2. Explain the difference between a plant cell and an animal cell?
advertisement

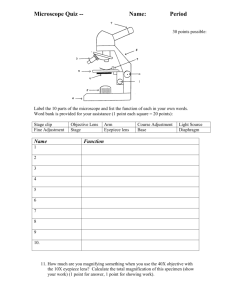
BELLRINGERS 1. What are the 3 main parts of a typical cell and what are their functions? 2. Explain the difference between a plant cell and an animal cell? (4 differences) 3. Compare and contrast plant cells and animal cells. 4. Define the following: levels of organization, cell, tissue, organ, organ system, organism. 5. List and give examples of each of the 5 levels of organization. 1.Take out one sheet of notebook paper. 2.At the top of the page, put your name and “Levels of Organization Pretest”. 3.Number the paper 1 – 10. 4.The pretest is under the basket on your desk. 5.You have 5 minutes. 6.Place the Pretest back under the basket when finished. How to Use a Microscope 1. Turn the revolving nosepiece to the scanner lens. 2. Using the course adjustment knob, lower the body tube to its lowest point. 3. Place the slide on the stage & secure it with the clip. 4. Look through the eyepiece and turn the course adjustment knob backwards slowly so that the lens is moving UP. Object should come into focus. How to Use a Microscope 5. Take your eye away from the eyepiece & turn the nosepiece to the low power objective lens. 6. Look through the eyepiece & turn the fine adjustment knob slowly. The object should come into sharper focus. 7. Take your eye away from the eyepiece & turn the nosepiece to the high power objective lens. How to Use a Microscope 8. Look through the eyepiece & turn the fine adjustment knob slowly. The object should come into sharper focus. 9. When observations are complete, turn the nosepiece to the scanner power lens. 10. Remove the slide from the stage. Turn the course adjustment knob to lower the nosepiece to its lowest level. Calculating Magnification 1. Find the power of the lens. It is found on the side of the lens. Magnification power of a lens is always identified by the label of x (10x, 1000x) 2. Multiply the power of the eyepiece by the power of the objective lens. 3. Examples: eyepiece obj. lens 10x times 100x 10x times 50x 10x times 40x BELLRINGERS 1. What are the 3 main parts of a typical cell and what are their functions? 2. Explain the difference between a plant cell and an animal cell? (4 differences) 3. Compare and contrast plant cells and animal cells. 4. Define the following: levels of organization, cell, tissue, organ, organ system, organism. 5. List and give examples of each of the 5 levels of organization. CELLS • All cells (both plants & animals) have similar structures – Cell membrane • thin membrane that has tiny holes • controls what comes in or goes out of the cell • outer boundary of the cell (unless it has a cell wall) Cell membrane CELLS – Nucleus • control center of cell • Holds chromosomes that contain DNA – Cytoplasm • Jelly like substance • Helps support the organelles Vacuole • Helps give cell shape cytoplasm Nucleus CELLS ALSO HAVE: – Mitochondria mitochondria • Power house of cell • Breaks down food for energy • stores & releases energy – Ribosomes • Small round structures • Produce proteins ribosomes – Golgi bodies • Group of sacs & tubes Golgi bodies • Transports materials throughout cell • Releases materials to outside the cell CELLS – Endoplasmic reticulum • Maze of passage ways • Carries materials from one part of cell to another part of cell Endoplasmic reticulum CELLS • Plant & animal cells have structures that are alike & structures that are different – Plant cells • Cell wall – Stiff outer boundary outside the cell membrane – Made of cellulose – Gives support and structure to the cell •Shape •-most plant cells have a rectangular shape. This gives strength to the entire plant. CELLS • Chloroplast – Large green structures that have chlorophyll that allows the plant to trap energy from sunlight to produce food for the cell • Larger vacuole – Stores food & wastes – Stores extra water – Makes cell wall stiff therefore helps hold up the plant. Making a Wet Mount Slide 1. Use dropper to place a drop of water on the center of a clean slide. 2. Use tweezers to lay specimen on the drop of water. 3. Gently touch the cover slip to the edge of the drop of water to cover the specimen & the water. ELODEA LEAF High Power Medium Power http://botit.botany.wisc.edu/course s/Botany_130/Eukaryotic_Cell/mo vies/Cyclosis.html High Power CHEEK CELL Medium Power Low Power High Power AIR BUBBLE If it has a dark black rim, IT IS NOT A CELL