwort (Senecio jacobaea): an experimental analysis. - Journal of Applied Ecology, 29 (3): 589-596. Jeritta, A.L.R. & David, B.V. (1986) Some insects associated with euphorbiaceous weeds. - Pest Management, 1: 21-26. Julien, M. (2002) Biological control of tropical weeds with Central and South American origin: current activities by CSIRO Entomology. - 13th Australian Weeds Conference: weeds "threats now and forever?", Perth, Western Australia, 8-13 September 2002: papers and proceedings: 361-365. Julien, M.H. & Griffiths, M.W. (1998) Biological control of weeds: a world catalogue of agents and their target weeds. Ed. 4: 223pp. Julien, M.H. & Griffiths, M.W. (1998) Biological Control of Weeds: a World Catalogue of Agents and their Target Weeds. - Fourth Edition. Wallingford, UK: CAB International. Julien, M.H. (ed.) (1987) Biological control of weeds. A world catalogue of agents and their target weeds, 2nd edn. - CAB International: Wallingford, UK. Julien, M.H., Kassulke, R.C. & Harley, K.L.S. (1984) Lixus cribricollis (Col.: Curculionidae) for biological control of the weeds Emex spp. and Rumex crispus in Australia. - Entomophaga, 27 (4): 439-446. Kay, M. (2002) Variety in Buddleia Biocontrol. - Biocontrol News and Information. Wallingford, UK: CABI. http://www.pestscience.com/Bni23-3/Gennews.htm (accessed February 2012). Keary, I.P. & Hatcher, P.E. (2002) Prospects for the biological control of Rumex obtusifolius in competition with Lolium perenne: evidence from pot trials. – Proceedings of the 12th EWRS (European Weed Research Society) Symposium 2002, Wageningen, 230-231. Kinkorova, J. (1991) Life histories of Terellia serratulae and Urophora stylata (Diptera, Tephritidae) and their cooccurrence on Cirsium vulgare. - Acta Entomologica Bohemoslovaca, 88: 293-298. Klöppel, M., Smith, L. & Syrett, P. (2003) Predicting the impact of the biocontrol agent Aulacidea subterminalis (Cynipidae) on growth of Hieracium pilosella (Asteraceae) under differing environmental conditions in New Zealand. - Biocontrol Science and Technology, 13 (2): 207-218. Kluth, S., Kruess, A. & Tscharntke, T. (2002) Insects as vectors of plant pathogens: mutualistic and antagonistic interactions. - Oecologia, 133 (2): 193-199. 20 Kluth, S., Kruess, A. & Tscharntke, T. (20030 Influence of mechanical cutting and pathogen application on the performance and nutrient storage of Cirsium arvense. - Journal of Applied Ecology, 40 (2): 334-343. Kok, L.T., Andres, L.A. & Boldt, P.E. (1979) Host specificity studies on Ceutorhynchus trimaculatus (Col.: Curculionidae), a potential biological control agent of musk and plumeless thistle. - Environmental Entomology, 8 (6): 1145-1149. Kriticos, D.J., Alexander, N.S. & Kolomeitz, S.M. (2006) Predicting the potential geographic distribution of weeds in 2080. - Melbourne, Australia: Weed Science Society of Victoria. Kruess, A. (2002) Indirect interaction between a fungal plant pathogen and a herbivorous beetle of the weed Cirsium arvense. - Oecologia, 130 (4): 563-569. Kwon O.S., Park, J.Y., Lee I.Y. & Park J.E. (2006) General biology of Ostrinia palustralis memnialis (Walker), a potential biological control agent of Rumex spp. in Korea. - Entomological Research, 36 (3): 179-182. Lacasa, A., Contreras, J., Sanchez, J.A., Lorca, M. & Garcia, F. (1996) Ecology and natural enemies of Frankliniella occidentalis (Pergande, 1895) in south-east Spain. - In: Jenser, G., Adam, L., (eds.) Proceedings of the Fifth International Symposium on Thysanoptera. - Folia Entomologica Hungarica, 62 (Suppl.): 67-74. Landcare Research (2007) The Biological Control of Weeds Book: Heather beetle Lochmaea suturalis. http://www.landcareresearch.co.nz/research/biocons/weeds/book/documents/Heather_Beetle.pdf (accessed February 2012). Landcare Research (2008) Big Is Sometimes Best. What's new in the biological control of weeds? Issue 43 February 2008. http://www.landcareresearch.co.nz/publications/newsletters/weeds/wtsnew43.pdf (accessed February 2012). Landcare Research (2009) Army Recruits One Million. What's new in the biological control of weeds? Issue 49 August 2009. http://www.landcareresearch.co.nz/publications/newsletters/weeds/wtsnew49.pdf (accessed February 2012). Laudonia S. & Viggiani, G. (1986). Natural enemies of the citrophilus mealybug (Pseudococcus calceolarip Mask.) in Campania. - Bollettino del Laboratorio di Entomologia Agraria "Filippo Silvestri", Italy, 43 (suppl.): 167-171. Lima, P.C.F. (1994) Comportamento silvicultural de especies de Prosopis, em Petrolina-PE, Regi¦o Semi-Arida Brasileira. - PhD Thesis. Curitiba, Brazil: Universidade Federal do Parana. Louda, S.M. & O'Brien, C.W. (2002) Unexpected ecological effects of distributing the exotic weevil, Larinus planus (F.), for the biological control of Canada thistle. - Conservation Biology, 16 (3): 717-727. Mann, J. (1969) Cactus-feeding insects and mites. Bulletin 256. - Smithsonian Institution, Washington DC, USA: Smithsonian Institution Press. Markin, G.P., Conant, P., Killgore, E. & Yoshioka, E. (2002) Biological control of gorse in Hawaii. - In: Smith, C.W., Denslow, J. & Hight, S. (eds.) Proceedings of a workshop on biological control of invasive plants in native Hawaiian ecosystems. Honolulu, Hawaii: Pacific Cooperative Studies Unit, University of Hawaii. Markin, G.P., Yoshioka, E.R. & Conant, P. (1996) Biological control of gorse in Hawaii. - Proceedings of the 9th international symposium on biological control of weeds, Stellenbosch, South Africa, 19-26 January 1996: 371-375. McAvoy, T.J., Kok, L.T. & Mays, W.T. (1987) Dispersal of Trichosirocalus horridus (Panzer) (Coleoptera: Curculionidae) in southwest Virginia. - Journal of Entomological Science, 22 (4): 324-329. McCarren, K.L. & Scott, J.K. (2008) Two biological control options for Sonchus oleraceus in Australia.Proceedings of the 16th Australian Weeds Conference, Cairns, Australia: 259-261. McEvoy, P.B., Cox, C. & Coombs, E. (1991) Successful biological control of ragwort, Senecio jacobaea, by introduced insects in Oregon. - Ecological Applications, 1 (4): 430-442. McFadyen, R.E. & Marohasy, J.J. (1990) A leaf feeding moth, Euclasta whalleyi (Lep.: Pyralidae) for the biological control of Cryptostegia grandiflora (Asclepiadaceae) in Queensland, Australia. -Entomophaga, 35 (3): 431-435. McFadyen, R.E.C. (1998) Biological control of weeds, Annual Review of Entomology 43: pp.369-393. McFayden, R.E. & Harvey, G.J. (1990) Distribution and control of rubber vine, Cryptostegia grandiflora, a major weed in northern Queensland. - Plant Protection Quarterly, 5: 153-155. 