The Food Pyramid
advertisement
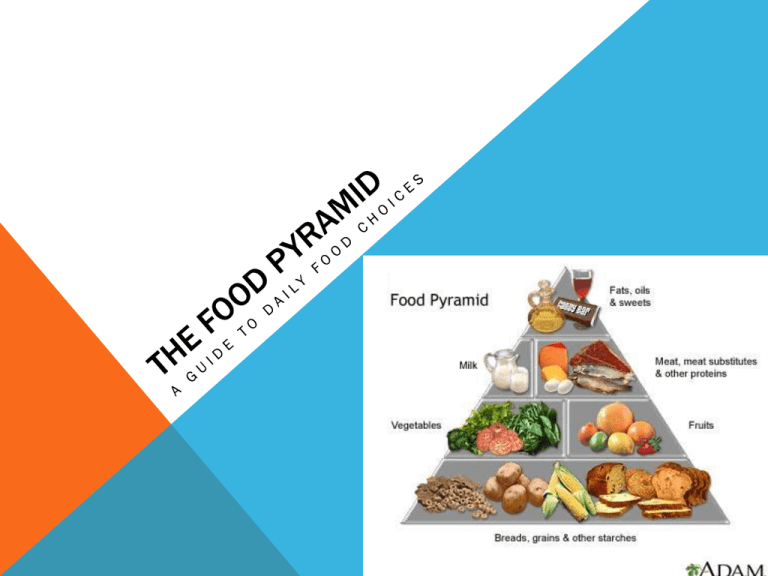
KEY TERMS Nutrients Whole grain Refined grains NUTRITION Nutrients are chemical substances in food that help maintain the body Some nutrients supply energy to the body Some nutrients provide the building blocks for the body’s cells and tissues, such as kin, bones, and muscles Some nutrients are necessary for the chemical reactions that take place in the body NUTRIENTS The food people eat has a major impact on their health The U.S. Department of Agriculture and the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services have developed guidelines for healthy eating HEALTHY DIETS For a healthy diet, a person must eat a variety of foods A healthy diet also includes all the nutrients a person needs to stay healthy To help people make wise choices, the Food Guide Pyramid was developed The Food Guide Pyramid is a diagram that organizes food into groups that have similar nutrients It then recommends how many servings one should eat from each group each day THE FOOD PYRAMID THE FOOD GUIDE PYRAMID IN WITH THE NEW: MY PLATE GRAINS 6 ounces each day Make half your grains whole Any food made from wheat, rice, oats, cornmeal, barley or another cereal grain is a grain product. Bread, pasta, oatmeal, breakfast cereals, tortillas, and grits are examples of grain products. Grains are divided into 2 subgroups: • whole grains • refined grains. GRAINS Whole grains contain the entire grain kernel ― the bran, germ, and endosperm. Examples include: • whole-wheat flour • bulgur (cracked wheat) • oatmeal • whole cornmeal • brown rice GRAINS Refined grains have been milled, a process that removes the bran and germ. This is done to give grains a finer texture and improve their shelf life, but it also removes dietary fiber, iron, and many B vitamins. Some examples of refined grain products are: • white flour • degermed cornmeal • white bread • white rice GRAINS Some commonly eaten grain products are: Whole grains: • whole grain cornmeal Refined grains: • brown rice • buckwheat • whole rye • bulgur (cracked wheat) • whole wheat bread • couscous whole wheat • crackers crackers • flour tortillas whole wheat pasta • grits whole wheat sandwich buns and • noodles rolls Pasta: • • oatmeal • popcorn • • Ready-to-eat breakfast cereals: • • whole wheat cereal • flakes • whole grain barley • whole wheat tortillas wild rice • cornbread • corn tortillas • spaghetti • macaroni • pitas • pretzels Ready-to-eat breakfast cereals: • corn flakes • white bread • white sandwich buns and rolls • white rice VEGETABLES 2 ½ cups per day Any vegetable or 100% vegetable juice counts as a member of the Vegetable Group. Vegetables may be: • Raw • Cooked • Fresh • Frozen • Canned • Dried/dehydrated • May be whole, cut-up, or mashed VEGETABLES Vegetables are organized into 5 subgroups, based on their nutrient content. Some commonly eaten vegetables in each subgroup are: Starchy vegetables Beans and peas Dark green vegetables Red & orange Other vegetables vegetables • broccoli • corn • black beans • artichokes • acorn squash • collard greens • black-eyed peas • black-eyed peas) • asparagus • butternut squash (not dry) • dark green leafy • kidney beans • brussel sprouts lettuce • carrots • green bananas • lentils • cabbage • mustard greens • pumpkin • green peas • navy beans • cauliflower • romaine lettuce • red peppers • green lima beans • pinto beans • celery • spinach • sweet potatoes • plantains • soy beans • cucumbers • turnip greens • tomatoes • potatoes • split peas • eggplant • tomato juice • white beans • green beans • green peppers • Iceberg lettuce • mushrooms • okra • onions • turnips FRUITS 1 ½ cups per day Any fruit or 100% fruit juice counts as part of the Fruit Group. Fruits may be: Fresh Canned Frozen Dried may be whole, cut-up, or pureed FRUITS Some commonly eaten fruits are: • Apples • Prunes Berries: • Apricots • Raisins • strawberries • orange • Bananas • Tangerines • blueberries • apple • Nectarines • Cherries • raspberries • grape • Oranges • Grapefruit Melons: • grapefruit • Peaches • Grapes • cantaloupe • Pears • Kiwi fruit • honeydew • Papaya • Lemons • watermelon • Pineapple • Limes Mixed fruits: • Plums • Mangoes • fruit cocktail 100% Fruit juice: MILK, YOGURT & CHEESE 3 cups per day All fluid milk products and many foods made from milk are considered part of this food group. Most Dairy Group choices should be fat-free or low-fat. Foods made from milk that retain their calcium content are part of the group. Foods made from milk that have little to no calcium, such as cream cheese, cream, and butter, are not. Calcium-fortified soymilk (soy beverage) is also part of the Dairy Group. MILK, YOGURT & CHEESE Choose fat-free or low-fat milk, yogurt, and cheese. If sweetened milk products are chosen (flavored milk, yogurt, drinkable yogurt, desserts), the added sugars also count against your maximum limit for "empty calories” For those who are lactose intolerant, smaller portions (such as 4 fluid ounces of milk) may be