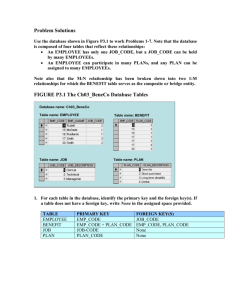
Integrating EMP into Operational Manual
advertisement

World Bank Safeguard Training Workshop Dushanbe, Tajikistan September, 2009 Reference for all aspects of project implementation: who does what, when and how Usually prepared after project Appraisal, before Effectiveness, updated as needed Emphasis on decision-making processes; “fiduciary” mechanisms (procurement, financial management & accounting, environment); monitoring & reporting Prepared by Client (Implementing Agency); approved by Govt. (higher level); acceptable to WB Cited in Legal Agreement, legally binding commitments Need to specify procedure for amending it Provides clear, detailed, definitive guidance and procedures for implementing the project – follow the rules & all will be well Facilitates efficient project monitoring and supervision Simplifies Legal Agreement (only one reference needed to cover all Client/WB agreements) Provides continuity in case of staff changes Project objectives, description, components Applicable laws, regulations, rules Sub-project eligibility criteria (beneficiaries, locations, activities), or “Menu” of eligible projects Sub-project application, evaluation, selection process Institutional structures/responsibilities EMP or Environmental Guidelines Disbursement procedures (including for Sub-grants) Procurement procedures Financial management & accounting Monitoring & Reporting (Table of Progress & Impact Indicators) Annexes: Work Plan (updated annually) Application & Reporting formats Terms of Reference (PIU, major consultancies) 1. 2. 3. EMP as a chapter of POM EMP as an annex to POM Elements of EMP inserted throughout OM where relevant Recommended - 1 & 3 or 2 & 3 Provides small grants to individuals or groups for enterprise development (sub-projects) Typically based on applications, sometimes competitive Grants typically finance small works (rehabilitation, small-scale construction), equipment, inputs, TA Usually sub-projects Category B (Category A subprojects specifically excluded) Framework EA/EMP covering the whole project sets out procedures for site-specific EA/EMP for subprojects Kazakhstan Kyrghyz Rep. Croatia Serbia Program objective: demonstrate positive linkages between Protected Areas/biodiversity conservation and rural development (economic opportunities from sustainable use; awareness-raising and education) Grant size: Euro 2,000 – 25,000 Eligibility Screening of proposals Submission of proposals (Assisted) preparation of applications Training Workshops for Applicants 5 4 6 Sub-Project approval 3 6 22 Program Advertisement 1 Final report & accounting Evaluation/selection of eligible proposals Agreement on work plan, contract signing 7 sub-project cycle 8 11 10 First tranche disbursement Progress report, 9 Accounting, verification Second tranche disbursement Awareness & Training - advice to prospective applicants on eligible/ineligible activities, potential environmental issues e; potential impacts and mitigation measures for different types of sub-projects Grant application: identify potential environmental issues and proposed mitigation measures; Screening of application: review of eligibility of proposal, excluding any with high environmental risk Grant evaluation & selection: EA screening, evaluation of env. issues and proposed mitigations; indicate whether specific EA/EMP required Preparation/signing of Grant contract: Environmental mitigation measures included in Sub-project contract; Includes specific environmental provisions for procurement, contracting Procurement: includes environmental provisions in bidding documents, specifications, contracts (including penalties for non-compliance) Grant disbursement/Progress reporting: environmental measures maybe triggers for disbursement; PIU verifies environmental measures implemented and are effective Monitoring & reporting on Grant Implementation: includes EMP compliance, environmental indicators Insufficient understanding or appreciation of issues on part of applicants; inadequate up-front education and advice Insufficient use of environmental consultants for screening, EA, monitoring Inadequate coverage of environmental responsibilities in beneficiary contracts Inadequate coordination between environmental and procurement specialists in PIU Monitoring only process and inputs rather than impacts; vague or unclear indicators and targets