21 McLaren, D.A. (1992) Observations of the life cycle and establishment of Cochylis atricapitana (Lep: Cochylidae), a moth used for biological control of Senecio jacobaea in Australia. - Entomophaga, 37 (4): 641-648. McLaren, D.A., Ireson, J.E. & Kwong, R.M. (2000) Biological control of ragwort (Senecio jacobaea L.) in Australia. - In: Spencer, N.R. (ed.) Proceedings of the X International Symposium on Biological Control of Weeds. Bozeman, Montana, USA: Montana State University: 67-79. Miller, D. (1970) Biological control of weeds in New Zealand 1927-48. - New Zealand Department of Industrial and Scientific Research, Information Series, 74: 27-58. Miyazaki, M. & Naito, A. (1981) Studies on the biological control of Rumex obtusifolius L., a grassland weed, by Gastrophysa atrocyanea Mots. (Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae). III. Survival rate and mortality factors of G. atrocyanea. - Bulletin of the National Grassland Research Institute, 20: 103-111. Miyazaki, M., Naito, A. & Wapshere, A. J. (1974) Studies on the host specificity of Gastrophysa atrocyanea Mot. (Col.:Chrysomelidae), a potential biological control agent against Rumex obtusifolius L. (Polygonaceae) in Japan. - Miscellaneous Publication, Commonwealth Institute of Biological Control, 1974, 8: 97-107. Mo, J., Trevino, M. & Palmer, W.A. (2000) Establishment and distribution of the rubber vine moth, Euclasta whalleyi Popescu - Gorj & Constantinescu (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae), following its release in Australia. Australian Journal of Entomology, 39: 344-350. Monnig, E. (1987) A summary of the status of biological control of major noxious weed species in Idaho, Montana, and North Dakota. Report - Northern Region, USDA Forest Service, No. 87-3:ii + 12 pp. Moore, D. (1988) Agents used for biological control of mealybugs (Pseudococcidae). – Biol. Control News Inf., 9 (4): 209–225. Moore, R.J. (1975) The biology of Canadian weeds. 13. Cirsium arvense (L.) Scop. - Canadian Journal of Plant Science, 55 (4): 1033-1048. Morin, L. & Syrett, P. (1996) Prospects for biological control of Hieracium pilosella with the rust Puccinia hieracii var. piloselloidarum in New Zealand. - Proceedings of the 9th international symposium on biological control of weeds, Stellenbosch, South Africa, 19-26 January 1996: 199-204. Mune, T.L. & Parham, J.W. (1967) The declared noxious weeds of Fiji and their control, 3rd edn. - Fiji Department of Agriculture Bulletin, 48: 1-87. Myers, J.H. and Bazely, D. (2003) Ecology and control of introduced plants. Cambridge University Press. Cambridge, UK. Nagel, W.P. & Isaacson, D.L. (1974) Tyria jacobaeae and tansy ragwort in western Oregon. - Journal of Economic Entomology, 67 (4): 494-496. Naito, A., Miyazaki, M. & Emura, K. (1979) Studies on the biological control of Rumex obtusifolius L. a grassland weed by Gastrophysa atrocyanea Mots. (Chrysomelidae, Coleoptera) 1. On the host specificity of the insect. - Bulletin of the National Grassland Research Institute, Japan, 14: 117-123. Naito, A., Miyazaki, M. & Kanda, K. (1979) Studies on the biological control of Rumex obtusifolius L. a grassland weed, by Gastrophysa atrocyanea Mots. (Col.; Chrysomelidae). 2. Dispersal of overwintered adult insects. - Applied Entomology and Zoology, 14 (1): 51-55. Nakahara, L.M., Burkhart, R.M. & Funasaki, G.Y. (1992) Review and status of biological control of clidemia in Hawai'i. In: Stone, C.P., Smith, C.W., Tunison, J.T. (eds.) Alien plant invasions in native ecosystems of Hawai'i: management and research. Honolulu, USA: University of Hawaii Press: 452-465. Neser, S. (1994) Conflicts of interest? The Leucaena controversy. - Plant Protection News (South Africa), 6: 8. Neumann Brebaum, S. & Boland, G.J. (1999) First report of Phoma herbarum and Phoma exigua as pathogens of dandelion in southern Ontario. - Plant Disease, 83: 200. Neumann Brebaum, S. (1998) Development of an inundative biological weed control strategy for Taraxacum officinale Weber in turf. - PhD Thesis. Guelph, ON, Canada: University of Guelph. Neumann, S., & Boland, G.J. (2002) Influence of host and pathogen variables on the efficacy of Phoma herbarum, a potential biological control agent of Taraxacum officinale. - Canadian Journal of Botany, 80 (4): 425-429. 22 Norambuena, M.H., Escobar, S.S. 7 Rodríguez, A.F. (2001) Biological control of Ulex europaeus L.: introduction to Chile of two populations of the moth Agonopterix ulicetella (Stainton) (Lepidoptera: Oecophoridae). Agricultura Tecnica, 61 (1): 82-88. Park, J.Y.,Lee, I.Y., Park, J.E. & Kwon, O.S. (2008) Allantus luctifer (Hymenoptera: Tenthredinidae), a candidate agent for the biological control of Rumex spp. - Entomological Research, 38 (3): 221-225. Parsons, W.T. & Cuthbertson, E.G. (1992) Noxious Weeds of Australia. - Melbourne, Australia: Inkata Press. Pemberton, R.W. & Turner C.E. (1990) Biological control of Senecio jacobaea in northern California, an enduring success. - Entomophaga, 35 (1): 71-77. Perju, T., Teodor, L.A., Berchez, O. & Oltean, I. (1995) Entomofauna of Cirsium spp. and possibilities of biological control of these weeds with insects. - Buletinul Universităţii de Ştiinţe Cluj-Napoca. Seria Agricultura şi Horticultură, 49 (2): 137-143. Peschken, D.P. & Beecher, R.W. (1973) Ceutorhynchus litura (Coleoptera: Curculionidae): biology and first releases for biological control of the weed Canada thistle (Cirsium arvense) in Ontario, Canada. Canadian Entomologist, 105 (12): 1489-1494. Peschken, D.P. & Wilkinson, A.T.S. (1981) Biocontrol of Canada thistle (Cirsium arvense): releases and effectiveness of Ceutorhynchus litura (Coleoptera: Curculionidae) in Canada. - Canadian Entomologist, 113 (9): 777-785. Peschken, D.P. (1981) Biological control of Canada thistle. - Proceedings North Central Weed Control Conference, 36: 169-173. Peschken, D.P., Hunter, J.H. & Thomas, A.G. (1980). Damage in dollars caused by Canada thistle in wheat in Saskatchewan. - In: Canada Thistle Symposium. Agric. Canada Regina Research Station: 37-43. Peschken, M.P. (1984) Sonchus arvensis L., perennial sow-thistle, S. oleraceus L., annual sow-thistle, and S. asper (L.) Hill, spiny annual sow-thistle (Compositae). - In: Kelleher, J.S., Hulme, M.A. (eds.) Biological control programmes against insects and weeds in Canada 1969-80. - Slough, UK. Commonwealth Agriculture Bureau: pp. 205-209. PIER (2007) Pacific Islands Ecosystems at Risk. - USA: Institute http://www.hear.org/pier/index.html (accessed February 2012). of Pacific Islands Forestry. Piesik, D. (2000) The occurrence of Gastroidea viridula Deg. and Gastroidea polygoni L. (Col. Chrysomelidae) on Rumex confertus Willd. As biological representatives of weed population control. - Journal of Plant Protection Research, 40 (3/4): 219-230. Piesik, D. (2001) The occurrence of Hypera rumicis L. (Col., Curculionidae) on Rumex confertus Willd. as an interesting option for biological weed population control. - Journal of Plant Protection Research, 41 (3): 209-215. Piesik, D. (2002) Pegomya nigritarsis Ztt. (Diptera, Anthomyiidae) as an interesting option for biological control of Rumex confertus Willd. - Journal of Plant Protection Research, 42 (1): 45-51. Polk, K.L. & Ueckert, D.N. (1973) Biology and ecology of a mesquite twig girdler, Oncideres rhodosticta, in West Texas. - Annals of the Entomological Society of America, 66 (2): 411-417. Prasad, R. (2002) Cytisus scoparius (L.) Link, Scotch broom (Fabaceae). - In: Mason, P.G. & Huber, J.T. (eds.) Biological Control Programmes in Canada, 1981-2000. - Wallingford, UK: CABI Publishing: 343-345. Prasad, R. (2002) Pacific Forestry Centre, Victoria, British Columbia. - IBG News, 11 (2): 6. Pratt, P.D., Coombs, E.M. & Croft, B.A. (2002) Phytoseiid mite fauna on gorse, Ulex europaeus L., in Western Oregon, USA with new records for Phytoseiulus persimilis Athias-Henriot and Amblyseius graminis (Chant) (Acari: Phytoseiidae). - Pan-Pacific Entomologist, 78 (3): 215-218. Rees, N.E. (1990) Establishment, dispersal, and influence of Ceutorhynchus litura on Canada thistle (Cirsium arvense) in the Gallatin valley of Montana. - Weed Science, 38 (2): 198-200. Reichard, S. (2000) Hedera helix L. - In: Bossard, C.C., Randall, J.M. & Hoshovsky, M.C. (eds.) Invasive plants of California's wildlands. - Berkeley, USA: University of California Press: 212-216. Riddle, G.E., Burpee, L.L. & Boland, G.J. (1991) Virulence of Sclerotinia sclerotiorum and S. minor on dandelion (Taraxacum officinale). - Weed Science, 39 (1): 109-118. 23 Schubiger, F. (1986) Biological control of Rumex obtusifolius L. and R. crispus L. with Uromyces rumicis (Schum.). - Wint.Dissertation Abstracts International, C (European Abstracts), 47 (3): 605. Schubiger, F.X., Defago, G., Kern, H. & Sedlar, L. (1986) Damage to Rumex crispus L. and Rumex obtusifolius L. caused by the rust fungus Uromyces rumicis (Schum.) Wint. - Weed Research, UK, 26 (5): 347-350. Scott, J.K. & Jourdan, M. (2005) Biological control of Sonchus species (Sowthistles). Unpubl.report. Scott, J.K. & Sagliocco, J.L. (1989) Biology and host-specificity of Pegomya solennis (Diptera; Anthomyiidae), a possible biological control agent for Rumex spp. in Australia. - Acta Oecologica, Oecologia Applicata, 10 (2): 157-163. Scott, J.K. & Sagliocco, J.L. (1989) Biology and host-specificity of Pegomya solennis (Diptera; Anthomyiidae), a possible biological control agent for Rumex spp. in Australia. - Acta Oecologica, Oecologia Applicata, 10 (2): 157-163. Scott, J.K. & Sagliocco, J.L. (1991) Chamaesphecia doryliformis (Lep.: Sesiidae), a second root borer for the control of Rumex spp. (Polygonaceae) in Australia. - Entomophaga, 36 (2): 245-251. Scott, J.K. & Sagliocco, J.L. (1991) Host-specificity of a root borer, Bembecia chrysidiformis (Lep.: Sesiidae), a potential control agent for Rumex spp. (Polygonaceae) in Australia. - Entomophaga, 36 (2): 235-244. Scott, J.K. & Shivas, R.J. () Occurrence of the rust fungus Uromyces rumicis, a biological control agent of Fiddle Dock (Rumex pulcher) in Western Australia. ?? Scott, J.K. (1985) Candidate insects for the biological control of Rumex pulcher. - Proceedings of the VI International Symposium on Biological Control of Weeds., 829-835. Scott, J.K. (1990) Prospects for the biological control of Rumex species in Australia. - Proceedings of the VIII International Symposium on Biological Control of Weeds., 425-428. Scott, J.K. (1990) Prospects for the biological control of Rumex species in Australia. - Proceedings of the VIII International Symposium on Biological Control of Weeds Rome, Italy; Istituto Sperimentale per la Patologia Vegetale, Ministero dell'Agricoltura e delle Foreste: 425-428. Sharma, M.B. (1977) Role of the common house-sparrow in the control of weeds of major crops in Meerut district. - Indian Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 47 (5): 224-225. Smith, C.W. (1985) Impact of alien plants on Hawaii's native biota. In: Stone, C.P., Scott, J.M. (eds.) Hawaii's Terrestrial Ecosystems: Preservation and Management. Honolulu, Hawaii, USA: University of Hawaii Press, 180-250. Smith, C.W. (1992) Distribution, status, phenology, rate of spread, and management of Clidemia in Hawai'i. In: Stone, C.P., Smith, C.W., Tunison, J.T. (eds.) Alien plant invasions in native ecosystems of Hawai'i: management and research. Honolulu, USA: University of Hawaii Press: 241-253. Smith, C.W. (1998) Pest Plants of Hawaiian Native Ecosystems. - University of Hawaii, USA: Department of Botany. http://www.botany.hawaii.edu/faculty/cw_smith/aliens.htm (accessed February 2012). Smith, L., Winks, C., Waipara, N., Gianotti, A., Wilkie, P. & McKenzie, E. (2004) Fungi and invertebrates associated with barberry (Berberis spp.) in New Zealand. - Landcare Research Contract Report LC0405/026. Prepared for regional councils and the Department of Conservation. 41 p. Smith, L.A., Winks, C.J., Waipara, N.W., Gianotti, A.F., Wilkie, J.P. & McKenzie, E.H.C. (2004) A survey of fungal plant pathogens associated with weed infestations of barberry (Berberis spp.) in New Zealand and their biocontrol potential - Landcare Research Contract Report: LC0405/026. Speight, R.I. & Whittaker, J.B. (1987) Interactions between the chrysomelid beetle, Gastrophysa viridula, the weed Rumex obtusifolius and the herbicide asulam. - Journal of Applied Ecology, 24: 119-129. Spencer, N.R. (1981) Exploration for biotic agents for the control of Rumex crispus. - Proceedings of the 5th International Symposium on Biological Control of Weeds. Commonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research Organization. Australia: 125-151. Stewart-Wade, S.M., Neumann, S., Collins, L.L. & Boland, G.J. (2002) The biology of Canadian weeds. 117. Taraxacum officinale, G. H.Weber ex Wiggers. – Canadian Journal of Plant Science: 825-853. Swarbrick, J.T., Wison, B.W. & Hannan-Jones, M.A. (1995) The biology of Australian weeds. 25. Lantana camara L. - Plant Protection Quarterly, 10: 82-95. Swearingen, J.M. (1997) Melaleuca quinquenervia, Plant Conservation Alliance, Alien Plant Working Group. http://www.nps.gov/plants/alien/fact/meqe1.htm (accessed February 2012). 24 Syrett, P. & Smith, L.A. (1998) The insect fauna of four weedy Hieracium (Asteraceae) species in New Zealand. New Zealand Journal of Zoology, 25 (1): 73-83. Syrett, P. (1983) Biological control of ragwort in New Zealand: a review. - Australian Weeds, 2 (3): 96-101. Syrett, P., Fowler, S.V., Coombs, E.M., Hosking, J.R., Markin, G.P., Paynter, Q.E. & Sheppard, A.W. (1999) The potential for biological control of Scotch broom (Cytisus scoparius) (Fabaceae) and related weedy species. - Biocontrol News and Information, 20 (1): 17N-34N. Syrett, P., Grindell, J.M., Hayes, L.M. & Winks, C.J. (1991) Distribution and establishment of two biological control agents for ragwort in New Zealand. - Proceedings of the forty-fourth New Zealand Weed and Pest Control Conference: 292-295. Syrett, P., Grosskopf, G., Meurk, C. & Smith, L. (1999) Predicted contributions of a plume moth and a gall wasp to biological control of hawkweeds in New Zealand. - Proceedings of the 7th Australasian Conference on Grassland Invertebrate Ecology: 219-226. TAS (2003) Department of Primary Resources, Water and Environment. Weed Information Resources. http://www.dpiwe.tas.gov.au/inter.nsf/WebPages/RPIO-4ZW3NH?open#Identification (accessed February 2012). Taylor, E.E. (1989) A history of biological control of Lantana camara in New South Wales. - Plant Protection Quarterly, 4 (2): 61-65. Tomar, I.S. & Singh, O.P. (1980) Note on the contribution of the Indian ring dove in the control of winter weeds of major crops in Meerut district of Uttar Pradesh. - Indian Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 50 (9): 728-729. Tomley, A.J. (1995) The biology of Australian weeds. 