well tolerated. Calcium-fortified foods and beverages such as cereals, orange juice, or rice or almond beverages may provide calcium, but may not provide the other nutrients found in dairy products. MILK, YOGURT & CHEESE Some commonly eaten choices in the Dairy Group are: Milk Milk-based desserts Soft cheeses: all fluid milk: puddings ricotta fat-free (skim) ice milk cottage cheese low fat (1%) frozen yogurt Processed cheeses: reduced fat (2%) ice cream American whole milk Calcium-fortified soymilk Flavored milks: (soy beverage) Yogurt chocolate Cheese All yogurt: strawberry Hard natural cheeses: fat-free lactose-reduced milks cheddar low fat lactose-free milks mozzarella reduced fat Swiss whole milk yogurt Parmesan MEAT & BEANS 5 ounces per day All foods made from meat, poultry, seafood, beans and peas, eggs, processed soy products, nuts, and seeds are considered part of the Protein Foods Group. Beans and peas are also part of the Vegetable Group. Select a variety of protein foods to improve nutrient intake and health benefits, including at least 8 ounces of cooked seafood per week. Meat and poultry choices should be lean or low-fat. MEAT & BEANS Some commonly eaten choices in the Protein Foods Group, with selection tips, are: Meats Lean cuts of: • beef • ham • lamb • pork Game meats: • bison • rabbit • venison Lean ground meats: • beef • pork • lamb Lean luncheon or deli meats Organ meats: • liver • giblets Poultry • chicken • duck goose turkey ground chicken and turkey Eggs • chicken eggs • duck eggs Beans and peas • black beans • black-eyed peas • lima beans (mature) • navy beans • pinto beans Processed soy products: • tofu • white beans • bean burgers • veggie burgers • texturized vegetable • protein (TVP) Nuts and seeds • almonds • cashews • • • • mixed nuts • peanuts • peanut butter • pecans • pistachios • pumpkin seeds • sesame seeds • sunflower seeds • walnuts Seafood • Finfish such as: • catfish • flounder • halibut • mackerel • salmon • sea bass • snapper • swordfish • trout • tuna Shellfish such as: • clams • crab • lobster • mussels • octopus • oysters • scallops • squid (calamari) • shrimp Canned fish such as: • anchovies • clams • tuna • sardines FATS, OILS, & SWEETS Oils are fats that are liquid at room temperature, like the vegetable oils used in cooking. Oils come from many different plants and from fish. Oils are NOT a food group, but they provide essential nutrients. Therefore, oils are included in USDA food patterns. Some common oils are: • • • • • • • canola oil corn oil cottonseed oil olive oil safflower oil soybean oil sunflower oil FATS, OILS, & SWEETS Some oils are used mainly as flavorings, such as walnut oil and sesame oil. A number of foods are naturally high in oils, like: • nuts • olives • some fish • avocados Foods that are mainly oil include mayonnaise, certain salad dressings, and soft (tub or squeeze) margarine with no trans fats. FATS, OILS, & SWEETS A few plant oils, however, including coconut oil, palm oil, and palm kernel oil, are high in saturated fats and for nutritional purposes should be considered to be solid fats. Solid fats are fats that are solid at room temperature, like butter and shortening. Solid fats come from many animal foods and can be made from vegetable oils through a process called hydrogenation. Some common solid fats are: • butter • milk fat • beef fat (tallow, suet) • chicken fat • pork fat (lard) • stick margarine • shortening • partially hydrogenated oil DIETARY GUIDELINES FOR AMERICANS The Dietary Guidelines for Americans were then developed The guidelines suggest actions to promote health Choose Sensibly Build a Healthy Base • Aim for Fitness • • Aim for a healthy weight Be physically active each day • • • Let the Pyramid guide your food choices Choose a variety of grains daily, especially whole grains Choose a variety of fruits and vegetables daily Keep food safe to eat • • • Choose a diet that is low in saturated fat and cholesterol and moderate in total fat Choose beverages and foods to moderate your intake of sugars Choose and prepare foods with less salt EATING OUT People who eat in commercial restaurants have a wide choice of what to eat • You can eat one meal in a restaurant, and the rest of the meals at home • you can eat all your meals at restaurants • You can eat all your meals at home For this reason, restaurants are concerned with taste and appearance However, restaurants do try to provide offerings from each part of the Food Guide Pyramid EATING OUT: MCDONALD’S Fats, Oils, & Sweets Milk, Yogurt, & Cheese Vegetable Bread, Cereal, Rice & Pasta Meat, Poultry, Fish, Dry Beans, Eggs, & Nuts Fruit INSTITUTIONAL FOODSERVICES Institutional foodservices are much more concerned with nutrition In many cases, people who eat in institutional foodservices have no choice in where to eat For example: • People in hospitals • Soldiers in the armed services • People in prison facilities Therefore, institutional foodservices pay close attention to the nutritional content of each meal they serve



