Supply
advertisement

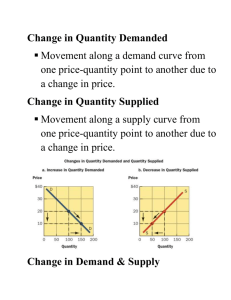
SUPPLY Factors that shift supply TODAY’S AGENDA Objective: To identify the factors that shift supply and which direction the curve shifts. Essential Skill: To explicitly assess information and draw conclusions. CHANGE IN QUANTITY SUPPLIED Price (per unit) S0 B $15 A Change in quantity supplied (a movement along the curve) 1,250 1,500 Quantity supplied (per unit of time) SHIFT IN SUPPLY Price (per unit) S0 $15 A S1 B Shift in Supply (a shift of the curve) 1,250 1,500 Quantity supplied (per unit of time) “ROTTEN” NON-PRICE DETERMINANTS OF SUPPLY: FACTORS THAT SHIFT THE SUPPLY CURVE “R” IS FOR RESOURCE Changes in resource prices or input costs Elements of nature and political disruptions “O” IS FOR OTHER Change in Prices of other goods produced and offered for sale “T” IS FOR TECHNOLOGY Changes in technology “T” IS FOR TAXES Changes in taxes and subsidies “E” IS FOR EXPECTATIONS Change in expected future prices, (producer) expectations “N” IS FOR NUMBER Change in the number of suppliers in the market Elements of nature and political disruptions NON-PRICE DETERMINANTS OF SUPPLY Changes in resource prices or input costs Elements of nature and political disruptions Change in Prices of other goods produced and offered for sale Changes in technology Changes in taxes and subsidies Change in Expected future prices (producer) expectations Change in the number of suppliers in the market Elements of nature and political disruptions QUICK TIP Any factor that increases the cost of production decreases supply Any factor that decreases the cost of production increases supply COSTS INCREASE; PROFITS DECREASE Government Natural regulations increase cost disasters increase cost Expectations about future prices increase cost (put in inventory) Increased Costs taxes increase cost of inputs increase COSTS DECREASE; PROFITS INCREASE Technological Number advances of firms increase Subsidies Future Taxes Cost price decrease decrease of inputs decrease