26. Cryptostegia grandiflora R. Br. - Plant Protection Quarterly, 10 (4): 122-130. Trumble, J.T. & Kok, L.T. (1982) Integrated pest management techniques in thistle suppression in pastures of North America. - Weed Research, UK, 22 (6): 345-359. Uygur, S. (2000). Investigations on biological control of two common weeds, Cynodon dactylon (L.) Pers. (bermudagrass) and Cichorium intybus L. (common chicory) in Cukurova Region. Türkiye Herboloji Dergisi, 3 (2): 47-55. van der Westhuizen, L. & Mpedi, P. (2011) The initiation of a biological control programme against Argemone mexicana L. and Argemone ochroleuca Sweet subsp. ochroleuca (Papaveraceae) in South Africa. African Entomology, 19 (2): 223-229. Van Driesche, R.G., Carruthers, R.I., Center, T., Hoddle, M.S., Hough-Goldstein, J., Morin, L., Smith, L., Wagner, D.L., et al., 2010. Classical biological control for the protection of natural ecosystems. Biological Control Supplement 1, S2–S33 van Klinken, R.D. & Heard, T.A. (2000). Estimating fundamental host range: a host-specificity study of a biocontrol agent for Prosopis species (Leguminosae). - Biocontrol Science and Technology, 10: 331342. van Klinken, R.D., Fichera, G. & Cordo, H. (2003). Targeting biological control across diverse landscapes: the release, establishment and early success of two insects on mesquite (Prosopis) in rangeland Australia. Biological Control, 26: 8-20. van Klinken, R.D., Hoffmann, J.H., Zimmermann, H.G. & Roberts, A.P. (2009) 18 - Prosopis species (Leguminosae). – in: Muniappan, R., Reddy, G.V.P. & Raman, A. (eds.) Biological Control of Tropical Weeds using Arthropods. - Cambridge University Press: 353-377. von Hofsten, C.G. (1954) Studier over slaktet Taraxacum Wigg. med sraskild hansyn tillgruppen Vulgaria Dt. in Skandinavien (Studies on the genus Taraxacum with special reference to the group Vulgaria DT in Scandinavia). - Stockholm, Sweden: LTs Förlag. Waipara, N.W., Harvey, I.C. & Bourdot, G.W. (19930 Pathogenicity of Sclerotinia sclerotiorum on common thistle species and other pasture weeds. - Proceedings of the Forty Sixth New Zealand Plant Protection Conference, Christchurch, New Zealand, 10-12 August 1993 Rotorua, New Zealand; New Zealand Plant Protection Society: 261-264. Waterhouse, D.F. (1993) The Major Arthropod Pests and Weeds of Agriculture in Southeast Asia. ACIAR Monograph No. 21. - Canberra, Australia: Australian Centre for International Agricultural Research: 141pp. 25 Watson, A.K. & Keogh, W.J. (1980) Mortality of Canada thistle due to Puccinia punctiformis. - Proceedings V International Symposium on Biological Control of Weeds, Brisbane, Australia: 325-332. Watson, M. (2007) Buddleia biological control agent off to a good start. - Forest Health News. http://www.ensisjv.com/NewsEventsandPublications/Newsletters/ForestHealthNews/ForestHealthNewsA rchive/tabid/179/Default.aspx (accessed February 2012). Watson, M. (2008) Buddleia leaf weevil update. Forest Health News. http://www.ensisjv.com/NewsEventsandPublications/Newsletters/ForestHealthNews/ForestHealthNewsA rchive/tabid/179/Default.aspx (accessed February 2012). Wester, L.L. & Wood, H.B. (1977) Koster's curse (Clidemia hirta), a weed pest in Hawaiian forests. Environmental Conservation, 4 (1): 35-42. Windig, J.J. (1991) Life cycle and abundance of Longitarsus jacobaeae (Col.: Chrysomelidae), biocontrol agent of Senecio jacobaea. - Entomophaga, 36 (4): 605-618. Xiaoshui, W. (1991) Gastrophysa atrocyanea (Col: Chrysomelidae), an agent for biological control of the dock, Rumex japonicus (Polygonaceae) in China. - Tropical Pest Management, 37 (4): 383-386. Zaller, J.G. (2004) Ecology and non-chemical control of Rumex crispus and R. obtusifolius (Polygonaceae): a review. - Weed Research, 44: 414-432. Zhang, X., Xi, Y., Zhou, W. & Kay, M. (1993) Cleopus japonicus, a potential biocontrol agent for Buddleja davidii in New Zealand. - New Zealand Journal of Forestry Science, 23: 78-83. Zimmermann, H.G. (1990) Progress with biological control of spear thistle. - Plant Protection News, No. 19: 5. Zimmermann, H.G. (1991) Biological control of spear thistle, Cirsium vulgare (Asteraceae), in South Africa. Agriculture, Ecosystems and Environment, 37 (1-3): 199-205. BC and other control efforts of invertebrates Azab, A.K., Tawfik, M.F.S. & Awadallah, K.T. (1964) Insect enemies of common flies in Giza Region. - Bull. Soc. ent. Egypte, 47: 277-286. Azab, A.K., Tawfik, M.F.S. & Awadallah, K.T. (1967) Biology of Nasonia vitripennis Walker (Hymenoptera : Pteromalidae). - Bulletin de la Societe Entomologique d'Egypte, 51: 469-482. Azaizeh, H., Gindin, G., Said, O. & Barash, L. (2002) Biological control of the western flower thrips Frankliniella occidentalis in cucumber using the entomopathogenic fungus Metarhizium anisopliae. – Phytoparasitica, 30 (1): 18-24. Barker, G.M. & Watts, C. (2002) Management of the invasive alien snail Cantareus aspersus on conservation land.- DOC Science Internal Series, No.31: 30pp. Barlow, N.D., Beggs, J.R. & Moller, H. (1998) Spread of the wasp parasitoid Sphecophaga vesparum vesparum following its release in New Zealand. - New Zealand Journal of Ecology, 22 (2): 205–208. Barlow, N.D., Moller, H. & Beggs, J.R. (1996) A model for the effect of Sphecophaga vesparum vesparum as a biological control agent of the common wasp in New Zealand. - Journal of applied ecology, 33: 31–34. Barns, S.A. (2003) Tropical grass webworm (Herpetogramma licarsisalis): the right action at the right time. AERU Discussion Paper, 150: 76-84. Beggs, J.R. & Harris, R.J. (2000) Can the wasp parasitoid Sphecophaga vesparum significantly reduce the density of Vespula wasps? - New Zealand journal of zoology, 27: 73–74. Beggs, J.R. & Moller, H. (1991) New Zealand wasp research - uncoordinated goals or still stuck in the descriptive bottleneck? - New Zealand journal of zoology 18: 230–231. Beggs, J.R., Alspach, P.A., Moller, H., Toft, R.J. & Tilley, J.A.V. (1992) Impacts of the parasitoid Sphecophaga vesparum on colonies of the common wasp (Vespula vulgaris). - Proceedings 41st Annual Conference Entomological Society of New Zealand. Beggs, J.R., Harris, R.J. & Read, P.E.C. (1996) Invasion success of the wasp parasitoid Sphecophaga vesparum vesparum (Curtis) in New Zealand. - New Zealand Journal of Zoology, 23: 1–9. Beggs, J.R., Rees, J.S. & Harris, R.J. (2002) No evidence for establishment of the wasp parasitoid, Sphecophaga vesparum burra (Cresson) (Hymenoptera: Ichneumonidae) at two sites in New Zealand. New Zealand Journal of Zoology, 29: 205-211. 