No Slide Title - Science for Monks
advertisement
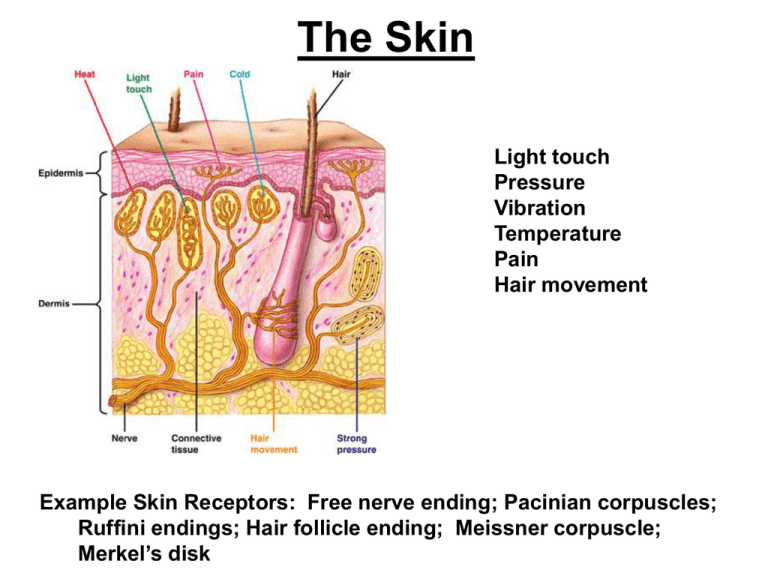
The Skin Light touch Pressure Vibration Temperature Pain Hair movement Example Skin Receptors: Free nerve ending; Pacinian corpuscles; Ruffini endings; Hair follicle ending; Meissner corpuscle; Merkel’s disk The Skin Example Skin Receptors: Free nerve ending; Pacinian corpuscles; Ruffini endings; Hair follicle ending; Meissner corpuscle; Merkel’s disk Different types of skin receptors Spinal Cord Spinal Cord 1. Sensory neurons Monosynaptic Reflex 2. Neurons in the spinal cord 3. Motor neurons which control muscle contraction Disynaptic Reflex Why does the reflex occur before perception takes place? Answer: • The sensation of heat reaches our perception only after the reflexive withdrawal took place, because the somatosensory information can travel very quickly to the spinal cord and then back down to the motor neurons, whereas it takes a longer time for this information to reach the higher areas of the brain, where it yields to perception. Spinal Cord Brain BRAIN SKIN Somatosensory pathway Spinal Cord Brain Cerebral Cortex Thalamus Medulla Note crossing! Spinal Cord The Thalamus: Anatomy The thalamus: Functions The major role of thalamus is to gate and otherwise modulate the flow of sensory information to cortex. The Thalamus: Functions The thalamus also play an important role in regulating states of sleep and wakefulness. Sensory processing hierarchy Cortex Thalamus Sensor Sensory processing is different areas of the brain The full somatosensory pathway Touch on left finger Heat on right finger The “Homunculus” The cortical representation of sensory information is not uniform, but emphasizes certain sensory parts of the body, such as the lips and fingers. Somatosensory - Brain CNS preserves the peripheral body map. Amount of CNS tissue is proportional to the distribution of peripheral receptors. Homunculus: Other Animals Brain Mapping Finding out what each part of the brain does Brain Areas are Specialized for Different Functions Demo: how many picks? • Use a fork for the following experiment. • Gently pressure your neighbor’s fingertip with 1, 2, or 3 of the fork’s picks. Can he tell (without looking) how many picks are touching his fingertip? • Now do the same on other body area, such as inside the arm, on the legs, on the lips, or on the back of the body. Can you still tell how many picks? Where? Somatosensory discrimination varies throughout the body surface Somatosensory - Brain |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||| ? |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||| Somatosensory - Brain Site Fingers Upper Lip Cheek Nose Palm Forehead Foot Belly Forearm Upper arm Back Shoulder Thigh Calf Threshold Distance 2-3 mm 5 mm 6 mm Influence of: 7 mm Ice 10 mm Distraction 15 mm Sound 20 mm 30 mm 35 mm 39 mm 39 mm 41 mm 42 mm 45 mm Pain! Gate Control Theory Proprioception 1 2 3 ?








