DFSS Basic Staistics
advertisement

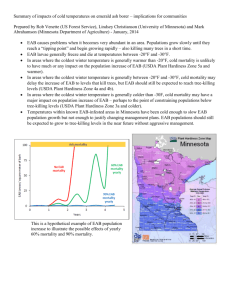
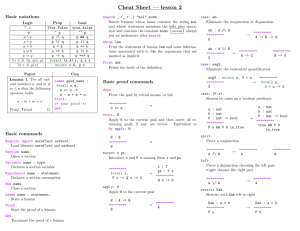
Basic Statistics DFSS Basic Staistics 2004-09-27 1 EAB/JN Stefan Andresen Cornerstones of a successful use of 6 Results World Class Business Performance Methodology DFSS Basic Staistics Change Management 2004-09-27 2 EAB/JN Stefan Andresen Yield Lower Tolerance Limit Upper Tolerance Limit Yield Defects Yield = Pass / Trials p(d) = (1- Yield)/100 DFSS Basic Staistics 2004-09-27 4 EAB/JN Stefan Andresen Discrete data - First Time Right (First Time Yield) Measures the units that avoid the hidden costs. Step A Good? Yes Step B Good? No Fix It? Yes Ship It! No No SCRAP No Fix It? Yes Yes Rework Rework COPQ DFSS Basic Staistics 2004-09-27 5 EAB/JN Stefan Andresen Discrete data - Rolled Thru Yield Most processes are complex interrelationships of many sub-processes. The overall performance is usually of interest to us. First Process FTY First Process 99% Second Process First pass yield or rolled through yield for these three processes is 0.99 x 0.89 x 0.95 = .837, almost 84% DFSS Basic Staistics Rolled yield is a realistic assessment of the cumulative effect of sub-processes Rework FTY Second Process 89% Third Process Rework FTY Third Process 95% Rework Terminator 2004-09-27 6 EAB/JN Stefan Andresen YIELD (process yield)no of operations Yield \No of op. 0,8 0,95 0,9999 0,999997 3 0,512000 0,857375 0,999700 0,999991 DFSS Basic Staistics 10 0,107374 0,214639 0,999000 0,999970 2004-09-27 100 0,000000 0,005921 0,990049 0,999700 7 1000 0,000000 0,000000 0,904833 0,997004 10000 0,000000 0,000000 0,367861 0,970445 EAB/JN Stefan Andresen Is it fair to compare processes and products that have different levels of complexity? DPO • DPO - Defects Per Opportunity DPO DPMO defects opportunities • DPMO - Defects Per Million Opportunities DPMO Opportunity DFSS Basic Staistics defects opportunities *1 000 000 Measurable The number of opportunities for a defect to occur, is related to the complexity involved. 2004-09-27 8 EAB/JN Stefan Andresen Yeild to DPMO? (-dpu) Y=e dpu=-lnY dpu = defects per unit = DPMO*(opportunities/unit)/1 000 000 DFSS Basic Staistics 2004-09-27 9 EAB/JN Stefan Andresen Product yield vs dpmo 100000 opp. 10000 opp. 1000 opp. 100 opp. 50 0 0 1 10 dpmo 6 DFSS Basic Staistics 100 5 2004-09-27 10 The automation wall The Design & supply wall 100 1000 10000 100000 4 3 EAB/JN Stefan Andresen Variation Output power Standard deviation (std, s, ) Special cause variation Average, Mean-value (x, m or µ, M) Common cause variation Measurement no DFSS Basic Staistics 