26 Beggs, J.R., Rees, J.S., Toft, R.J., Dennis, T.E. & Barlow, N.D. (2008) Evaluating the impact of a biological control parasitoid on invasive Vespula wasps in a natural forest ecosystem. - Biological Control, 44: 399407. Beggs, J.R., Toft, R.J., Malham, J.P., Rees, J.S., Tilley, J.A.V., Moller, H. & Alspach, P. (1998) The difficulty of reducing introduced wasp (Vespula vulgaris) populations for conservation gains. - New Zealand Journal of Ecology, 22: 55-63. Beggs, J.R.; Rees, J.S.; Toft, R.J.; Dennis, T.E. & Barlow, N.D. (2008) Evaluating the impact of a biological control parasitoid on invasive Vespula wasps in a natural forest ecosystem. - Biological Control, 44: 399407. Beggs. J.R. (1999) The ecological impact and control of introduced wasps (Vespula spp) in Nothofagus forest. PhD thesis, University of Otago, Dunedin, New Zealand, 197pp. Berndt, O., Poehling, H.M. & Meyhofer, R. (2004) Predation capacity of two predatory laelapid mites on soildwelling thrips stages. - Entomologia Experimentalis et Applicata, 112 (2): 107-115. Berry, J.A., Harris, R.J., Read, P.E.C. & Donovan, B.J. (1997) Morphological and colour differences between subspecies of Sphecophaga vesparum (Curtis) (Hymenoptera:Ichneumonidae). - New Zealand journal of zoology, 24: 35–46. Bilashini, Y., Singh, T.K., Singh, R.K.R. (2007) Biological control potential of Coccinella septempunctata Linnaeus (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae) on major homopteran pests of rapeseed. Journal of Biological Control, 21: 157-162. Bishop, D.M., Heath, A.C.G. & Haack, N.A. (1996) Distribution, prevalence and host associations of Hymenoptera parasitic on Calliphoridae occurring in flystrike in New Zealand. - Medical and Veterinary Entomology, 10 (4): 365-370. Brownbridge, M., Toft, R., Rees, J., Nelson, T.L. & Bunt, C. (2009) Towards better mitigation technologies for invasive wasps, Vespula spp. - Plant Protection Society Conference, Dunedin August 2009. Cameron, P.J., Hill, R.L., Bain, J., Thomas, W.P. (1989) A review of biological control of invertebrate pests and weeds in New Zealand 1874 to 1987. - Commonwealth Institute of Biological Control, Technical Communication, no. 10: 424 pp. Cammack, J.A., Adler, P.H., Tomberlin, J.K., Arai, Y. & Bridges, W.C. (2010) Influence of parasitism and soil compaction on pupation of the green bottle fly, Lucilia sericata. - Entomologia Experimentalis et Applicata, 136 (2): 134-141. Charles, J. G. (2011) Using parasitoids to infer a native range for the obscure mealybug, Pseudococcus viburni, in South America. - BioControl, 56 (2): 155-161. Chouvenca, T., Sua, N.-Y. & Graceb, J.K. (2011) Fifty years of attempted biological control of termites – Analysis of a failure. - Biological Control, 59 (2): 69-82. Chow, A., Chau, A. & Heinz, K.M., (2010) Compatibility of Amblyseius (Typhlodromips) swirskii (Athias-Henriot) (Acari: Phytoseiidae) and Orius insidiosus (Hemiptera: Anthocoridae) for biological control of Frankliniella occidentalis (Thysanoptera: Thripidae) on roses. - Biological Control, 53 (2): 188-196. Cloutier, C. & Johnson, S.G. (1993) Predation by Orius tristicolor (Hemiptera, Anthocoridae) on Phytoseiulus persimilis (Acarina, Phytoseiidae) – Testing for compatibility between biocontrol agents. – Environmental Entomology, 22 (2): 477-482. Cruickshank, I. & Wall, R. (2002) Population dynamics of the sheep blowfly Lucilia sericata: seasonal patterns and implications for control. - Journal of Applied Ecology, 39 (3): 493-501. Daane, K.M., Cooper, M.L., Triapitsyn, S.V., Andrews, J.W. & Ripa, R. (2008) Parasitoids of obscure mealybug, Pseudococcus viburni (Hem.: Pseudococcidae) in California: establishment of Pseudaphycus flavidulus (Hym.: Encyrtidae) and discussion of related parasitoid species. - Biocontrol Science and Technology, 18 (1/2): 43-57. Davis, C.J. & Chong, M. (1969) Recent Introductions for Biological Control in Hawaii. -Proceedings, Hawaiian Entomological Society,20: 317-322. Dimick, R.E. & Mote, D.C. (1934) Progress report regarding the introduction in Oregon of Digonocheata setipennis, a tachinid parasite of the European earwig. - Journal of Economic Entomology 27: 863-865. Donovan, B.D. (1991) Life cycle of Sphecophaga vesparum (Curtis) (Hymenoptera: Ichneumonidae), a parasitoid of some vespid wasps. - New Zealand journal of zoology, 18: 181–192. 27 Donovan, B.J. & Read, P.E.C. (1987) Attempted biological control of social wasps, Vespula spp., (Hymenoptera:Vespidae) with Sphecophaga vesparum (Curtis) (Hymenoptera:Ichneumonidae) in New Zealand. - New Zealand journal of zoology, 14: 329–335. Donovan, B.J. (1989) Potential enemies of the introduced wasp parasitoid Sphecophaga vesparum (Hymneoptera:Ichneumonidae) in New Zealand. - New Zealand journal of zoology, 16: 365–367. Donovan, B.J., Moller, H., Plunkett, G.M., Read, P.E.C. & Tilley, J.A.V. (1989) Release and recovery of the introduced wasp parasitoid, Sphecophaga vesparum vesparum (Curtis) (Hymenoptera:Ichneumonidae) in New Zealand. - New Zealand journal of zoology, 16: 355–364. Drees, B.M., Miller, R.W., Vinson, S.B. & Georgis, R. (1992) Susceptibility and behavioral response of of red imported fire ant (Hymenoptera: formicidae) to selected entomogenous nematodes (Rhabditida: Steinernematidae & Heterorhabditidae). - Journal of Economic Entomology. 85: 365-370. Dreistadt, S.H., Clark, J.K. & Flint, M.L. (2004) Pests of landscape trees and shrubs. An integrated pest management guide. Davis, USA - University of California, Division of Agriculture and Natural Resources, 501pp. Dridah, A., Louadi, K. & Berchi, S. (2009) An African Gecko Hemidactylus mabouia (Squamata, Gekkonidae) to control the wax moths of hives Galleria mellonella and Achroia grisella (Lepidoptera, Pyralidae). Bulletin de la Société Entomologique de France, 114 (4): 423-427. Edwards R. & Mill P. (1986) Termites in buildings. Their biology and control. East Grinstead, UK; Rentokil Ltd., 261pp. Fritsch, E. (1988) Biological control of the false codling moth, Cryptophlebia leucotreta (Meyrick) (Lep., Tortricidae), with a granulosis virus. - Mitteilungen der Deutschen Gesellschaft für Allgemeine und Angewandte Entomologie, 6 (1-3): 280-283. Froggatt, J.L. (1919) An economic Study of Nasonia brevicornis, a Hymenopterous Parasite of Muscid Diptera. Bulletin of Entomological Research, 9 (3): 257-262. Froggatt, W. W.; Froggatt, J. L. (1917) Sheep-Maggot Flies, No. 3.. - Farmer's Bulletin. New South Wales Department of Agriculture, 113: 37 pp. Froggatt, W.W. & Froggatt, J.L. (1916) Sheep-Maggot Flies, No. 2.. - Farmer's Bulletin. New South Wales Department of Agriculture, 110: 30 pp. Froggatt, W.W. & Froggatt, J.L. (1918) Sheep-Maggot Flies, No. 4. - Farmers' Bulletin, New South Wales Department of Agriculture, 122: 24 pp. Froggatt, W.W. & McCarthy, T. (1914) The Parasite of the Sheep-maggot Ply (Nasonia brevicornis): Notes and Observations in the Field and Laboratory. - Agric. Gaz. N.S.W., 25, (9): 759-764. Froggatt, W.W. (1915) Sheep-Maggot Flies. - Dept. Agric., New South Wales, 95: 52 pp. Funderburk, J., Ripa, R., Espinoza, F. & Rodriguez, F. (2002) Parasitism