Development of the Cell Theory
advertisement

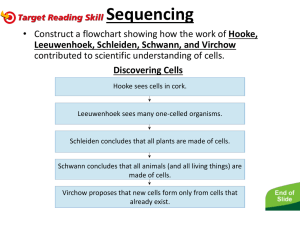
Development of the Cell Theory Big Question • Where do living things come from? 1600s. Ideas of the time • For centuries, people accepted the prevailing explanation for the sudden appearance of some organisms (flies, maggots, mice, bees) • Scholars of the day gave a name to their accepted theory: spontaneous generation 1590. Zacharias & Hans Janseen (DUTCH) • Credit for the first compound (more than one lens) microscope is usually given to Zacharias Jansen, of Middleburg, Holland, around the year 1595. • HUGE impact on development of the theory could see small stuffs 1655. Robert Hooke (ENGLISH) • Using a microscope, looks at a thin slice of cork. • Calls the spaces in the cork “Cells” first person to use the word to describe these microscopic structures 1688. Francesco Redi (ITALIAN) • Performed an experiment to see if rotting meat changed into flies; hypothesis of spontaneous generation was not supported. 1674. Anton van Leevwenhoek (DUTCH) • Developed his own microscope & looked at pond samples identified simple microorganisms (bacteria & protozoa) which he called “animacules” • Also looked at blood samples from plants and animals to see cells. 150-200 Year Gap??? • Between the Hooke/Leuwenhoek discoveries and the mid 19th century, very little cell advancements were made. • This is due to the widely accepted, traditional belief in Spontaneous Generation. 1838. Matthias Schleiden (GERMAN) • Looked at numerous plant samples under a microscope, concludes all plants are made of cells. • Has dinner with colleague and zoologist Theodor Schwann… 1839. Theodor Schwann (GERMAN) • After looking at numerous animal samples, concludes all animals are made of cells. • Publishes “Microscope Investigations on the Accordance in the Structure of Growth of Plants and Animals,” which stated first statement of the cell theory: – ALL LIVING THINGS ARE MADE OF CELLS 1855. Rudolph Virchow (GERMAN) • Extends work of Schleiden & Schwann by proposing that all living cells must rise from pre-exisiting cells. • RADICAL idea (spontaneous generation still widely accepted) 1858. CELL THEORY • The 3 Basic Components of the Cell Theory were now complete: 1. All organisms are composed of one or more cells. (Schleiden & Schwann)(1838-39) 2. The cell is the basic unit of life in all living things. (Schleiden & Schwann)(1838-39) 3. All cells are produced by the division of preexisting cells. (Virchow)(1858) • Cell Theory is accepted by scientific community, but skepticism exists due to belief in spontaneous generation Modern Cell Theory • Adds 4 more statements: 1. Cells contains hereditary information which is passed from cell to cell during cell division. (The first cell is the exception because it could not have come from a previously existing cell) 2. All cells are basically the same in chemical composition. 3. All energy flow (metabolism & biochemistry) of life occurs within cells. 4. Cell activity depends on the activities of sub-cellular structures within the cell(organelles, nucleus, plasma membrane) 1864. Louis Pasteur (FRENCH) • Set out to denounce the ideas of spontaneous generation; is successful How is the Cell Theory Used Today? • The basic discovered truths about cells, listed in the Cell Theory, are the basis for things such as: – Disease/Health/Medical Research and Cures(AIDS, Cancer, Vaccines, Cloning, Stem Cell Research, etc.) 1970. Lynn Marguilis (AMERICAN) • Proposes the idea that certain organelles (chloroplasts & mitochondria) were once free living cells themselves ENDOSYMBIOTIC THEORY is added