Weekly Questions Week 3_4
advertisement

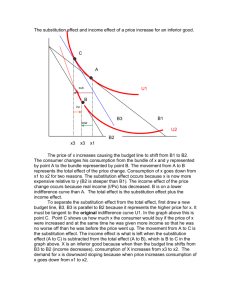
Econ 355 Weekly Questions Week 1_2 1. Briefly describe the scientific method and its application to economics. 2. Assess the following statement: Economics is not really a science because it tries to analyze human beings whose basic natures are not rational. 3. Briefly describe what economist mean by rationality and the basic rule that rational people will follow to maximize their well-being for any one activity. 4. Derive and briefly discuss the three versions of the MB=MC for one activity in the two-activity case. 5. If the marginal product of domestic labor is 10Q/L and their wage rate is $15/L and the marginal product of foreign labor is 5Q/L and their wage is $5/L, what strategy should a firm follow to minimize costs? 6. Using the above information, show how a firm could make a marginal adjustment and produce more output keeping costs constant. Then demonstrate that firm could keep output constant and reduce costs. 7. What is the marginal rate of substitution leisure for income and how is it related to: a. The marginal utilities of leisure and income, b. The slope of the indifference curve, and c. Whether a person is a leisure- vs. a work-preferer. 8. What is an indifference curve and what can it and an indifference map tell us about workers. 9. What is the income constraint? How is it related to the wage rate? 10. How will the income constraint change with a change in: a. The wage rate, b. Non-labor income, c. Over-time pay, and d. A tax on wages. 11. Build a spreadsheet that models a budget constraint for over-time pay. 12. Build a spreadsheet that models a budget constraint that allows for different taxes on welfare benefits . 13. Show how the supply curve of labor is derived using indifference curves and the income constraint. 14. Does an increase in wages always lead to an increase in labor supply? Why or why not? 15. Assume that we hold other factors constant that affect a workers’s labor supply decision. We then change wages and observe the change in hours worked. When we perform this exercise are we really holding everything ceteris paribus? Why or why not? 16. What is the income effect? Give some example of things that produce and income effect on hours worked. 17. What is the substitution effect? Why does it occur? 18. Discuss factors that will strengthen or weaken the income and substitution effects. 19. Explain how the size of the substitution and income effects changes the elasticity of labor supply with respect to wages. 20. Is the wage elasticity of supply different for men than women in the U.S.? for part-time versus full-time workers? For teenagers vs. adults? Econ 355 Weekly Questions Week 3_4 1. Decompose graphically the income and substitution effects for an increase in wages. 2. Do the above for a decrease in wages. For questions 3-6 be sure and link the determinants to the income and substitution effect. 3. Summarize the determinants of the declining participation for young workers. 4. Explain the trends in the participation rate for females since WWII. What has been happening to their participation rate in recent years? Be sure to list and discuss the underlying determinants of the trend. 5. Why has the participation rate of males between 24 and 55 of age been falling? 6. Discuss the historical and recent trends in the participation rates of older males (55+) and the underlying causes of the trends. 7. What is the discouraged worker effect? 8. What has happened to the number of discouraged workers recently? How does this affect the unemployment statistics and potential growth rates of national output? 9. Describe and provide a plausible example of the added worker effect. 10. Contrast the age-earning profiles for men and for women. What are the primary differences between the two? Provide explanations for these differences. 11. Why are the age-earnings profiles concave? Why are they higher for persons with more education? Why do they tend to spread for different educational levels? 12. Briefly describe the theory of human capital investment. 13. What is the reservation wage? 14. Explain the role of the substitution and income effects for a person that goes from a nonparticipant to a participant in the labor force. 15. Explain the role of the substitution and income effects for a person that goes from a participant to a non-participant in the labor force. 16. Discuss the difference between negative-, zero-, and positive-wage welfare programs on the incentive to work. 17. Is over-time pay likely to induce non-workers to go to work? What is the likely effect of an increase in over-time pay on people who are already working significant amounts of over-time? 18. Briefly describe the impacts of PRWORA on labor force participation of low-income individuals. 19. What is the internal rate of return? 20. Contrast the social and the private return to education. 21. According to human capital theory, what factors are likely to increase the amount of education that an individual elects to receive? 22. The fact that women receive less OJT than men is caused solely by employer discrimination against women. 23. Define the internal rate of return and briefly discuss how it is used in human capital theory. 24. Will general training always be paid for by the employee? Why or why not? 25. Will specific training always be paid by the employer? Why or why not?