2004-09-27 12 EAB/JN Stefan Andresen Every Normal Curve can be defined by two numbers: •Mean: a measure of the center •Standard deviation: a measure of spread DFSS Basic Staistics 2004-09-27 15 EAB/JN Stefan Andresen Observation 6 4 X1 X2 X3 X4 X5 X6 X7 X8 X9 X10 2 0 0,1 0,2 x-m)2 n-1 DFSS Basic Staistics 0,3 0,4 0,5 0,6 0,7 0,4 0,3 0,4 0,6 0,5 0,4 0,2 0,3 0,5 0,4 0,8 sample = n-1 population = n 2004-09-27 value 16 The range method: N<10: Range/3 N>10 Range/4 EAB/JN Stefan Andresen Exercise Calculate Range, Variance and Standard deviation. Draw a normal probability plot of the result. Formulas Data Value (xi-x) R = X max X min s2 s 2 n i 1 xi x n 1 DFSS Basic Staistics 2 5 6 5 7 6 9 7 8 6 8 1 2 n xi x i 1 n 1 (xi-x) Sum n-1 Variance Std. dev. 2004-09-27 19 EAB/JN Stefan Andresen Average, Range & Spread Diagram 1 Faults Each diagram has an average of 10, range of 18 and a variation of approx. 5,8. Imagine only looking at the result and not on the graphs. 20 18 16 14 12 10 8 6 4 2 0 0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 8 10 12 14 Number Diagram 3 20 18 16 14 12 10 8 6 4 2 0 Faults Faults Diagram 2 0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 0 Number DFSS Basic Staistics 20 18 16 14 12 10 8 6 4 2 0 2 4 6 Number 2004-09-27 20 EAB/JN Stefan Andresen The normal distribution -6 -5 -4 -3 -2 -1 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 68.27% 95.45% 99.73% 99.9937% 99.999943% 99.9999998% DFSS Basic Staistics 2004-09-27 21 EAB/JN Stefan Andresen The Z-table Area under the normal curve is equal to the probability (p, also named dpo) of getting an observation beyond Z (see the Z-table) Z DFSS Basic Staistics 2004-09-27 22 EAB/JN Stefan Andresen Normalizing standard deviations The expected probability of having a specific value Observed value - Mean Value = Z-value Standard deviation ( the Z-table gives the probability occurrence) |x-M| std DFSS Basic Staistics =Z 2004-09-27 23 EAB/JN Stefan Andresen Z-VALUES AND PROBABILITIES 68,3% -1+1 95,4% -2+2 99,7% -3+3 99,999997% -6+6 DFSS Basic Staistics 2004-09-27 24 EAB/JN Stefan Andresen Z – Table Area Z 0.0 0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4 0.5 0.6 0.7 0.8 0.9 0 5.00E-01 4.60E-01 4.21E-01 3.82E-01 3.45E-01 3.09E-01 2.74E-01 2.42E-01 2.12E-01 1.84E-01 0.01 4.96E-01 4.56E-01 4.17E-01 3.78E-01 3.41E-01 3.05E-01 2.71E-01 2.39E-01 2.09E-01 1.81E-01 0.02 4.92E-01 4.52E-01 4.13E-01 3.75E-01 3.37E-01 3.02E-01 2.68E-01 2.36E-01 2.06E-01 1.79E-01 0.03 4.88E-01 4.48E-01 4.09E-01 3.71E-01 3.34E-01 2.98E-01 2.64E-01 2.33E-01 2.03E-01 1.76E-01 0.04 4.84E-01 4.44E-01 4.05E-01 