Chapter 17
advertisement

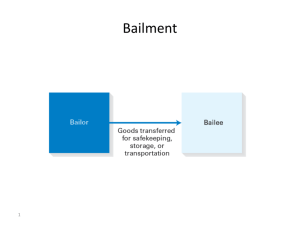
Chapter 17 Personal Property and Bailment Personal Property • Real Property: Land and anything permanently attached to it. • Personal Property: Anything that can be owned other than real property. • Tangible: Property that has substance and can be touched. • Intangible: Property that has no substance and cannot be touched. Gifts of Personal Property Three Requirements: – Donor (one making the gift) must intend to make the gift – The gift must be delivered – Donee (one receiving the gift) must accept the gift Lost Property • Finder of property has the legal duty to return the property to the owner • (Local laws may vary) Rewards and Reimbursement • Finders of lost property are entitled to any reward offered if they knew about it when returning property. • No reward??? They are entitled to be reimbursed for any expenses incurred. Misplaced Property • If property is found “left behind” in a public or semi-public place, it is considered misplaced not lost • Example: purse left in dressing room Abandoned Property • Property that has been discarded by the owner without intent to reclaim ownership. • You have the right to keep abandoned property (may be some exceptions). Stolen Personal Property • A thief has no title to stolen goods • An innocent purchaser of stolen goods is obliged to return it to the owner Intellectual Property • Original work fixed in a tangible medium of expression Patents • An exclusive right granted by the federal government to make, use, or sell an invention • Not only on products, but may consist of a process or an article of manufacture • U.S. Patent and Trademark Office = 17 years Copyrights • The right granted to an author, composer, photographer, or artist to exclusively publish and sell work. • Protected for life of author plus 70 years • In 1989, the use of the copyright notice was made optional Fair Use Doctrine: Copyrighted material may be reproduced without permission in certain cases...education. Downloading and uploading music on the Internet for others’ use is a violation of copyright law Trademarks • A distinctive mark, symbol or slogan used by a business to identify goods and distinguish them from other products. • Once established, others cannot use it. • Example: Words, names, symbols • A registered trademark continues for 10 years and may be renewed in 10 year increments. Mutuum • When you loan goods to someone with the understanding that they will be used and later replaced with different identical goods. i.e.: borrowing a cup of sugar Bailments of Personal Property • Bailment: The transfer of possession and control of personal property to another with the intent that the same property will be returned later. • Bailee: To whom the property is transferred • Bailor: The person who transfers the property See examples 4 and 5 on p. 368. Main Types of Bailments • Bailments for Sole Benefit of Bailor • Bailments for Sole Benefit of Bailee • Mutual-Benefit Bailments • Most are based on contracts; if a bailment contains consideration, then there is a valid contract. Gratuitous Bailments • Transfer of property without either party giving or asking for payment • Usually considered favors Bailments for Sole Benefit of Bailor • The bailee owes a duty to use only slight care, as the bailee is receiving no benefit from the arrangement • Only refrain from “Gross Negligence” Bailments for Sole Benefit of Bailee • The bailee is required to use great care because possession of the goods is intended solely for the bailee’s benefit • Responsible for “Slight Negligence” Mutual-Benefit Bailments • One in which both parties receive some benefit • The bailee owes a duty to use reasonable care. • Responsible for “Ordinary Negligence” Tortious Bailee: • One who wrongfully retains possession of lost property of another or is knowingly in possession of stolen property. • Burden of Proof is on the bailee. Special Bailments • Hotel Keeper – Duty to Accept All Guests (Civil Rights Act 1964) – Duty of Reasonable Care (See bullets top p. 376) – Lien and Credit Card Blocking Special Bailments • Common Carriers – Carrier: a business that transports persons, goods, or both – Common Carrier: Provides transportation to the general public • Common Carriers of Goods Not Liable… – – – – – Acts of God Acts of a public enemy Acts of public authorities Acts of the shipper The inherent nature of the goods (perishable) Special Bailments • Common Carriers of Passengers – A carrier must use reasonable care in protecting passengers. – Not responsible if injuries are not foreseeable or preventable Special Bailments • Bumped Airline Passengers – When overbooked, airlines must ask for volunteers to give up their seats – Passengers “bumped” may be entitled to compensation plus the money back for the ticket – If the airline can arrange alternative travel within 1 hour…no compensation Special Bailments • Passengers Baggage – Carriers are obligated to accept a reasonable amount of passengers baggage – A carrier is an insurer of all luggage that is checked – Federal rules place limits… • U.S. travel maximum $2,500 per passenger