Reproduction

Reproduction
All organisms have the desire to pass on their genes to offspring and to do so, know that their offspring need to be successful. Hence the competition in nature which will usually result in only the strongest of the males reproducing. Humans are one of the few species that do not follow the rule of nature when it comes to reproduction because we often allow feelings to come into play.
Asexual vs. Sexual
A great resource: http://www.biotopics.co.uk/genes1/asexual_and_sexual_reproduction.html
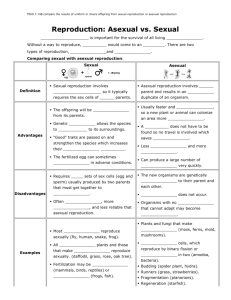
Asexual Sexual
Number of parents
Make up of offspring
Cell division
Advantages
Disadvantages
1
Genetically identical
2 (male and female)
Genetic variation of parents
Mitosis, normal cell division Meiosis to make gametes,
Followed normal cell division
Quick, builds numbers
Disease may affect all
Variation, evolution
Slower, requires gametes to
Fertilize, protection needed for the zygote and embryo
The Keys:
Asexual – new individuals from one parent, no gametes are needed, increase in numbers quick
Sexual – gametes are needed to join, one from each parent, increase in genetic variation
Please note: Some organisms have the ability to do both. A potatoe can have buds (the eyes), or a sea star can regenerate body parts from an arm.
External vs. Internal Fertilization
External – egg cells are laid, male moves over and fertilizes. Frogs and fish have females that lay their eggs in the water, the male swims over and fertilizes, the sperm needs the water to swim to the egg
Internal – Sperm put into the body, egg is fertilized inside the body. Does not mean that embryo develops within the body, but fertilization takes place inside.
1.
Oviparous – Lay egg outside of the body a.
Reptiles and Class Aves (birds) and some mammals use what is called an Amniotic Egg. b.
Allows for reproduction and development of the egg away from water
c.
Much larger, self contained with a leathery, calcified shell d.
There are four membranes used for nourishment and protection: i.
Amnion – fluid filled sac which cushions and protects the embryo. It also allows for exchanged of CO2 and O2 through the shell ii.
Yolk Sac – contains stored food iii.
Allantois – Holds wastes produced by embryo iv.
Chorion – lines inside of cell and encloses the other three membranes http://biology-pictures.blogspot.ca/2011/11/amniotic-egg-diagram.html
2.
Ovoviviparous – live off of yolk supply, but develops in a pouch on the mother’s back, some snakes develop this way.
3.
Viviparous – Development within the womb a.
Placenta – developed to help exchange materials between mother and young b.
Present only during pregnancy from both maternal and fetal tissues c.
Born after a period of time, can be single or multiple
Human Development:
To begin a discussion on human development, you must first understand the female organs and the process of menstruation. Please look at the following link: http://www.femalehealthmadesimple.com/female_organs.html
If pregnancy occurs, human development in the womb: www.webmd.com/baby/ss/slideshow-fetaldevelopment
How does the birth control pill work? http://kidshealth.org/teen/sexual_health/contraception/contraception_birth.html
Please answer the following questions:
1.
What is invitro fertilization?
2.
What are some fertility drugs and why are they used?
3.
What is meant by amniocentesis?
4.
What is meant by genetic screening?
5.
Is there a link between diet and health of the mother and the fetus?