3.67E-01 3.30E-01 2.95E-01 2.61E-01 2.30E-01 2.01E-01 1.74E-01 0.05 4.80E-01 4.40E-01 4.01E-01 3.63E-01 3.26E-01 2.91E-01 2.58E-01 2.27E-01 1.98E-01 1.71E-01 0.06 4.76E-01 4.36E-01 3.97E-01 3.59E-01 3.23E-01 2.88E-01 2.55E-01 2.24E-01 1.95E-01 1.69E-01 0.07 4.72E-01 4.33E-01 3.94E-01 3.56E-01 3.19E-01 2.84E-01 2.51E-01 2.21E-01 1.92E-01 1.66E-01 0.08 4.68E-01 4.29E-01 3.90E-01 3.52E-01 3.16E-01 2.81E-01 2.48E-01 2.18E-01 1.89E-01 1.64E-01 0.09 4.64E-01 4.25E-01 3.86E-01 3.48E-01 3.12E-01 2.78E-01 2.45E-01 2.15E-01 1.87E-01 1.61E-01 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 1.7 1.8 1.9 1.59E-01 1.36E-01 1.15E-01 9.68E-02 8.08E-02 6.68E-02 5.48E-02 4.46E-02 3.59E-02 2.87E-02 1.56E-01 1.34E-01 1.13E-01 9.51E-02 7.93E-02 6.55E-02 5.37E-02 4.36E-02 3.52E-02 2.81E-02 1.5 39E01 1.31E-01 1.11E-01 9.34E-02 7.78E-02 6.43E-02 5.26E-02 4.27E-02 3.44E-02 2.74E-02 1.52E-01 1.29E-01 1.09E-01 9.18E-02 7.64E-02 6.30E-02 5.16E-02 4.18E-02 3.36E-02 2.68E-02 1.49E-01 1.27E-01 1.08E-01 9.01E-02 7.49E-02 6.18E-02 5.05E-02 4.09E-02 3.29E-02 2.62E-02 1.47E-01 1.25E-01 1.06E-01 8.85E-02 7.35E-02 6.06E-02 4.95E-02 4.01E-02 3.22E-02 2.56E-02 1.45E-01 1.23E-01 1.04E-01 8.69E-02 7.21E-02 5.94E-02 4.85E-02 3.92E-02 3.14E-02 2.50E-02 1.42E-01 1.21E-01 1.02E-01 8.53E-02 7.08E-02 5.82E-02 4.75E-02 3.84E-02 3.07E-02 2.44E-02 1.40E-01 1.19E-01 1.00E-01 8.38E-02 6.94E-02 5.71E-02 4.65E-02 3.75E-02 3.01E-02 2.39E-02 1.38E-01 1.17E-01 9.85E-02 8.23E-02 6.81E-02 5.59E-02 4.55E-02 3.67E-02 2.94E-02 2.33E-02 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 2.5 2.6 2.7 2.8 2.9 2.28E-02 1.79E-02 1.39E-02 1.07E-02 8.20E-03 6.21E-03 4.66E-03 3.47E-03 2.56E-03 1.87E-03 2.22E-02 1.74E-02 1.36E-02 1.04E-02 7.98E-03 6.04E-03 4.53E-03 3.36E-03 2.48E-03 1.81E-03 2.17E-02 1.70E-02 1.32E-02 1.02E-02 7.76E-03 5.87E-03 4.40E-03 3.26E-03 2.40E-03 1.75E-03 2.12E-02 1.66E-02 1.29E-02 9.90E-03 7.55E-03 5.70E-03 4.27E-03 3.17E-03 2.33E-03 1.70E-03 2.07E-02 1.62E-02 1.26E-02 9.64E-03 7.34E-03 5.54E-03 4.15E-03 3.07E-03 2.26E-03 1.64E-03 2.02E-02 1.58E-02 1.22E-02 9.39E-03 7.14E-03 5.39E-03 4.02E-03 2.98E-03 2.19E-03 1.59E-03 1.97E-02 1.54E-02 1.19E-02 9.14E-03 6.95E-03 5.23E-03 3.91E-03 2.89E-03 2.12E-03 1.54E-03 1.92E-02 1.50E-02 1.16E-02 8.89E-03 6.76E-03 5.09E-03 3.79E-03 2.80E-03 2.05E-03 1.49E-03 1.88E-02 1.46E-02 1.13E-02 8.66E-03 6.57E-03 4.94E-03 3.68E-03 2.72E-03 1.99E-03 1.44E-03 1.83E-02 1.43E-02 1.10E-02 8.42E-03 6.39E-03 4.80E-03 3.57E-03 2.64E-03 1.93E-03 1.40E-03 DFSS Basic Staistics 2004-09-27 25 EAB/JN Stefan Andresen Z – Table Z 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 3.5 3.6 