of Frankliniella australis (Thysanoptera: Thripidae) by Thripinema khrustalevi (Tylenchida: Allantonematidae) isolate Chile. - Florida Entomologist, 85 (4): 645-649. Gambino, P. (1984) Susceptibility of western yellowjacket, Vespula pensylvanica to three species of three entomogenous nematodes. - International Research Communications System Medical Science: Microbiology, Parasitology and Infectious Diseases, 12: 264. Gitonga, L.M., Overholt, W.A., Lohr, B., Magambo, J.K. & Mueke, J.M. (2002) Functional response of Orius albidipennis (Hemiptera: Anthocoridae) to Megalurothrips sjostedti (Thysanoptera: Thripidae). – Biological Control, 24 (1): 1-6. Glare, T.R., Harris, R.J. & Donovan B.J. (1996): Aspergillus flavus as a pathogen of wasps, Vespula spp., in New Zealand, New Zealand Journal of Zoology, 23:4, 339-344. Gold, C.S. & Messiaen, S. (2000) The banana weevil, Cosmopolites sordidus. - Réseau international pour l’amélioration de la banane et de la banane plantain - Musa Pest Fact Sheet No. 4: 4pp. Gold, C.S. (2001) Biology and integrated pest management of banana weevil, Cosmopolites sordidus (Germar). – In: Advancing banana and plantain R & D in Asia and the Pacific, Vol. 10: 28-33. Greathead, D.J. & Greathead, A.H. (1992) Biological control of insect pests by insect parasitoids and predators: the BIOCAT database. - Biocontrol News and Information, 13 (4): 61N-68N. 28 Guzman, R.F. 1984. Preliminary evaluation of the potential of Steinernema feltiae for controlling Vespula germanica. - New Zealand Journal of Zoology, 11: 100. Harcourt, S.J., Harris, R.J., Rose, E.A.F., Glare, T.R. & Nelson, T.L. (1997) The potential of Beauveria bassiana for the control of common and German wasps (Vespula vulgaris L. and V. germanica F.) in New Zealand. - Proceedings of 4th international workshop on microbial control of soil dwelling pests. Harris, R.J. & Read, P.E.C. (1999) Enhanced biological control of wasps. - Science for conservation 115: 39pp. Harris, R.J. & Rose, E.A.F. (1999) Factors influencing reproductive strategies of the vespid parasitoid Sphecocphaga vesparum vesparum (Hymenoptera: Ichneumonidae). - New Zealand journal of zoology, 26: 89–96. Harris, R.J. & Rose, E.A.F. (1999) White and yellow cocoon production in the vespid parasitoid Sphecophaga vesparum (Hymenoptera: Ichneumonidae). - New Zealand journal of zoology, 26: 89–96. Harris, R.J., Harcourt, S.J., Glare, T.R., Rose, E.A, & Nelson, T.J. (2000) Susceptibility of Vespula vulgaris (Hymenoptera: vespidae) to generalist entomopathogenic fungi and their potential for wasp control. - J Invertebr Pathol., 75 (4): 251-258. Harris, R.J., Maitland, M., Beggs, J.R. & Toft, R.J. (2004) Management of Vespula in New Zealand - a roller coaster ride! In: Entomology : Strength in Diversity : XXII International Congress of Entomology, 15-21 August 2004, Brisbane, Queensland, Australia. Heath, A.C.G., Bishop, D.M., Cameron, P.J., Hill, R.L., Bain, J. & Thomas, W.P. (1989) Calliphoridae, blow flies (Diptera). – In: CAB International, Wallingford, UK, A review of biological control of invertebrate pests and weeds in New Zealand 1874 to 1987, 381-386. Higley, L.G. & Pedigo, L.P. (eds.) (1996) Economic Thresholds for Integrated Pest Management. - University of Nebraska Press: 327 pp. (references to impact of Protophormia terraenovae) Hodson, A.K., Friedman, M.L., Wu, L.N. & Lewis, E.E. (2011) European earwig (Forficula auricularia) as a novel host for the entomopathogenic nematode Steinernema carpocapsae. - Journal of Invertebrate Pathology, 107 (1): 60-64. Huth, C., Schirra, K.J., Seitz, A. & Louis, F. (2009) Investigations of the population ecology and population control of the European earwig Forficula auricularia (Linnaeus) (Dermaptera: Forficulidae) in vineyards of the Palatinate. (Untersuchungen zur Populationsökologie und zur Populationskontrolle des Gemeinen Ohrwurms Forficula auricularia (Linnaeus) (Dermaptera: Forficulidae) in Rebanlagen der Pfalz.). Mitteilungen der Deutschen Gesellschaft für allgemeine und angewandte Entomologie, 17: 207-210. Jacobson, R.J., Croft, P. & Fenlon, J. (2001) Suppressing establishment of Frankliniella occidentalis Pergande (Thysanoptera: Thripidae) in cucumber crops by prophylactic release of Amblyseius cucumeris Oudemans (Acarina: Phytoseiidae). - Biocontrol Science and Technology, 11 (1): 27-34. Jensen, J.G. (2002) A record of parasitism of tropical grass webworm Herpetogramma licarsisalis (Walker) (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae) by Lissopimpla excelsa (Costa) (Hymenoptera: Ichneumonidae) in New Zealand. - New Zealand Entomologist, 25: 93-94. Jiang, H., Zhou, L., Zhang, J.M., Dong, H.F., Hu, Y.Y. & Jiang, M.S. (2008) Potential of Periplaneta fuliginosa densovirus as a biocontrol agent for smoky-brown cockroach, P-fuliginosa. – Biological Control, 46 (2): 94-100. Johnston, T.H. & Tiegs, O.W. (1921) On the Biology and Economic Significance of the Chalcid Parasites of Australian Sheep Maggot-flies. - Proceedings of the Royal Society of Queensland, 33 (6): 99-128. Karamaouna, F. & Copland, M.J. (2009) Fitness and life history parameters of Leptomastix epona and Pseudaphycus flavidulus, two parasitoids of the obscure mealybug Pseudococcus viburni. - BioControl, 54 (1): 65-76. Khater, H.F., Hanafy, A., Abdel-Mageed, A.D., Ramadan, M.Y. & El-Madawy, R.S. (2011) Control of the myiasisproducing fly, Lucilia sericata, with Egyptian essential oils. - International Journal of Dermatology, 50 (2): 187-194. King, P.E. & Rafai, J. (1970) Host discrimination in a gregarious parasitoid Nasonia vitripennis (Walker) (Hymenoptera: Pteromalidae). - Journal of Experimental Biology, 53 (1): 245-254. Kinjo, N., Tanaka, E. & Tanaka C. (2006) Studies on Cordyceps sphecocephala parasitizing in Vespula schrenckii. - Bulletin of the College of Liberal Arts and Sciences, 36: 21-30. 29 Kuhlmann, U. (1994) Ocytata pallipes (FallCn) (Dipt., Tachinidae), a potential agent for the biological control of the European earwig. - Journal of Applied Entomology, 117: 262-267. Kuhlmann, U., Sarazin, M. J., O'Hara, J. E., Mason, P. G. & Huber, J. T. (2001): Forficula auricularia L., European earwig (Dermaptera: Forficulidae). - Biological Control Programmes in Canada, 1981-2000, CABI Publishing, Wallingford, UK: 127-131. Kumashiro, B.R., Lai, P.Y., Funasaki, G.Y. & Teramoto, K.K. (1983) Efficacy of Nephaspis amnicola and Encarsia? haitiensis in controlling Aleurodicus dispersus in Hawaii. - Proceedings of the Hawaiian Entomological Society, 24 (2-3): 261-270. Lai, P.Y. & Funasaki, G.Y. (1983) [List of biological control introductions in Hawaii.] - Hawaii Department of Agriculture Division of Plant Industry Plant Pest Control Branch. Landcare (2011) Biological control of wasps. http://www.landcareresearch.co.nz/research/biocons/invertebrates/Wasps/biocontrol.asp February 2012). (accessed Lebeck, L.M. (1991) A review of the hymenopterous natural enemies of cockroaches with emphasis on biological control. – Entomophaga, 