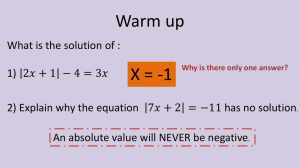Solving Systems of Linear Equations
advertisement

Introduction The solution to a system of equations is the point or points that make both equations true. Systems of equations can have one solution, no solutions, or an infinite number of solutions. On a graph, the solution to a system of equations can be easily seen. The solution to the system is the point of intersection, the point at which two lines cross or meet. 1 2.2.2: Solving Systems of Linear Equations Key Concepts • There are various methods to solving a system of equations. One is the graphing method. 2 2.2.2: Solving Systems of Linear Equations Key Concepts, continued Solving Systems of Equations by Graphing • Graphing a system of equations on the same coordinate plane allows you to visualize the solution to the system. • Use a table of values, the slope-intercept form of the equations (y = mx + b), or a graphing calculator. • Creating a table of values can be time consuming depending on the equations, but will work for all equations. 3 2.2.2: Solving Systems of Linear Equations Key Concepts, continued • Equations not written in slope-intercept form will need to be rewritten in order to determine the slope and y-intercept. • Once graphed, you can determine the number of solutions the system has. • Graphs of systems with one solution have two intersecting lines. The point of intersection is the solution to the system. These systems are considered consistent, or having at least one solution, and are also independent, meaning there is exactly one solution. 4 2.2.2: Solving Systems of Linear Equations Key Concepts, continued • Graphs of systems with no solution have parallel lines. There are no points that satisfy both of the equations. These systems are referred to as inconsistent. • Systems with an infinite number of solutions are equations of the same line—the lines for the equations in the system overlap. These are referred to as dependent and also consistent, having at least one solution. 5 2.2.2: Solving Systems of Linear Equations Key Concepts, continued Intersecting Lines Parallel Lines Same Line One solution No solutions Infinitely many solutions Consistent Independent Inconsistent Consistent Dependent 6 2.2.2: Solving Systems of Linear Equations Key Concepts, continued • Graphing the system of equations can sometimes be inaccurate, but solving the system algebraically will always give an exact answer. 7 2.2.2: Solving Systems of Linear Equations Key Concepts, continued Graphing Equations Using a TI-83/84: Step 1: Press [Y=] and key in the equation using [X, T, Θ, n] for x. Step 2: Press [ENTER] and key in the second equation. Step 3: Press [WINDOW] to change the viewing window, if necessary. Step 4: Enter in appropriate values for Xmin, Xmax, Xscl, Ymin, Ymax, and Yscl, using the arrow keys to navigate. Step 5: Press [GRAPH]. 2.2.2: Solving Systems of Linear Equations 8 Key Concepts, continued Step 6: Press [2ND] and [TRACE] to access the Calculate Menu. Step 7: Choose 5: intersect. Step 8: Press [ENTER] 3 times for the point of intersection. 9 2.2.2: Solving Systems of Linear Equations Key Concepts, continued Graphing Equations Using a TI-Nspire: Step 1: Press the home key. Step 2: Arrow over to the graphing icon (the picture of the parabola or the U-shaped curve) and press [enter]. Step 3: At the blinking cursor at the bottom of the screen, enter in the equation and press [enter]. Step 4: To change the viewing window: press [menu], arrow down to number 4: Window/Zoom, and click the center button of the navigation pad. 10 2.2.2: Solving Systems of Linear Equations Key Concepts, continued Step 5: Choose 1: Window settings by pressing the center button. Step 6: Enter in the appropriate XMin, XMax, YMin, and YMax fields. Step 7: Leave the XScale and YScale set to auto. Step 8: Use [tab] to navigate among the fields. Step 9: Press [tab] to “OK” when done and press [enter]. Step 10: Press [tab] to enter the second equation, then press [enter]. 