3.7 3.8 3.9 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 4.4 4.5 4.6 4.7 4.8 4.9 5.0 5.1 5.2 5.3 5.4 5.5 5.6 5.7 5.8 5.9 6.0 0 1.35E-03 9.68E-04 6.87E-04 4.84E-04 3.37E-04 2.33E-04 1.59E-04 1.08E-04 7.25E-05 4.82E-05 3.18E-05 2.08E-05 1.34E-05 8.62E-06 5.48E-06 3.45E-06 2.15E-06 1.33E-06 8.18E-07 4.98E-07 3.00E-07 1.80E-07 1.07E-07 6.27E-08 3.66E-08 2.12E-08 1.22E-08 6.98E-09 3.96E-09 2.23E-09 1.25E-09 0.01 1.31E-03 9.35E-04 6.64E-04 4.67E-04 3.25E-04 2.24E-04 1.53E-04 1.04E-04 6.96E-05 4.63E-05 3.05E-05 1.99E-05 1.29E-05 8.24E-06 5.23E-06 3.29E-06 2.05E-06 1.27E-06 7.79E-07 4.73E-07 2.85E-07 1.71E-07 1.01E-07 5.95E-08 3.47E-08 2.01E-08 1.16E-08 6.60E-09 3.74E-09 2.11E-09 1.18E-09 DFSS Basic Staistics 0.02 1.26E-03 9.04E-04 6.41E-04 4.50E-04 3.13E-04 2.16E-04 1.47E-04 9.97E-05 6.69E-05 4.44E-05 2.92E-05 1.91E-05 1.23E-05 7.88E-06 5.00E-06 3.14E-06 1.96E-06 1.21E-06 7.41E-07 4.50E-07 2.71E-07 1.62E-07 9.59E-08 5.64E-08 3.29E-08 1.90E-08 1.09E-08 6.24E-09 3.53E-09 1.99E-09 1.11E-09 Area 0.03 1.22E-03 8.74E-04 6.19E-04 4.34E-04 3.02E-04 2.08E-04 1.42E-04 9.59E-05 6.42E-05 4.26E-05 2.80E-05 1.82E-05 1.18E-05 7.53E-06 4.77E-06 3.00E-06 1.87E-06 1.15E-06 7.05E-07 4.28E-07 2.58E-07 1.54E-07 9.10E-08 5.34E-08 3.11E-08 1.80E-08 1.03E-08 5.89E-09 3.34E-09 1.88E-09 1.05E-09 0.04 1.18E-03 8.45E-04 5.98E-04 4.19E-04 2.91E-04 2.00E-04 1.36E-04 9.21E-05 6.17E-05 4.09E-05 2.68E-05 1.75E-05 1.13E-05 7.20E-06 4.56E-06 2.86E-06 1.78E-06 1.10E-06 6.71E-07 4.07E-07 2.45E-07 1.46E-07 8.63E-08 5.06E-08 2.95E-08 1.70E-08 9.78E-09 5.57E-09 3.15E-09 1.77E-09 9.88E-10 2004-09-27 0.05 1.14E-03 8.16E-04 5.77E-04 4.04E-04 2.80E-04 1.93E-04 1.31E-04 8.86E-05 5.92E-05 3.92E-05 2.57E-05 1.67E-05 1.08E-05 6.88E-06 4.35E-06 2.73E-06 1.70E-06 1.05E-06 6.39E-07 3.87E-07 2.32E-07 1.39E-07 8.18E-08 4.80E-08 2.79E-08 1.61E-08 9.24E-09 5.26E-09 2.97E-09 1.67E-09 9.31E-10 26 0.06 1.11E-03 7.89E-04 5.57E-04 3.90E-04 2.70E-04 1.86E-04 1.26E-04 8.51E-05 5.68E-05 3.76E-05 2.47E-05 1.60E-05 1.03E-05 6.57E-06 4.16E-06 2.60E-06 1.62E-06 9.96E-07 6.08E-07 3.68E-07 2.21E-07 1.31E-07 7.76E-08 4.55E-08 2.64E-08 1.53E-08 8.74E-09 4.97E-09 2.81E-09 1.58E-09 8.78E-10 0.07 1.07E-03 7.62E-04 5.38E-04 3.76E-04 2.60E-04 1.79E-04 1.21E-04 8.18E-05 5.46E-05 3.61E-05 2.36E-05 1.53E-05 9.86E-06 6.28E-06 3.97E-06 2.48E-06 1.54E-06 9.48E-07 5.78E-07 3.50E-07 2.10E-07 1.25E-07 7.36E-08 4.31E-08 2.50E-08 1.44E-08 8.26E-09 4.70E-09 2.65E-09 1.49E-09 8.28E-10 0.08 1.04E-03 7.36E-04 5.19E-04 3.63E-04 2.51E-04 1.72E-04 1.17E-04 7.85E-05 5.24E-05 3.46E-05 2.26E-05 1.47E-05 9.43E-06 6.00E-06 3.79E-06 2.37E-06 1.47E-06 9.03E-07 