Lab – What Limits Cell Size? Background When cells reach a
advertisement

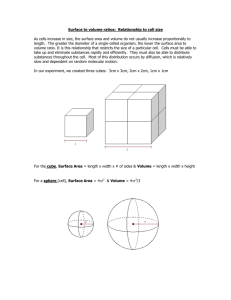
Lab – What Limits Cell Size? Background When cells reach a certain size, their rate of growth slows down. They will eventually stop growing. Each of these cells divides into two smaller cells, which begin to grow. What causes this? An easy way to investigate such questions is to build models. A model is often thought of as a small copy of something larger. Here we will be making a larger model of something small. When a cell becomes too large, it is no longer as efficient as it used to be. It now has a greater volume and it takes much longer for materials that enter the cell to reach the center of the cell. This concept will be demonstrated in the lab. Part 1 – Prelab Research For this portion of the lab report, you will be writing a ONE PARAGRAPH introduction to this lab. This paragraph should be approximately 7-8 sentences. This paragraph should cover the following: Define the term diffusion and research why diffusion is important to living things o e.g. what materials/molecules diffuse in and out of cells? Why is it important that cells have access to these molecules all the time? Part 2 – Lab Purpose: To investigate how the size of a cell influence the distribution of chemicals throughout the cell. Hypothesis: Complete a hypothesis (use if… then…) Materials: Agar block Sodium hydroxide Knife Timer (on phone or watch) Ruler Camera (on phone or other device) Beakers Procedure: 1. Work in groups of 4. Obtain a large piece of nutrient agar. This agar has been made with phenolphthalein. Cut the following cubes out of your agar (measure carefully): 1cm x 1cm x 1cm 2cm x 2cm x 2cm 3cm x 3cm x 3cm Examine the cubes. Think of them as giant models of tiny cells. Ponder and Discuss: Which of your three differentsized cells do you think would be most likely to survive? Why do you think so? Materials used during cell activity and growth enter the cell from the outside and must travel through the cell to their destination. Waste products go through the cell surface to the outside. Do you think the cell with the greatest total surface area will do the best job of moving materials in and out of the cell? Why or why not? 2. Calculate the total surface area of each of your three models using the following formula: Surface area = 6 x (length x width), that is, the total surface area is 6 times the surface area of one side. 3. Record the total surface area for each cube in Table 2. Ponder and Discuss: Which cell has the greatest surface area? 4. The cells have different surface areas and they have different volumes (amounts of materials inside). Calculate the volume of each cube. Volume = length x width x height. 5. Record the volume of each cube in data Table 1. Ponder and Discuss: Look back at the prediction you make in #1. Do these new calculations change any of your earlier ideas? Why or why not? 6. Place each cube into a separate beaker. Pour enough sodium hydroxide solution to cover it. Record your starting time. Use a glass rod to turn the cubes often for the next 10 minutes (time using your phone or watch). Be careful not to cut or scratch the surface of the cubes. Blot them dry. 7. Slice each cube in half with the plastic knife. Complete the observation table below. 8. Calculate the ratio of surface area to volume for each cube. To do this, for each cube size, divide its surface area by its volume. The number obtained can be expressed as a ratio. For example, a surface area of 24cm 2 divided by a volume of 3 cm3 = 24/3 = 8/1 = 8:1. 9. Record this ratio on data Table 1. Ponder and Discuss: Which cell model is the most efficient? Why? How does this demonstrate why larger cells would want to divide? Observations What differences do you see? Draw a 3cm, 2cm and 1cm square below and draw what you see. Using your camera also take pictures of the cross section view of the cells to add to your final lab report. Measure the distance from the edge that the sodium hydroxide traveled and color code that on your drawings. Table 1: Phenolphthalein Cube Drawings 3 cm cube Results 2 cm Cube Table 2: Calculations Phenolphthalein – Agar Cubes Side of cube (cm) Total Surface Area (cm2) Volume (cm3) Surface area to Volume Ratio 1 cm Cube Conclusion: Write a ONE SENTENCE STATEMENT that summarizes the findings in this lab (i.e. respond to the statement at the beginning of the lab). This should be a general statement about cell size and diffusion (not specific to this lab). Discussion: Answer the following questions in FULL SENTENCES. 1. All good experiments have experimental controls. Using the Internet, define this term IN YOUR OWN WORDS and identify 2 controls used in this lab. 2. What surrounds a cell and controls what enters or leaves? 3. Materials move into and out of a cell by what process? 4. Is diffusion more efficient over short or long distances? 5. The size of a cell is limited by the ratio of what TWO characteristics of the cell? 6. Which increases faster --- surface area or volume of a cell? 7. Why is the surface area of a cell so important to life of a cell? 8. Did the phenolphthalein diffuse into each cube in the same amount? Why or why not? 9. If a cell activity takes place in the centre of the cell, but all materials enter and exit through the cell membrane, explain the importance of the surface area to volume ratio in a cell. 10. Imagine that sodium hydroxide represents a vital nutrient that is needed by all cells. Is the size of a cell important for it to function properly? Explain using evidence from your results. Formal Lab Report Guidelines General Format: Report should be typed HEADINGS should be used to separate sections of the report TONE should be impersonal (i.e. no 'I', 'we' 'you', etc) and FORMAL BE OBJECTIVE and CONCISE – more is NOT better Do NOT print – hand in your report at Turnitin 1. TITLE Information – At the top of the first page indicate the title of the lab, your names, your teacher's name, the course code and the due date. 2. PURPOSE - What question is being posed in this lab? Note that in FORMAL lab reports, the purpose should be written as a STATEMENT, NOT as a question!! (E.g. To determine whether ….) In the case of this lab you can copy and paste the procedure directly from this document. 3. HYPOTHESIS – If… then… 4. INTRODUCTION – This is the pre-lab research paragraph 5. MATERIALS – list all materials used. Be as detailed as possible. 6. PROCEDURE – This is where you outline step by step, the steps that were taken in the lab. Procedures should be written as a list of numbered instructions that any other student could follow, almost without thinking, and end up with the same results as you. Procedures should be written as if you are telling someone exactly what to do, in real time. If your procedure is written WELL, that means that anyone should be able to follow the instructions and replicate the lab. There are some things that are ‘assumed’ in labs (you don’t need to tell me that you walked to the cupboard, pulled out a beaker, set up your station, cleaned up, etc.) In the case of this lab you can copy and paste the procedure directly from this document. 7. OBSERVATIONS – this is where you put the pictures and/or sketches of the cross section of the cells. 8. RESULTS – this is where you put your data table 9. CONCLUSION – statement that generalizes results of lab 10. DISCUSSION– Answer all the post-lab questions in FULL SENTENCES. Elaborate when possible. 11. REFERENCES – List all references used. Names: ________________________________________________________________ Marking Scheme Thinking Title Information 0 1 2 3 0 1 2 3 Materials 0 1 Procedure 0 1 Introduction Paragraph 0 1 Covers basics of diffusion Purpose Written as a statement Hypothesis If… then… Relates to purpose 0 1 Accurately copied from lab instructions Observations Table Complete Detailed images are labeled Good title Results Correct and complete Good title 0 1 2 3 0 1 2 3 0 1 2 8 9 10 0 1 2 1 2 3 Conclusion Relates to purpose General to topic (not specific to lab) Discussion: 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Communication Calculations, Units, Grammar and Spelling Overall Clarity and Organization 0 TOTALS: INQUIRY /28 COMMUNICATION /5