Nuclear Chemistry
advertisement
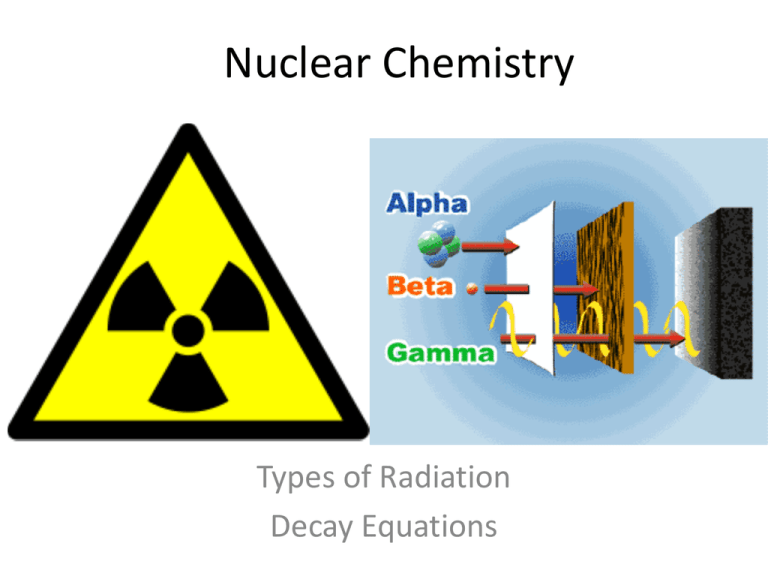
Nuclear Chemistry Types of Radiation Decay Equations What is radiation? • Energy traveling through medium with enough energy to ionize atoms • Ionize – cause to form an ion • occurs when an electron is stripped (or "knocked out") from an electron shell, which leaves the atom with a net positive charge What is radioactive decay? • Process where the nucleus of an unstable atom loses energy by emitting ionizing particles and emits radiation What is transmutation? • Process in which an atom, called the parent radionuclide, transforms into: – an atom with a nucleus in a different state – an atom with different nucleus containing different numbers of nucleons • Either of these products is named the daughter nuclide. • The decay process results in nuclear transmutation(creation of an atom of a new element) Synonyms and Symbols • Atom in nuclear chemistry is described as a nuclide – EX. Parent or daughter nuclide • Nucleus in nuclear chemistry is described as a nucleon = proton + neutron Types of Radiation ALPHA EMISSION • Radioactive decay process by which a particle with two neutrons + two protons is ejected from the nucleus of a radioactive atom. • The alpha particle is identical to the nucleus of a helium atom. Alpha Decay Equation ALPHA PROTECTION ALPHA ABSORBED BY PAPER + SKIN. BETA EMISSION • type of radioactive decay in which a beta particle (electron) is emitted from an atom as nucleus breaks apart BETA ABSORPTION BETA STOPPED BY METALLIC FOIL AND WOOD. BETA DECAY EQUATION BETA DECAY EQUATION GAMMA EMISSION • High energy ionizing radiation that is biologically hazardous • Produced from radioisotopes when electrons transition from excited to ground state GAMMA EMISSION VERY DANGEROUS VERY PENETRATING Radioactive Decay Equations Parent Material Daughter product Radiation Emission Decay Equations • Alpha Decay • Beta Decay • Gamma Decay • 240 Pu 236 U • +234 4ThHe 234 Pa + 0•e Occurs with others 94 92 90 91 2 -1 What is a Half-Life? • Time is takes for one half of a sample of radioactive material to decay over time • Rate of decay ~ every isotope has its’ own rate of decay • SOME ARE SLOW Ex. Uranium 4.5 billion years • SOME ARE FAST Ex. Radon 3.8 days Half-Life Example Problems • There are 3.29 g of iodine-126 remaining in a sample originally containing 26.3 g of iodine-126. The half-life of iodine-126 is 13 days. How old is the sample? 39 days old • If you started with 32 million radioactive atoms, how many would you have left after five half-lives? 1 million • The radioactive radon-222 has a half-life of 3.8 days. How much of an initial 20.0g sample of radon-222 would remain after 15.2 days? 1.25 g Fission vs. Fusion






