Cells
advertisement

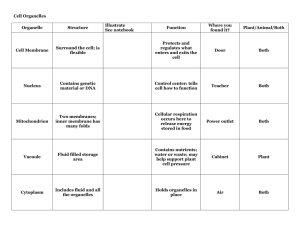
Cells =the basic unit of life Cell Theory All living organisms are made up of one or more cells and their products The cell is the simplest unit that carries out all life processes All cells come from other living cells (first cell ~ 4 billion years ago) The activity of an organism depends on the activity of all of its cells! Classification of Cells Organism Prokaryote Eukaryote • No nucleus •Nucleus present Multicellular organism Plants Animals Single-celled organism Cell Structure Cells have specific purposes within the organism Each cell is made up of many structures to enable it to achieve its function Structures are called ORGANELLES Each organelle has a specific function ORGANELLES *http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=aczbMlS Mr8U *https://www.khanacademy.org/science/biolog y/cell-division/v/parts-of-a-cell Cytoplasm Fluid that suspends all the organelles Contains nutrients Medium for chemical reactions Changes in viscosity from jelly to liquid Cell Membrane Flexible double layer Semi-permeable – allows some molecules to pass through while preventing others Provides support and structure Nucleus Spherical Contains chromosomes Chromosomes are one form of DNA (coded instructions for all cell activities) Surrounded by the nuclear membrane Contains the nucleolus (contains RNA- important for making protein) Mitochondria Oblong (sausage-like) structure with finger like projections throughout Produces all energy for the cell Contain enzymes to convert stored energy into easy to use form (cellular respiration) Cells that require more energy contain more mitochondria Contain their own DNA Mitochondrion Checkpoint Write the word and chemical equation for cellular respiration C6H12O6 + 6O2 6CO2 + 6H2O + Energy Endoplasmic Reticulum (E.R.) 3D network of tubing throughout the cell Connects cell membrane to nuclear membrane Functions as transport system Parts of the E.R. have ribosomes attached to them and are called rough E.R. Smooth ER is the area where fats or lipids are made Endoplasmic Reticulum Ribosomes Small bodies that receive instructions from the nucleus to make proteins. They are found throughout the cytoplasm or attached to rough E.R. Proteins are widely used in cells to serve diverse functions. Some proteins provide the structural support for cells while others act as enzymes to catalyze biochemical reactions. There are a lot of rough E.R. in cells that secrete digestive enzymes (cells lining stomach). Ribosome What protein do you want me to make? Golgi Bodies (aka Golgi Apparatus) They are tube-like membranes that have many sacs at the end- appear like a stack of pancakes Modifies and packages proteins from ribosomes http://www.johnkyrk.com/golgiAlone.html G.B also make and secrete mucus (e.g. cells lining intestine) Active cells contain more G.B. than less active cells Golgi Apparatus Vacuoles Fluid filled sac enclosed by membrane Variety of functions Store substances for use (water, food, minerals & waste) Remove unwanted substances from cell Bring substances into cell Maintain internal pressure in plant cells which is why they have large vacuoles compared to animal cells Organelles Specific to Plants Cell wall Just outside of the cell membrane Rigid but porous Provides support and protection to cell Organelles Specific to Plants cont’d Chloroplasts Contain chlorophyll giving leaves their green colour Chloroplasts absorb light energy used in photosynthesis Note: There are other pigment containing organelles in plants e.g. chromoplasts Checkpoint Write the word and chemical equation for photosynthesis 6CO2 + 6H2O + Energy (sunlight) C6H12O6 + 6O2 Organelles Specific to Plants cont’d Vacuoles While not specific to plants, in plants there is usually only one large vacuole Helps maintain a plant’s turgor pressure Organelles Specific to Animals Centriole Barrel shaped tube Consists of 9 triplets of microtubules Involved in organization of miotic spindle (for Mitosis) Organelles Specific to Animals cont’d Lysosomes (rare in plants) Break down large molecules and cell parts within the cytoplasm by releasing digestive enzymes Also an important component of the human body’s defense mechanism (immune system) White bloods cells contain many lysosomes since they engulf invading bacteria Lysosomes ensure infected cells are destroyed “suicide sacs” Animal vs Plant Cells Checkpoint Draw a Venn Diagram for plants and animals containing all the organelles Copy this into your notes