Name __Lauren O'Donnell___ Date ___11/23/14____ Lesson Title
advertisement

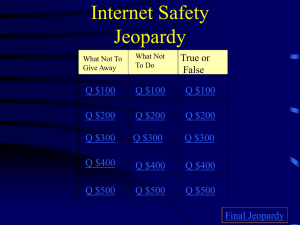
Name __Lauren O’Donnell___ Date ___11/23/14____ Lesson Title __3D Geometry- Volume of Solids____ Grade/Subject Area ____8th/Resource Setting Math (Special Education)_______ Brief Lesson Summary: Students will review the 3D Geometry unit on volume of 3D solids using the game Jeopardy. The types of assessment that will be used during this lesson is the feedback from the answers given during the Jeopardy game, an exit slip at the end of the game reflecting on the day’s lesson and/or questions students may still have about the 3D geometry unit, and teacher observation during the review game. While the students are working on solving the question’s problem, I will be rotating around to each team while they work and observe how well the students are understanding the content. Rationale: Ongoing, formative assessment of your students’ learning will likely indicate instances when you need to spend more time on a concept, skill or process; reteach in a new way; or extend/enrich learning to address the specific needs of your students (Heacox, 2009, p. 10). Established Goals (State / Common Core Standards): Common Core State Standards http://www.corestandards.org/Math/ Domain: Geometry Cluster: Solve real-world and mathematical problems involving volume of cylinders, cones, and spheres. Standard #: Standard: Know the formulas for the volumes of cones, cylinders, and spheres and use them to 8.G.9 solve real-world and mathematical problems. Stage 1—Desired Results (What understandings are desired?) Transfer Goals Students will be able to independently use their learning to……. find the volume of a 3D prism and cylinder measure the length, width, height, and/or bases of the solids to find the volume use the area formula to find the area of the triangular prism before calculating its volume Understandings: Students will understand that… Meaning Essential Questions What essential questions will be considered? volume is related to 3D solids that different shapes have different volumes and formulas for finding volume. What is a 3-dimensional figure? How can I find the volume of a 3-dimensional figure? How can the volume of a 3-dimensional figure help me solve real world problems? Acquisition of Knowledge and Skill Students will know…. Students will be able to … how to find the volume using formulas for 3D use the formulas to find the volumes of a shapes. prism and cylinder, and later on in the next lesson, pyramids, cones, and spheres. Stage Two – Assessment Evidence (Students will need to show their learning by….) Transfer Task (s): Students will show their learning by answering the Jeopardy questions correctly Rationale: Tasks should be engaging and appropriately leveled so work at the centers spurs student growth (Tomlinson & Imbeau, 2010, p. 164). *Reasoning behind game setup and content creation: This game offers my students to become engaged in a review for an upcoming mathematics unit test. I chose Jeopardy because many students are familiar with the game concept, but most of all because the game play works perfectly for the review of the unit. The five categories offer questions related to different 3D solids seen, discussed, and practiced in the unit. This game provides a fun yet educational way to review for a unit test. *Intended Outcome of Game: The intended outcome of the game is for the students to feel comfortable and be successful finding the volume of different 3D shapes using the proper formulas. As Osterweil, Groff, and Hass (2009) state, “games are active, challenging, and demanding of focus and concentration to solve problems in innovative ways” (as cited in Maloy, et. al., 2014, p. 171). Through this game, my students will be exposed to the type of problems that they may see on their final written assessment. This game also allows for team collaboration and cooperative learning with peers. Evaluative Criteria: Performance is judged in terms of…. Observations made during the Jeopardy review game Jeopardy question result on an individual level Performance is judged in terms of students answering the Jeopardy questions correctly Other Evidence (quizzes, tests, prompts, observations, dialogues, work samples, etc.) Dialogue between students on calculating the volume formulas Observation of students during the review game (performing the calculations correctly, using correct volume formula, arithmetic, etc.) After the Jeopardy review game, students will complete a final written assessment on 3D geometry Exit Slip Student Self-Assessment and Reflection Students will be able to self-assess by knowing whether they answered the Jeopardy questions correctly or not. After the Jeopardy game, students will have the opportunity to reflect on their progress and the day’s lesson by completing an Exit Slip on the day’s lesson and the material/content taught. Rationale: Assessment informs instruction; without it, purposeful differentiation is simply