display
advertisement

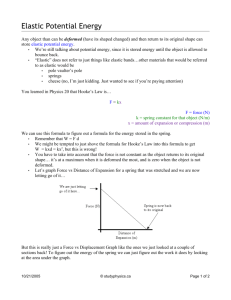
MECE 102: Engineering Mechanics Lab A First Year Course in Newtonian Mechanics, Experimentation, and Computer Tools Created by the Faculty of the Mechanical Engineering Department in the Kate Gleason College of Engineering at RIT Week 8 Lecture Hooke’s Law This week we will study the response of Linear Elastic Materials. • A spring with a hanging mass will be used in Lab to demonstrate the response of a Linear Elastic material. iCLICKER: The week 8 Lab Experiment studies Hooke’s Law for linear elastic materials. Which one of the following materials would NOT be considered a linear elastic material? • Select your Answer: A. B. C. D. E. Steel Aluminum Rubber Titanium None of the above. iCLICKER: The week 8 Lab Experiment studies Hooke’s Law for linear elastic materials. Which one of the following materials would NOT be considered a linear elastic material? • Select your Answer: A. B. C. D. E. Steel Aluminum Rubber Titanium None of the above. iCLICKER: Which phase of matter is Hooke’s Law valid for? • Select your Answer: A. B. C. D. Gas Liquid Solid Gas and Solid iCLICKER: Which phase of matter is Hooke’s Law valid for? • Select your Answer: A. B. C. D. Gas Liquid Solid Gas and Solid FORMULATE: State the Known Information • Given the mass, m, of a dead weight suspended from a linear elastic spring • Determine the spring constant, K, of the spring, and the change in energy stored within the spring as a result of the work done by mass, m, upon the spring as the spring, S, moves from its initial position, i , to its final position, f. FORMULATE: Identify the Desired Information iCLICKER: For our Week 8 experiment, which one of the following assumptions is TRUE? • Select your Answer: A. The initial velocity of the mass hanging on the spring is not zero. B. The mass of the spring being analyzed is negligible. C. Heat Transfer is significant between the spring and its surroundings. D. Elastic Spring Energy is negligible. iCLICKER: For our Week 8 experiment, which one of the following assumptions is TRUE?? • Select your Answer: A. The initial velocity of the mass hanging on the spring is not zero. B. The mass of the spring being analyzed is negligible. C. Heat Transfer is significant between the spring and its surroundings. D. Elastic Spring Energy is negligible. FORMULATE: Identify Assumptions FORMULATE: Identify Assumptions FORMULATE: Identify Assumptions What other Engineering relationship is commonly associated with Hooke’s Law? FORMULATE: Identify Assumptions What other Engineering relationship is commonly associated with Hooke’s Law? 𝑆𝑡𝑟𝑒𝑠𝑠 = 𝐸 𝑆𝑡𝑟𝑎𝑖𝑛 𝜎=𝐸𝜀 This relationship will be studied extensively in your Strength of Materials and Materials Science Courses. CHART: Schematic Diagram Note that the Neutral Condition of the spring, with no external mass applied, is an important position to consider when analyzing the system. Figure 8.1: Schematic Diagram of a mass suspended from a spring in tension. CHART: Schematic Diagram Figure 8.1: Schematic Diagram of a mass suspended from a spring in tension (zoomed-in). CHART: Schematic Diagram Figure 8.3: Schematic Diagram of a spring unloaded, loaded in tension, and loaded in compression. CHART: Free Body Diagram CHART: Data Table • Each row in the STATE TABLE corresponds to one unique position of the Spring. • This Lab Experiment will reinforce the importance of defining an appropriate elevation datum, z = 0, and displacement datum, d = 0. Hooke’s Law • Hooke’s Law states that Strain is directly related to Stress. • For this experiment we are investigating the response of a solid linear elastic material under either compression or tension. • In the case of a Spring, Hooke’s Law states that the restoring force exerted by the material is proportional to the magnitude of displacement, and the direction of the restoring force is in the opposite direction of the displacement. EXECUTE: Apply and Simplify the Governing Equations Applying Newton’s Laws when analyzing the FBD of the Spring-Mass system gives: Recall that the work done by the Mass upon the Spring from state i to state f is the integral of the fore along the displacement: EXECUTE: Apply and Simplify the Governing Equations Based on Hooke’s Law: When the spring achieves it final equilibrium state after the Mass is added, the spring deflected length will be z1: EXECUTE: Apply and Simplify the Governing Equations Recall that the work done on the Spring by the Mass from state i to state f is given by: EXECUTE: Apply and Simplify the Governing Equations Similarly, the work done by the Spring on the Mass from state i to state f is given by: EXECUTE: Apply and Simplify the Governing Equations EXECUTE: Apply and Simplify the Governing Equations The important equations used in the Week 8 Lab Experiment are summarized below: Example Problem A 200 gram mass is suspended from a spring causing it to stretch from 5 cm to 7 cm. What is the spring constant [N/m] of the spring? Example Problem A 200 gram mass is suspended from a spring causing it to stretch from 5 cm to 7 cm. What is the spring constant [N/m] of the spring? K = 98.1 N/m BONUS POINT Problem A spring has an unloaded length of 37 cm and a spring constant of 1500 N/m. What is the new length [cm] of the spring if a 75 N compressive load is applied to the spring? Example Problem A spring has an unloaded length of 37 cm and a spring constant of 1500 N/m. What is the new length [cm] of the spring if a 75 N compressive load is applied to the spring? The new length of the spring is 32 cm. Week 8 Lab Experiment Homework • Prior to LAB tomorrow • Read section 8.2 of the textbook • Watch LAB Videos • Complete the on-line LAB quiz in myCourses • Attempt to solve all assigned Homework problems in your logbook before RECITATION. • WEEK 8 Problem Set: • From Section 8.5: Problems 2, 3, 5, 6, 7 • Lab Report is due Monday by 6pm! • The Scribe must upload the LAB REPORT to the myCourses Dropbox. Questions?? Example Problem A spring has an unloaded length of 37 cm and a spring constant of 1500 N/m. What is the new length [cm] of the spring if a 300 N compressive load is applied to the spring? The new length of the spring is 17 cm.