Cells - Body Systems
advertisement

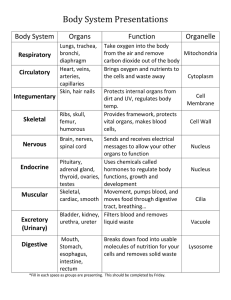
OBJECTIVE: identify cells as the basic unit of life describe how cells form tissues, organs and body systems CELLS ◦100 trillion cells in the human body ◦over 200 different types of cells ◦skin, muscle, brain, blood, bone, ……… WHAT DO CELLS NEED TO GROW? Food for high energy and good growing power Cells need energy to grow, move, talk, think and play Eat lots of fresh fruit and vegetables milk whole grains, cereal, pasta meat …protein not too much junk food Food is digested … it is broken down into molecules tiny enough for the blood to deliver it to the body’s cells Water Oxygen for survival … it helps turn food into energy Where do cells get oxygen? we breathe in air, it goes into the lungs, then enters the bloodstream then the heart pumps moving the oxygen to the cells The average person breathes about 2,500 gallons of air each day Do all cells in your body live as long as you do? No – some cells only live for a short period of time but when they die new cells take there place … example skin cells … live a few days – Other cells, like brain cells, live as long as you do … once they are destroyed they are not replaced – Our body’s grow when more cells are produced than actually die Cells tiny compartments of life that make up all living things • the building blocks of life • cells work together to help your body function well • cells come in different shape and sizes • each cell does a special job … they make up – your skin cells, muscles, bones, your brain, and are in your blood Parts of cells 1) nucleolus (2) nucleus (3) ribosome (4) vesicle (5) rough endoplasmic reticulum (ER) (6) Golgi apparatus (7) Cytoskeleton (8) smooth endoplasmic reticulum (9) mitochondria (10) vacuole (11) cytoplasm (12) lysosome (13) centrioles within centrosome Parts of cells • Most cells have the same 3 basic parts: – cell membrane – cell nucleus – cytoplasm OBJECTIVE: describe how cells form tissues, organs and body systems explain how body systems are interrelated identify ways to keep your body systems healthy Body Systems – groups of similar cells that do the same kind of work tissues – a structure that is made up of different types of tissues that do a particular job organ – formed by a group of organs that perform a related task systems Body Systems a group of organs that work together to support an important body function ??????? EXAMPLES ?????? examples: Nervous System Circulatory System Skeletal System Muscular System Digestive System Excretory System Respiratory System they work together to keep you alive and safe the systems of the body are organized by what they do, not where they are example - mouth and small intestine - digestive system interrelated – the systems work together and are dependent on one another to keep the body functioning properly The Body Systems and Their Function Supports the body, protects organs & helps you move Moves body parts and controls organs Skeletal System Muscular System Circulatory System Transports materials, (food, oxygen, hormones), to cells and removes waste from cells …. Carried in blood Digestive System Breaks down food into substances that your cells can use. Excretory System Removes waste and controls the body’s water levels Respiratory System Supplies blood with oxygen and removes carbon dioxide Nervous System Sends and receives messages to control all body systems Ways To Keep Your Body Systems Healthy Eat a balanced diet drink plenty of water exercise … be active stay away from drugs and alcohol don’t smoke … stay away from second hand smoke manage your stress exercise safely … warm-up, stretch, cool down get enough rest Follow common sense safety rules wear protective equipment when required wear a helmet wear seat belts