5.50E-07 3.32E-07 1.99E-07 1.18E-07 6.98E-08 4.08E-08 2.37E-08 1.37E-08 7.81E-09 4.44E-09 2.50E-09 1.40E-09 7.81E-10 0.09 1.00E-03 7.11E-04 5.01E-04 3.50E-04 2.42E-04 1.66E-04 1.12E-04 7.55E-05 5.03E-05 3.32E-05 2.17E-05 1.40E-05 9.01E-06 5.73E-06 3.62E-06 2.26E-06 1.40E-06 8.59E-07 5.23E-07 3.16E-07 1.89E-07 1.12E-07 6.62E-08 3.87E-08 2.24E-08 1.29E-08 7.39E-09 4.19E-09 2.36E-09 1.32E-09 7.36E-10 EAB/JN Stefan Andresen Capability CP Tolerance width divided by 6 times the standard deviation. A CP value greater than 2 is good (thumb rule) Tolerance width TÖ - TU CP = ----------6 *6 DFSS Basic Staistics 2004-09-27 27 EAB/JN Stefan Andresen Capability Cpk Difference between nearest tolerance limit and average, divided by 3 times the standard deviation. A Cpk value greater than 1,5 is good (thumb rule) TU CPK TÖ Min(TÖ alt. TU) = ---------------------- 3 *3 DFSS Basic Staistics 2004-09-27 28 EAB/JN Stefan Andresen Continuous data and possible Pitfalls Can be divided in to two types of variation Common cause Special cause (e.g. within batch variation) -The shift between and (e.g. batch variation) -Outliers or non-rare occasions will appear and may ruin the analyze Output power 22 20 Effect (dBm) 18 16 14 12 10 0 5 10 15 20 25 30 Number DFSS Basic Staistics 2004-09-27 29 EAB/JN Stefan Andresen Short-Term Capabilities (within group variation) „Shift Happens“ Time 1 (between group variation) Time 2 Time 3 Time 4 Long-Term Capability (all variation) LSL DFSS Basic Staistics 2004-09-27 Target 30 USL EAB/JN Stefan Andresen Z long term and Z short term Z _ long _ term Tol Tol T Z _ Short _ term s p overall Z B Single sided Single Sided The sample and the population sigma are often almost the same, but the average will probably differ. Therefore is zST (zB ) and shift & drift preferably used to estimate the “true” fault rate. Shift & Drift = Zshort term - Zlong term What will the long term fault rate be in exercise 5 with a S&D of 1.5? DFSS Basic Staistics 2004-09-27 31 EAB/JN Stefan Andresen ZB Lower Tolerance Limit Upper Tolerance Limit Ptot=Pupper+Plower ZB – From table with Ptot DFSS Basic Staistics 2004-09-27 32 Rev C Peter Häyhänen 9805 EAB/JN Stefan Andresen Is Six Sigma corresponding to a defect level of 3,4ppm? LSL USL 1.5 Short-term Short-term -6 -5 -4 -3 -2 -1 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 99.9999998% or 0.002 ppm 99.99966% or 3.4 ppm Yes, with a S&D of 1,5!! DFSS Basic Staistics 2004-09-27 33 EAB/JN Stefan Andresen Shift & Drift Z short term inProcess a typical process 4,02 on approx. 