Digital Data - Brian Kiehl
advertisement

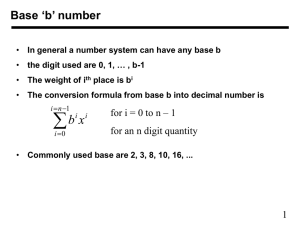
Method of representing or encoding numbers Two main notation types Sign-value Roman numerals Positional (place-value) Modern decimal notation Several number systems are commonly used in computing Decimal Binary Hexadecimal “Shorthand” for binary Digital Data 2 We count in “decimal” or base 10 by powers of 10: 100 = 1 101 = 10 102 = 10*10 = 100 103 = 10*10*10 = 1,000 106 = 1,000,000 Computers count in “binary” or base 2: 20 = 1 21 = 2 22 = 2*2 = 4 23 = 2*2*2 = 8 210 = 1,024 Digital Data 3 Bit (b): binary digit -- 0 or 1 value 0 or 1 correspond to the electrical values of off or on, respectively All computer data is represented in bits Byte (B): grouping of 8 bits Considered the basic unit of digital information 8 bits = 1 byte is the de facto standard (also called an octet) File sizes and network data are measured in bytes You can’t have a 5-bit file Physical network media transmit bits, but network protocols are based on bytes Unit multiples Kilobyte: 210 = 1,024 bytes (≈ 1,000) Megabyte: 220 = 1,048,576 bytes (≈ 1,000,000) Gigabyte: 230 = 1,073,741,824 bytes (≈ 1,000,000,000) Terabyte: 240 = 1,099,511,627,776 bytes (≈ 1,000,000,000,000) Digital Data 4 Base (also called radix) Number around which system is organized Number of symbols used to Number System Decimal Binary Hexadecimal Base 10 2 16 Digits 0,1,…, 9 0, 1 0, 1,…, 9, A – F represent each digit of a number Digits Set of symbols used in forming numbers Additional symbols may be defined for bases > 10 Ex: hexadecimal (see chart at right) Positional Notation Digit Position Position of a digit conveys its significance Rightmost digit represents the zero- power of the base value Moving left, each digit represents an increasing power of the base number Digital Data Number System Decimal Binary Hexadecimal 4 3 2 1 0 104 10,000 24 16 164 65,536 103 1,000 23 8 163 4,096 102 100 22 4 162 256 101 10 21 2 161 16 100 1 20 1 160 1 5 Decimal Digit Position (k) Weight (bk) Decimal Weight Digit (ak) Decimal Value 2 102 100 0 0 1 101 10 0 0 0 100 1 2 2 = 2,002 Binary Digit Position (k) Weight (bk) Decimal Weight Digit (ak) Decimal Value 3 103 1,000 2 2,000 10 210 1,024 1 1,024 9 29 512 1 512 8 28 256 1 256 7 27 128 1 128 6 26 64 1 64 5 25 32 0 0 4 24 16 1 16 3 23 8 0 0 2 22 4 0 0 1 21 2 1 2 0 20 1 0 0 = 2,002 Hexadecimal Digit Position (k) Weight (bk) Decimal Weight Digit (ak) Decimal Value 2 162 256 7 1,792 1 161 16 D 208 Digital Data 0 160 1 2 2 = 2,002 6 Hexadecimal used as shorthand notation for binary One hex digit represents four binary digits Hexadecimal numbers are usually prefixed with “0x” Tells someone reading the number it is a hex value 7D216 → 0x7D2 Digital Data 7 Decimal Binary Hex Decimal Binary Hex 0 0000 0 8 1000 8 1 0001 1 9 1001 9 2 0010 2 10 1010 A 3 0011 3 11 1011 B 4 0100 4 12 1100 C 5 0101 5 13 1101 D 6 0110 6 14 1110 E 7 0111 7 15 1111 F Digital Data 8 Convert the decimal value 150 to binary What decimal value does the bit pattern 110100100 Convert the binary pattern 1 0 0 1 0 1 1 1 0 0 0 1 To hex Digital Data 10 Convert 2,016 to hexadecimal (base 16) remainder 1 7 / 16 = 0 3/2= 1 remainder 1 126 / 16 = 7 7/2= 3 remainder 1 2,016 / 16 = 126 15 / 2 = 7 remainder 1 31/ 2 = 15 remainder 1 63 / 2 = 31 remainder 1 126 / 2 = 63 remainder 0 252 / 2 = 126 remainder 0 504 / 2 = 252 remainder 0 1,008 / 2 = 504 remainder 0 2,016 / 2 = 1,008 remainder 0 Binary Digits Left to Right 1/2= 0 201610 = 111111000002 remainder 7 remainder E (14) Remainder 0 200210 = 7E016 11 Digital Data Hex Digits Left to Right Convert 2,016 to binary (base 2) American Standard Code for Information Interchange (ASCII) Character-encoding scheme based on the ordering of the English alphabet Maps digital bit pattern and character symbol Includes Printable characters Alphabet, numbers, symbols Graphics characters ■┌┐╔╗ Control characters Backspace, tab, line feed, carriage return Many of these characters are non-printable Digital Data 12 Digital Data 13 Strings are a sequence of bytes Bytes represent ASCII characters Characters can be represented as Character value: ‘m’ Decimal value: 109 Hexadecimal value: 0x6d Try entering these URLs in a browser http://%67%6f%6f%67%6c%65%2e%63%6f%6d http://%66%61%63%65%62%6f%6f%6b%2e%63%6f%6d ‘%’ tells the program what follows is a hex value Digital Data 14 A file is a collection of binary data Format determines the interpretation of bit patterns Specifies the type of data a file contains Text, image, sound, Word, Excel, etc. Example 01010101 01010011 01000001 USA (ASCII text file) (24-bit bitmap) Digital Data 15 Executable programs are just files Sequence of bytes Computers interpret the byte sequence as instructions Executable file formats Windows – Portable Executable (PE) format .exe, .dll (libraries), .sys (device drivers) UNIX – Executable and Linkable Format (ELF) Also used by UNIX variants Linux, BSD, Solaris Mac OS X – Mach object file (Mach-O) Earlier Mac OSs use Preferred Executable Format (PEF) Digital Data 16 Convention for naming files <filename>.<extension> Extension is usually three letters .txt (text), .jpg (JPEG image), .mp3 (MP3 audio), .doc (Word), .xls (Excel) Can be more or less .c (C source code), .gz (GNU zip), .docx (Word), .xlsx (Excel) Extension DOES NOT determine bit interpretation Operating systems and applications make decisions based on file extension Determined by file format .doc *ought* to be a Word document…I should use Microsoft Word to open it Extensions can be changed without changing the file format Example: change .zip to .txt to email a ZIP file Can still open the “.txt” file with a program that recognizes the ZIP file format Digital Data 17 What string is represented by the ASCII values : 85 83 78 65 What exactly is displayed when we open the file yay.txt in notepad which consists of the following bytes: 1010101 1010011 1001101 1000011 What exactly would be displayed in Frhed when we open yay.txt? Digital Data 18 Number Systems Decoded http://www.globalknowledge.ca/articles/whitepaper detail.asp?wpid=315 RFC 20: ASCII format for Network Interchange http://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc20 File Signatures Table http://www.garykessler.net/library/file_sigs.html Comparison of Executable File Formats http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Comparison_of_execut able_file_formats Digital Data 19