Biological Limitations to Classical Conditioning
advertisement

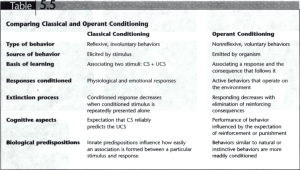
Biological Limitations to Classical Conditioning Remember Watson’s conditioning of Albert? Could he have just as easily conditioned that fear response to a flower or a piece of ribbon? Probably not • Humans and animals have certain biological predispositions that aide or hinder conditioning. • Humans have an adaptive fear of things like snakes or other threatening animals “Snakes. I hate snakes.” - Indiana Jones Conditioning principles don’t tell the whole story about learning. Biological Influences: • Unconditioned Responses • Genetic Predispositions • Adaptive Responses Psychological Influences: • Previous Experiences • Predictability of Associations • Generalization LEARNING Socio-cultural Influences: • Culturally learned preferences • Motivation, affected by the presence of others Biological Predispositions • Martin Seligman (1972): most common fears "are related to the survival of the human species through the long course of evolution“ • Taste Aversion • the intense dislike and/or avoidance of particular foods that have been associated with nausea or discomfort • biologically adaptive for survival Biological Predispositions • Garcia & Koelling • Exposed rats to 3-way conditioned stimulus: • bright light, clicking noise, flavored water • One group was exposed to US producing nausea and vomiting several hours after exposure. Biological Predispositions • Garcia & Koelling • Rats formed an association between nausea and flavored water ingested several hours earlier. • contradicted the principle that CS must be presented shortly before the US • Animals are biologically predisposed to make associations: taste & food in rats, sight & food in birds, etc. • Taste aversion works in humans Biological Predispositions • Scapegoat effect • People undergoing chemotherapy sometimes associate food they ate before treatment, or the place they receive treatment with nausea. • Bernstein (1982) came up with a novel-tasting, maple-flavored ice cream before chemo. • Patients less likely to associate nausea with healthy food or place. Biological Predispositions • What about Operant Conditioning? • Condition hamsters to dig or rear-up using food as a reinforcer • natural food-searching behavior • not as successful face washing or other non-food searching behaviors • Pigeons flap wings to avoid shock or peck to get food Biological Predispositions • Bottom line Biological constraints predispose organisms to learn associations that are naturally adaptive. Classical Conditioning in Everyday Life • Why can diet soda make people hungry? • The sweet taste of soda becomes a CS. • elicits insulin increase (UR) • leads to feelings of hunger • The pancreas pumps out insulin (lowers blood sugar) in response to any sweet taste such as diet soda. Vocabulary Assignment In preparation for the next modules, please (1) define the following terms and (2) use them in a contextual sentence. • • • • cognitive map latent learning insight intrinsic motivation ● ● ● ● extrinsic motivation learned helplessness external locus of control internal locus of control