36 (3): 335-352. Lecuonaa, R.E., Turicaa, M., Taroccoa, F. & Crespo, D.C. (2005) Microbial Control of Musca domestica (Diptera: Muscidae) with Selected Strains of Beauveria bassiana - Journal of Medical Entomology, 42 (3): 332336. Li, H.Y., Shen, L.R., Gu, S., Chen, X.Y. & Yang, X.G. (2007) Optimal preparation of cassia oil emulsion and its ovicidal action against Lucilia sericata (Meigen) on kippers. - Journal of Zhejiang University (Agriculture and Life Sciences),33 (3): 316-321. Magdy, Y.E. & El Sayed, M.A.K.E. (2009) Biological control of Thrips tabaci (lind.) and Aphis gossypii (Glover) using different predatory Phytoseiid mites and the biocide vertimec on Eggplant at Behaira Governorate. - Egypt. Acad. J. biolog. Sci., 2 (2): 13-22. Merino, L., France, A. & Gerding, M. (2007) Selection of native fungi strains pathogenic to Vespula germanica (HYMENOPTERA: VESPIDAE) - Selección de aislamientos nativos de hongos patogénicos a Vespula germanica (Hymenoptera: Vespidae). – Agricultura Tecnica (Chile), 67 (4):335-342. Miller, D. (1922) Sheep Maggot-fly Control by Insect Parasites. The Introduction of Nasonia brevicornis. - New Zealand Journal of Agriculture, 24 (4): 211-212. Miller, D. (1927) Parasitic Control of Sheep Maggot-flies. - New Zealand Journal of Agriculture, 35 (4): 219-220. Mohan, C.M., Lakshmi, K.A. & Devi, K.U. (1999) Laboratory evaluation of the pathogenicity of three isolates of the entomopathogenic fungus Beauveria bassiana (Bals.) vuillemin on the American cockroach (Periplaneta americana). – Biocontrol Science and Technology, 9 (1): 29-33. Moller, H., Plunkett, G.M., Tilley, J.A.V., Toft, R.J. & Beggs, J.R. (1991) Establishment of the wasp parasitoid, Sphecophaga vesparum (Hymenoptera: Ichneumonidae), in New Zealand. - New Zealand Journal of Zoology, 18: 199–208. Moore, S.D. (2002) Entomopathogens & microbial control of citrus pests in South Africa: a review. SA Fruit Journal, 1: 30-32. Morgan, W.L. (1929) Alysia manducaior Pz. An introduced Parasite of the Sheep Blowfly Maggot. - Agric. Gaz. N.S.W., 11: 818-829. Morris, R.F. (1984) Forficula auricularia, European earwig (Dermaptera: Forficulidae). In: Kelleher, J.S. & Hulme, M.A. (eds.) Biological Control Programmes Against Insects and Weeds in Canada 1969–1980. Commonwealth Agriculture Bureaux, Slough, UK, pp. 39–40. Neuenschwander, P., Borgemeister, C. & Langewald, J. (2003) Biological Control in IPM Systems in Africa, CABI 320pp. Newton, P.J.; Odendaal, W.J. (1990) Commercial inundative releases of Trichogrammatoidea cryptophlebiae (Hym: Trichogrammatidae) against Cryptophlebia leucotreta (Lep.: Tortricidae) in citrus.- Entomophaga, 35 (4): 545-556. North, J.P., Cuthbertson, A.G.S. & Walters, K.F.A. (2006) The efficacy of two entomopathogenic biocontrol agents against adult Thrips palmi (Thysanoptera: Thripidae). – Journal of Invertebrate Pathology, 92 (2): 89-92. 30 Orr, M.R., Seike, S.H., Benson, W.W. & Dahlsten, D.L. (2001) Host specificity of Pseudacteon (Diptera: Phoridae) parasitoids that attack Linepithema (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) in South America. Environmental Entomology, 30: 742-747. Querner, P. & Biebl, S. (2011) Using parasitoid wasps in Integrated Pest Management (IPM) against beetle and moth infestation, a critical evaluation. http://www.scienceblogs.de/deutschesmuseum/Pest%20Odyseey%20Parasitoids%202011.pdf (accessed February 2012). Rao, V.P., Ghani, M.A., Sankaran, T. & Mathur, K.C. (1971) A review of the biological control of insects and other pests in south-east Asia and the Pacific region. - Commonwealth Institute of Biological Control, Technical Communication no. 6, 149 pp. Reitz, S.R., Funderburk, J.E. & Waring, S.M. (2006) Differential predation by the generalist predator Orius insidiosus on congeneric species of thrips that vary in size and behaviour. – Entomologia Experimentalis et Applicata, 119 (3): 179-188. Reyes-Hernandez, E. (2003) pers comm. (Ref 74 from the CABI database, cited in JNCC database). Ripa, S.R. (1990) Biological control of muscoid flies in Easter Island. – In: Biocontrol of arthropods affecting livestock and poultry. - Westview Press, Boulder, Colorado: 111-119. Rivers, D.B., Hink, W.F. & Denlinger, D.L. (1993) Toxicity of the venom from Nasonia vitripennis (Hymenoptera: Pteromalidae) toward fly hosts, nontarget insects, different developmental stages, and cultured insect cells. – Toxicon, 31 (6): 755-765. Rose, E.A.F., Harris, R.J. & Glare, T.R. (1999) Possible pathogens of social wasps (Hymenoptera: Vespidae) and their potential as biological control agents. - New Zealand journal of zoology, 26: 179–190. Sakovich, N.J. (2002) Integrated management of Cantareus aspersus (Müller) (Helicidae) as a pest of citrus in California. In: Molluscs as crop pests (Barker, G.M., ed.) Wallingford, UK: CABI Publishing, 353-360. http://www.cabi.org/CABeBooks/default.aspx?site=107&page=45&LoadModule=PDFHier&BookID=104 (accessed February 2012). Sanchez-Pena, S.R., Lara, J.S.J. & Medina, R.F. (2011) Occurrence of entomopathogenic fungi from agricultural and natural ecosystems in Saltillo, Mexico, and their virulence towards thrips and whiteflies. – Journal of Insect Science, 11. Sankaran, T. & Girling, D.J. (1980) The current status of biological control of the potato tuber moth. - Biocontrol News and Information, 1 (3): 207-211. Sargison, N. (2008). The Management of Ectoparasitic Diseases of UK Sheep. - World Veterinary Congress. Royal School of Veterinary Studies, Easter Bush Veterinary Center, Roslin, Midlothian, Scotland. (chemical control of L. sericata costly) Schmale, K.I. (2001) Biological control of the bean weevil, Acanthoscelides obtectus, by a hymenopteran parasitoid, as part of an IPM system. - Diss. ETH Zuerich, No. 14126: 98pp. Schmale, K.I., Wackers, F.L., Cardona, C., Dorn, S. (2006) Biological control of the bean weevil, Acanthoscelides obtectus (Say) (Col.: Bruchidae), by the native parasitoid Dinarmus basalis (Rondani) (Hym.: Pteromalidae) on small-scale farms in Colombia. - Journal of Stored Products Research, 42 (1): 31. Schwabe, C.W. (1948) Observations on the Life History of Pycnoscelus surinamensis (JLinn.), the Intermediate Host of the Chicken Eyeworm in Hawaii. – PHES 13: 433-436. Sharaf-El-Din, H.A., & Kolaib, M.O. (1991) Biological control of the greater wax moth, Galleria mellonella L. (Lepidoptera:pyralidae). - Minufiya Journal of Agricultural Research (Egypt), 16 (2): 1881-1889. Simberloff, D. (2001) Fire ant: an eradication program that failed. Case Study 5.10 In (Wittenberg, R. & Cock, M.J.W. eds.) Invasive Alien Species: A toolkit of best prevention and management practices - CAB International, Wallingford, UK. Skovgård H, & Nachman G. (2004) Biological control of house flies Musca domestica and stable flies Stomoxys calcitrans (Diptera: Muscidae) by means of inundative releases of Spalangia cameroni (Hymenoptera: Pteromalidae). - Bull Entomol Res., 94 (6): 555-67. Smit, B. (1929) The Biological Control of Sheep Blow-flies in South Africa. - South African Journal of Science, 26: 441-448. Smith, G.J.C. (1969) Host selection and oviposition behavior of Nasonia vitripennis (Hymenoptera: Pteromalidae) on two host species. - Canadian Entomologist, 101 (5): 533-538. 