11 2.2.2: Solving Systems of Linear Equations Key Concepts, continued Step 11: Enter the second equation and press [enter]. Step 12: Press [menu] and choose 6: Analyze Graph. Step 13: Choose 4: Intersection. Step 14: Select the lower bound. Step 15: Select the upper bound. 12 2.2.2: Solving Systems of Linear Equations Common Errors/Misconceptions • incorrectly graphing each equation • misidentifying the point of intersection 13 2.2.2: Solving Systems of Linear Equations Guided Practice Example 1 Graph the system of equations. Then determine whether the system has one solution, no solution, or infinitely many solutions. If the system has a solution, name it. ì4x - 6y = 12 í î y = -x + 3 14 2.2.2: Solving Systems of Linear Equations Guided Practice: Example 1, continued 1. Solve each equation for y. The first equation needs to be solved for y. 4x – 6y = 12 Original equation –6y = 12 – 4x 2 y = -2 + x 3 2 y = x-2 3 Subtract 4x from both sides. Divide both sides by –6. Write the equation in slopeintercept form (y = mx + b). The second equation (y = –x + 3) is already in slopeintercept form. 2.2.2: Solving Systems of Linear Equations 15 Guided Practice: Example 1, continued 2. Graph both equations using the slopeintercept method. The y-intercept of y = 2 3 x - 2 is –2. The slope is 2 3 . The y-intercept of y = –x + 3 is 3. The slope is –1. 16 2.2.2: Solving Systems of Linear Equations Guided Practice: Example 1, continued 17 2.2.2: Solving Systems of Linear Equations Guided Practice: Example 1, continued 3. Observe the graph. The lines intersect at the point (3, 0). This appears to be the solution to this system of equations. To check, substitute (3, 0) into both original equations. The result should be a true statement. 18 2.2.2: Solving Systems of Linear Equations Guided Practice: Example 1, continued 4x – 6y = 12 First equation in the system 4(3) – 6(0) = 12 Substitute (3, 0) for x and y. 12 – 0 = 12 Simplify. 12 = 12 This is a true statement. 19 2.2.2: Solving Systems of Linear Equations Guided Practice: Example 1, continued y = –x + 3 Second equation in the system (0) = –(3) + 3 Substitute (3, 0) for x and y. 0 = –3 + 3 Simplify. 0=0 This is a true statement. 20 2.2.2: Solving Systems of Linear Equations Guided Practice: Example 1, continued ì4x - 6y = 12 4. The system í has one î y = -x + 3 solution, (3, 0). ✔ 21 2.2.2: Solving Systems of Linear Equations Guided Practice: Example 1, continued 22 2.2.2: Solving Systems of Linear Equations Guided Practice Example 3 Graph the system of equations. Then determine whether the system has one solution, no solution, or infinitely many solutions. If the system has a solution, name it. ì-6x + 2y = 8 í î y = 3x - 5 23 2.2.2: Solving Systems of Linear Equations Guided Practice: Example 3, continued 1. Solve each equation for y. The first equation needs to be solved for y. –6x + 2y = 8 Original equation 2y = 8 + 6x Add 6x to both sides. y = 4 + 3x Divide both sides by 2. y = 3x + 4 Write the equation in slopeintercept form (y = mx + b). The second equation (y = 3x – 5) is already in slopeintercept form. 2.2.2: Solving Systems of Linear Equations 24 Guided Practice: Example 3, continued 2. Graph both equations using the slopeintercept method. The y-intercept of y = 3x + 4 is 4. The slope is 3. The y-intercept of y = 3x – 5 is –5. The slope is 3. 25 2.2.2: Solving Systems of Linear Equations Guided Practice: Example 3, continued 26 2.2.2: Solving Systems of Linear Equations Guided Practice: Example 3, continued 3. Observe the graph. The graphs of –6x + 2y = 8 and y = 3x – 5 are parallel lines and never cross. There are no values for x and y that will make both equations true. 27 2.2.2: Solving Systems of Linear Equations Guided Practice: Example 3, continued ì-6x + 2y = 8 4. The systemí has no solutions. î y = 3x - 5 ✔ 28 2.2.2: Solving Systems of Linear Equations Guided Practice: Example 3, continued 29 2.2.2: Solving Systems of Linear Equations