not possible (Heacox, 2009, p. 25). Stage 3—Learning Plan (Summary of Key Learning Events and Instruction) The teaching and learning needed to achieve the unit goals. Experience (Lesson Plan) 1: Focus Questions: How does finding the volume change based on the shape of the 3D solid? How does volume differ per 3D shape? Learning Target: During the Jeopardy review, game students will find the volume of a 3D solid using the proper formulas for each figure. Performance Indicator: All students will participate in the Jeopardy review game, and performance will be indicated based on correctly answered questions, showing proficient learning. An Exit Slip will be completed at the end of the review game demonstrating what the students have learned and/or questions they still may have based on the day’s lesson as formative assessment. During the review game, as well as being the host, I will be rotating from student to student observing the students on how they are finding the volume. Learning Activities: 1. Teacher will project the Prezi presentation that shows an overview of volume of 3D shapes, providing real life examples and solids. 2. Teacher will then explain to the students that they will be playing Jeopardy as a way to review the 3D Geometry unit on volume before they complete their final written assessment in two days. 3. Teacher will project the Haiku Deck presentation that explains the point of the game, as well as, the rules of the game and discuss these with the class. Teacher will also use this time to answer any questions that the students may have about the game. 4. Game Objective: To answer as many correct Jeopardy questions as possible to accumulate the most points at the end of the game to win. 5. Game Rules: 1. Teacher will be the host of the game. 2. Teacher will break the class into three teams of three students each (nine students total). 3. The host will announce the 5 categories. 4. Teacher will designate one person in each group to keep running score. 5. A chosen team will select the first category along with a point value. 6. After host reads the question, the team who arrives at the answer first will buzz in using the iPad. 7. If answer is correct, the team takes control of the board. 8. If answer is incorrect, that team loses their turn. 9. Then, another team can try to answer and take control of the board. 10. Each team will start with a score of zero. 11. Points will be added when a team gets an answer correct. 12. Points will be subtracted when a team gets an answer incorrect. 13. Team with the most points at the end of the game – WINS! 6. Teacher will divide the class up into three teams of three. Teacher will choose one player from each team to be the scorekeeper. 7. Each player will then receive an iPad, a reference sheet, a calculator, and a Smart Pal with a marker and eraser to perform their calculations on. 8. Once teams are in their designated areas, the teacher will then begin the game. 9. While hosting, teacher will monitor game play and observe student answers and performance. 10. At the end of the game, the teacher will have each team scorekeeper add up the points for the group and then report the score. 11. Teacher will then lead the students in a discussion reviewing some of the more frequently missed questions that the teacher noticed while observing. Students will also be able to ask any questions that they may have about the questions they came across during the game. 12. Students will wrap up the lesson by completing an Exit Slip reflecting on the areas that they did really well on during the game and the areas that they feel they need to study a little more on before the final assessment. Students are encouraged to ask any last questions they may have about the 3D Geometry unit on the Exit Slip as well. Resources and Materials NJASK Reference Sheet (providing volume formulas for 3D solids) Calculators SmartPals Markers Erasers Exit Slips iPads (one per student): to buzz in when student has an answer- http://www.ibuzzedfirst.com/ 3D Geometry Jeopardy Review game: http://www.superteachertools.com/jeopardyx/jeopardyreview-game.php?gamefile=1332171599 Haiku Deck: presentation of game, its main point, objective and rules that was created on my Haiku Deck account Prezi: a review presentation of 3D solids and volume, given real life exampleshttps://prezi.com/zj6zup84qxq8/volumes-of-3d-shapes/ Score sheet: used for the scorekeeper to record the points received and lost when answering a question correctly or incorrectly. This will also require students to use math skills and will be calculated at the end of the game to determine the team’s final score. References Heacox, D. (2009). Making differentiation a habit: How to ensure success in academically diverse classrooms. Minneapolis, MN: Free Spirit Publishing. Maloy, R. W., et. al. (2014). Transforming learning with new technologies (2nd ed.). Boston: Pearson. Tomlinson, C. A., & Imbeau, M. B. (2010). Leading and managing a differentiated classroom. Alexandria, VA: ASCD.