31 Steiner, M.Y., Goodwin, S., Wellham, T.M., Barchia, I.M. & Spohr, L.J. (2003) Biological studies of the Australian predatory mite Typhlodromips montdorensis (Schicha) (Acari: Phytoseiidae), a potential biocontrol agent for western flower thrips, Frankliniella occidentalis (Pergande) (Thysanoptera : Thripidae). – Australian Journal of Entomology, 42: 124-130. Talekar, N.S. & Shelton, A.M. (1993). Biology, ecology and management of the diamondback moth. - Annual Review of Entomology 38: 275–301. Talley, J. (2008) Management and characterization of stable fly larval habitats at round hay bale feeding sites in pastures. – Dissertation, Kansas State University: 109 pp. Tawfik, M.F.S., Awadallah, K.T. & Abdella, M.M.H. (1985) Natural enemies of the greater wax moth, Galleria mellonella L. with reference to the bionomics of the braconid Apanteles galleriae (Wilkinson). - Annals of Agricultural Science, 23 (1): 335-342. Thoms, E.M. & Robinson, W.H. (1987) Potential of the cockroach oothecal parasite Prosevania punctate (Hymenoptera, Evaniidae) as a biologicak control agent for the oriental cockroach (Orthoptera, Blattidae). – Environmental entomology, 16 (4): 938-944. Tipping, C., Nguyen, K.B., Funderburk, J.E. & Smart, G.C. (1998) Thripenema fuscum n. sp (Tylenchida: Allantonematidae), a parasite of the tobacco thrips, Frankliniella fusca (Thysanoptera). – Journal of Nematology, 30 (2): 232-236. Toft, R.J. & Harris, R.J. (2004) Can trapping control Asian paper wasp (Polistes chinensis antennalis) populations? - New Zealand Journal of Ecology, 28: 279-282. Toft, R.J., Malham, J.P. & Beggs, J.R. (1999) Mortality and emergence pattern of over-wintering cocoons of the wasp parasitoid Sphecophaga vesparum vesparum (Hymenoptera: Ichneumonidae) in New Zealand. Environmental entomology, 28 (1): 9–13. Tommasini, M. G. (2003) Evaluation of Orius species for biological control of Frankliniella occidentalis (Pergande) (Thysanoptera: Thripidae). Thesis Wageningen University, 214 pp. Uygun, N. & Sekeroglu, E. (1987) Potential use of imported natural enemies for biological control in Cukurova. Türkiye I. - Entomoloji Kongresi Bildirileri, 13-16 Ekim 1987, Ege Üniversitesi, Bornova, Izmir.: 553-562. van Lenteren, J.C. (2011) The state of commercial augmentative biological control: plenty of natural enemies, but a frustrating lack of uptake. – BioControl, DOI 10.1007/s10526-011-9395-1. Vanderveire, M. & Degheele, D. (1992) Biological control of the western flower thrips, Frankliniella occidentalis (Pergande) (Thysanoptera, Thripidae), in glasshouse sweet-peppers with Orius spp. (Hemiptera, Anthocoridae) - A comparative study between O. niger (Wolff) and O. insidiosus (SAY). – Biocontrol Science and Technology, 2 (4): 281-283. Various sources (2001) Rosy wolf snail Euglandina rosea, exterminates endemic island snails. Case Study 3.1 In Invasive Alien Species: A toolkit of best prevention and management practices (Eds. Wittenberg, R. & Cock, M.J.W.) CAB International, Wallingford, UK. Vazquez, R.J., Porter, S.D. & Briano, J.A. (2006) Field release and establishment of the decapitating fly Pseudacteon curvatus on red imported fire ants in Florida. - BioControl, 51 (2): 207-216. Walker, A.K. & Deitz, L.L. (1979) A review of entomophagous insects in the Cook Islands. - New Zealand Entomologist, 7: 70-82. Wang, C., Powell, J.E. & Nguyen, K. (2002) Laboratory Evaluation of four entomopathogenic nematodes for control of subterranean termites (Isoptera: Rhinotermitidae). - Environmental Entomology, 31: 381-387. Waterhouse, D. F. (1998) Biological Control of Insect Pests: Southeast Asian Prospects. - ACIAR Canberra: 523 pp. Waterhouse, D. F., & Norris, K.R. (1987) Biological Control Pacific Prospects. – Melbourne, Inkata Press: 454pp. Weston, R.J., Woolhouse, A.D., Spurr, E.B., Harris, R.J. & Suckling, D.M. (1997) Spiroacetals and other venom constituents as potential wasp (Hymenoptera:Vespidae) attractants. - Journal of chemical ecology, 23: 553–568. Wharton R.H. (1989) Control; classical biological control of fruit-infesting Tephritidae, In: Robinson AS, Hooper G, eds. Fruit Flies; their Biology, Natural Enemies and Control. World Crop Pests 3(B). Amsterdam, Netherlands: Elsevier, 303-313. 32 Wittmann, E.J. & Leather, S.R. (1997) Compatibility of Orius laevigatus Fieber (Hemiptera: Anthocoridae) with Neoseiulus (Amblyseius) cucumeris Oudemans (Acari: Phytoseiidae) and Iphiseius (Amblyseius) degenerans Berlese (Acari, Phytoseiidae) in the biocontrol of Frankliniella occidentalis Pergande (Thysanoptera: Thripidae). – Experimental & Applied Acarology, 21 (8): 523-538. Wu, H.J., Wang, Z.N., Ou, C.F., Tsai, R.S. & Chow, Y.S. (1991) Susceptibility of two Formosan termites to the entomogenous nematode Steinernema feltiae Filipjev. - Bulletin of the institute of Zoology, Academia Sinica, 30: 31-39. Xu, X.O., Borgemeister, C. & Poehling, H.M. (2005) Interactions in the biological control of western flower thrips Frankliniella occidentalis (Pergande) and two-spotted spider mite Tetranychus urticae Koch by the predatory bug Orius insidiosus Say on beans. – Biological Control, 36 (1): 57-64. Zhang, W.Z., Xiao, A.X., Wang, S.Q., Wu, W.J., Zhang, G.Y., Liang, G.D., Zhang, J., Chen, R.B., Xue, R.D., Zhang, W.Z., Xue, R.D., Xiao, A.X. & Yixue, D.F. (1990) An investigation of parasitic natural enemies of fly pupae in Shanxi Province. - Pest Control, 6 (4): 10-14. Zrubecz, P., Toth, F. & Nagy, A. (2008) Is Xysticus kochi (Araneae: Thomisidae) an efficient indigenous biocontrol agent of Frankliniella occidentalis (Thysanoptera: Thripidae)? – Biocontrol, 53 (4): 615-624. 33 contact CABI europe CABI Head Office Nosworthy Way, Wallingford, Oxfordshire, OX10 8DE, UK T: +44 (0)1491 832111 CABI Bakeham Lane, Egham, Surrey, TW20 9TY, UK T: +44 (0)1491 829080 CABI Rue des Grillons 1, CH-2800 Delémont, SWITZERLAND T: +41 (0)32 4214870 asia CABI C/o Internal Post Box 56, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, 12 Zhongguancun Nandajie, Beijing 100081, CHINA T: +86 (0)10 82105692 CABI 2nd Floor, CG Block, NASC Complex, DP Shastri Marg, Opp. Todapur Village, PUSA, New Delhi – 110012, INDIA T: +91 (0)11 25841906 CABI PO Box 210, 43400 UPM Serdang, Selangor, MALAYSIA T: +60 (0)3 89432921 CABI Opposite 1-A, Data Gunj Baksh Road, Satellite Town, Rawalpindi-PAKISTAN T: +92 (0)51 9290132 africa CABI ICRAF Complex, United Nations Avenue, Gigiri, PO Box 633-00621, Nairobi, KENYA T: +254 (0)20 7224450/62 americas CABI UNESP- Fazenda Experimental Lageado, Rua: José Barbosa de Barros, 1780 Botucatu – SP, CEP: 18610-307, BRAZIL T: (14) 3882 - 6300 / 3811 - 7127 CABI Gordon Street, Curepe, TRINIDAD AND TOBAGO T: +1 868 6457628 CABI 875 Massachusetts Avenue, 7th Floor, Cambridge, MA 02139, USA T: +1 617 3954051