30 values). Capability Analysis for (based Z-short term LSL Process Data USL Target LSL Mean Sample N StDev (ST) StDev (LT) ST LT * * 10,0000 12,5804 25 0,641863 0,641863 Potential (ST) Capability Cp CPU CPL Cpk Cpm * * 1,34 1,34 * Overall (LT) Capability Pp * PPU * PPL 1,34 Ppk 10 11 Observed Performance PPM < LSL 0,00 PPM > USL * PPM Total 0,00 12 13 Expected ST Performance PPM < LSL 29,08 PPM > USL * PPM Total 29,08 14 15 Expected LT Performance PPM < LSL 29,08 PPM > USL * PPM Total 29,08 1,34 DFSS Basic Staistics 2004-09-27 34 EAB/JN Stefan Andresen Shift & Drift Z long term in a Process typicalCapability processAnalysis 3,03 for (measurments from one and a Z-long term half year of production, “all values”) LSL Process Data USL Target LSL Mean Sample N StDev (ST) StDev (LT) ST LT * * 10,0000 12,2222 161 0,732048 0,732048 Potential (ST) Capability Cp CPU CPL Cpk Cpm * * 1,01 1,01 * Overall (LT) Capability Pp * PPU * PPL 1,01 Ppk 10 11 Observed Performance PPM < LSL 0,00 PPM > USL * PPM Total 0,00 12 13 Expected ST Performance PPM < LSL 1200,46 PPM > USL * PPM Total 1200,46 14 Expected LT Performance PPM < LSL 1200,46 PPM > USL * PPM Total 1200,46 1,01 DFSS Basic Staistics 2004-09-27 35 EAB/JN Stefan Andresen Shift & Drift Poverall = 1200ppm Z = 3,03 Z = 4,02 Psample = 29ppm Shift & Drift = Zshort term - Zlong term Shift & Drift = 4,02 - 3,03 Shift & Drift = 0,99 DFSS Basic Staistics 2004-09-27 36 EAB/JN Stefan Andresen Minitab Capability Output DFSS Basic Staistics 2004-09-27 37 EAB/JN Stefan Andresen Nomenclature dpmo - defects per million opportunities Yield - % of the number of approved units divided by the total number of units p(d) - probability for defects (1-Yield) Fty - First time yield, the yield when the units are tested for the first time TpY - Throughput yield, the yield in every unique process step Yrt - Yield rolled through, multiplied throughput yield DPU - Defects per units DPO - Defects per opportunity Opp - Opportunity, measurable opportunity for defect DFSS Basic Staistics 2004-09-27 38 EAB/JN Stefan Andresen Nomenclature Zst - Single side short term capability, calculated with the help of the target Zb - An estimate of the overall short term capability, used to calculate Zlt Zlt - A rating of the long term capability, normally based on S&D & Zb pl - Probability for defect beneath lower specification limit pu - Probability for defect above upper specification limit p - Summarized probability for defect, pl + pu S&D - An approximation of the drift in average, fundamentally 1,5 LSL - Lower specification limit USL - Upper specification limit DFSS Basic Staistics 2004-09-27 39 EAB/JN Stefan Andresen