External Water Treatment
advertisement
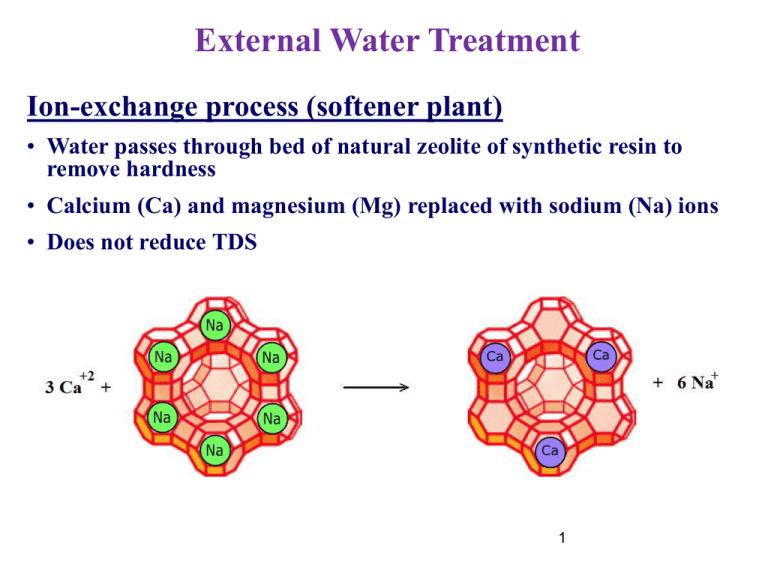
External Water Treatment Ion-exchange process (softener plant) • Water passes through bed of natural zeolite of synthetic resin to remove hardness • Calcium (Ca) and magnesium (Mg) replaced with sodium (Na) ions • Does not reduce TDS 1 Softener Plant 2 DM System 3 4 External Water Treatment Osmosis • Solutions of differing concentrations • Separated by a semi-permeable membrane • Water moves to the higher concentration 5 External Water Treatment Reversed Osmosis (RO) • Higher concentrated liquid pressurized • Water moves in reversed direction 6 RO System 7 8 Electrodialysis 9 Electrodialysis for Water Treatment 10 External Water Treatment & Internal Water Conditioning 11 Internal Water Conditioning Prevention of internal scale by forming deposits in sludge shape Injection of chemicals •Different chemicals for different water impurities •Conditions: For low amounts of feed water impurities For low pressure boilers, TDS content has higher limits Internal treatment alone not recommended 12 Internal Water Conditioning Scale control Injection of chemical additives • Minerals (Na2CO3, Na3PO4, Na2HPO4, NaH2PO4, (NaPO3)6 ,…) • Organics (Chelants, Lignins, Starches, Tannins, …) • Minerals + Organics Chelants (NTA, EDTA, …) 13 External Water Treatment De-aeration • Removal of various dissolved gases from water (O2, CO2, …) • These gases are corrosive. • De-aerator can decrease amount of dissolved gases in water. 14 External Water Treatment Mechanical de-aeration • O2 and CO2 removed by heating feed water • Economical treatment process Vent Spray Nozzles Boiler Feed Water • Vacuum type can reduce O2 to 0.02 mg/L Steam Scrubber Section (Trays) • Pressure type can reduce O2 to 0.005 mg/L Storage Section De-aerated Boiler Feed Water 15 Removal of Dissolved Oxygen Trace Pitting Corrosion control • Sodium sulphite: 2Na2 SO3 O2 2Na 2SO4 Increases TDS: increased blow down • Hydrazine N 2 H4 (NH 2 NH 2 ) O2 2H 2O N 2 Does not increase TDS: used in high pressure boilers 16 Causes of Carry Over Mechanical (Boiler design) High level of water in drums Deficiency on separator operation Sudden increasing boiler load (reduction of pressure) Chemical High TDS High alkalinity Oil and organic impurities 17 Water Conditioning Corrosion & scale control Acid (H+) attack Adjustment of water pH based on manufacturer recommendation 18 Water Conditioning Caustic embrittlement control Adjustment of water NaNO3/NaOH ratio depending to boiler pressure (According to manufacturer recommendation) 19 Boiler Blow Down • Controls TDS of the boiler water • Boiler sludge conditioning • Blows off water and replaces it with feed water • Conductivity measured as indication of TDS levels 20 Boiler Blow Down Benefits • Lower pretreatment costs • Reduced maintenance downtime • Increased boiler life • Lower consumption of chemicals 21 Boiler Blow Down Types of blow down • Batch (Periodic) • Manually operated valve reduces TDS • Large short-term increases in feed water • Substantial heat loss • Continuous • Ensures constant TDS and steam purity • Heat lost can be recovered • Common in high-pressure boilers 22 Water/Chemical Economics / Optimization • Application of proper external treatment • Application of accurate internal conditioning • Amounts of used chemical • Amounts of produced wastes/sludge • Amounts of wasted water (blow down) • Cost of monitoring & Control • Economy of water treatment/conditioning • Recirculation of used steam 23 THANKS FOR YOUR ATTENTION




