Vitamins, Minerals, and Water
advertisement

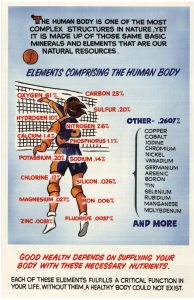
Vitamins, Minerals, and Water 1. 2. 3. Describe the function and food source of 7 vitamins. Describe the function and food source of 7 minerals. Identify the importance of drinking enough water evry day. Vitamins Vitamins: class of nutrients that contain carbon and are needed in small amounts to main tain health and allow growth. Fat Soluble Vitamins: A,D,E,and K…they dissolve in fat, most can be stored in fat tissue and remain in the body for a long time. Fat Soluble Vitamins • A … milk; yellow and orange fruits and vegetables; dark-green, leafy vegetables; eggs; cheese; butter • D…fish oils, fortified milk, liver, egg yolk, salmon, butter, tuna; produced in the body by exposure of skin to ultraviolet light (UV) in sunlight • E…vegetable oils, beans, peas, nuts, dark-green vegetables, whole grains • K…leafy vegetables such as spinach, kale, and broccoli; also produced in the intestine by bacteria Fat Soluble Vitamins • A…keeps eyes and skin healthy; needed for growth and for strong bones and teeth • D…promotes absorption of calcium and phosphorus in the intestine; needed for strong bones and teeth • E…protects cell membranes from damage by reactive oxygen (free radicals) • K…aids in blood clotting Water Soluble Vitamins All of the B vitamins and vitamin C are water soluble. Antioxidant is a substance that is able to protect body structures from a highly chemically reactive form of oxygen called a free radical. Free radicals are normal byproducts of metabolism. Water Soluble Vitamins • B1…most vegetables, pork, liver, peas, beans, enriched and whole grains and cereals, nuts, and seeds. • B2…milk; meat; eggs; whole grains; green, leafy vegetables; dried beans; enriched bread, cereal, pasta. • B3…meat, liver, fish, enriched and wholegrain breads and cereals, peas and beans, seeds • B5…whole grains, meat, liver, broccoli, eggs, nuts, peas, beans • B6…whole grains; liver; meat; fish; bananas; green, leafy vegetables; peas; beans • B12…meat, liver, dairy products, eggs • Folate…green vegetables, liver, whole and fortified grains, peas, beans, orange juice • Biotin…liver, yogurt, egg yolk, peas, beans, nuts • C…citrus fruits, melons, strawberries, green vegetables, peppers Water Soluble Vitamins • B1…needed to produce energy from carbohydrates; helps the nervous system to function properly • B2…needed to produce energy from carbohydrates; important for growth and healthy skin • B3…needed to produce energy from carbohydrate, fat, and protein; needed for the nervous system and healthy skin • B5…needed to produce energy from carbohydrate, fat, and protein • B6…needed for protein metabolism, the production of hemoglobin in red blood cells, and for the nervous system • B12…necessary for forming cells (including red blood cells) and for a healthy nervous system • Folate…needed for forming cells (including red blood cells); helps prevent birth defects • Biotin…necessary for metabolism • C…promotes healthy gums and teeth, the healing of wounds, and the absorption of iron; acts as an antioxidant to protect cells from damage Minerals Minerals: Chemical elements that are needed for certain processes, such as enzyme activity and bone formation. • • • • • • • Calcium…milk; dairy products; dark-green, leafy vegetables; tofu; legumes; shellfish; bony fish Iodine…iodized salt, seafood Iron…red meat, whole and enriched greens, dark green vegetables, peas, beans, eggs Potassium…meat; poultry; fish; bananas; oranges; dried fruits; potatoes; green, leafy vegetables; peas, beans Sodium…table salt, high-salt meats (ham), processed foods, dairy products, soy sauce Magnesium…milk; dairy products; green, leafy vegetables, peas, beans Phosphorus…cereals, meats, milk, poultry Minerals • Calcium…needed for development and maintenance of bones and teeth, transmission of nerve impulses, muscle contraction, blood clotting • Iodine…needed for production of thyroid hormones and normal cell function • Iron…necessary for production of hemoglobin • Potassium…needed for maintenance of fluid balance, transmission of nerve impulses, and muscle contraction • Sodium…needed for the regulation of water balance in cells and tissues and for transmission of nerve impulses • Magnessium…needed for bone growth, metabolism, and muscle contraction • Phosphorus…needed for bone formation and cell reproduction • Nutrient Deficiency: The state of not having enough of a nutrient to maintain good health. • Supplements are available for those who cannot meet their vitamin or mineral needs with foods. However, supplements are not normally recommended for healthy people who can meet their nutrient needs through their normal diet. Water • We can only live without water for a few days. • About 60% of the body is water. • Water is essential because it is necessary for almost every function that keeps us alive. • 64 oz. daily…our bodies loose water through excretion of urine and solid wastes, by evaporation through breathing, through the skin as we sweat. • Water cannot be stored so intake must balance with body loses. Why Water is Important • It transports nutrients and oxygen through the body and helps to get rid of wastes from the body. • It provides the proper environment for the body’s chemical reactions to occur. • It helps regulate body temperature. Dehydration This occurs when more water is lost than is taken in by drinking. Fevers, vomiting, and diarrhea all increase water loss. Exercising also makes your lose water…sweating. Exercising in hot weather can cause you to lose up to a quart of water in an hour. • Symptoms: thirst, headache, fatigue, loss of appetite, dry eyes and mouth, and dark colored urine. As dehydration becomes more severe it results in nausea, difficulty concentrating, confusion, and disorientation. If the dehydration is severe enough, death can occur.