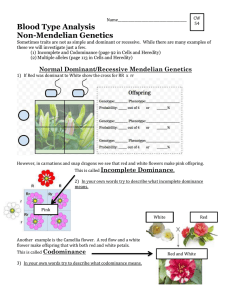
Types of Inheritances
advertisement

Warm up • Complete the punnet square for a Tall pea plant. T= tall t=short. – The parents are Tt x tt – What are the genotypes and phenotypes? – What are the genotype and phenotype ratios? Types of Inheritances Pp 237, 242-245 Types of Inheritance • • • • • • Complete Dominance Incomplete Dominance Codominance Sex-linked Polygenic Epistasis You will be responsible to complete punnett squares for the types bolded Complete Dominance • • • • One allele is completely dominant over the other Only two phenotypes exist One phenotype is masked The heterozygous phenotype shows dominant trait – – – – Ex: Tall peas are dominant to short peas TT= tall Tt= tall tt=short Complete Dominance Autosomal Genetic Disorders. Carrier: A heterozygote for a recessive disorder (ex/ Cc). • Carrier does not show symptoms but can pass recessive allele to offspring • Affected person must inherit two recessive alleles • Example Cystic Fibrosis, Tay-sachs, sickle-cell anemia • CC &Cc = unaffected • cc = affected Incomplete Dominance • Neither allele is completely dominant over the other Incomplete Dominance • Neither allele is completely dominant over the other • Three phenotypes exist • The heterozygous phenotype shows blended trait Incomplete Dominance • Neither allele is completely dominant over the other • Three phenotypes exist • The heterozygous phenotype shows blended trait • Ex: Flowers can be pink, red, or white. – RR=red – rr= white – Rr=pink Incomplete Dominance • Cross two pink flowers – Draw Punnet Square • What percent of their offspring will have white flowers? Incomplete Dominance • Cross two pink flowers • What percent of their offspring will have white flowers? • Fish can be green (GG), blue (BB), or teal (GB) Green (GG) Teal (GB) Blue (BB) Codominance • • • • Both alleles are dominant Three phenotypes exist Neither phenotype is masked The heterozygous phenotype shows both traits at once Codominance • • • • Both alleles are dominant Three phenotypes exist Neither phentoype is masked The heterozygous phenotype shows both traits at once. X red (RR) = white (WW) Codominance • • • • Both alleles are dominant Three phenotypes exist Neither phentoype is masked The heterozygous phenotype shows both traits at once. (Not a blend) X red (RR) = white (WW) red & white(WR) Codominance EX: In Smileys, eye shape can be starred, circular, or a circle with a star. Write ALL the phenotypes and genotypes that exist. Codominance EX: In Smileys, eye shape can be starred, circular, or a circle with a star. Write ALL the phenotypes and genotypes that exist. • CC = circle SS = star SC = circle-star Homework • Incomplete Dominance WS – 3 pages – Must be colored for credit. Single gene traits • controlled by only one gene - complete, incomplete, and codominant EX. Huntington Disease (D/d), Sickle Cell Anemia (N/S) , Cystic Fibrosis (R/r) Polygenic traits • controlled by additive effects of two or more genes EX. Skin color (controlled by 3-6 genes), eye color - each gene is responsible for adding pigment Multiple allele trait • controlled by more than two alleles in one gene • Still only inherit one copy from each parent for a total of two alleles but have a few to combine EX. Blood type: IAIA, IAi , IBIB , IBi , IAIB, ii Blood Typing Trait controlled by multiple alleles, with two that are codominant and one “null” Dominant Allele: I 2 Dominant Alleles: A: IA B:IB Recessive Allele: i 1 Recessive Allele: O= i • Trait controlled by multiple alleles, with two that are codominant and one “null” • Someone with AB blood can receive blood from A, B, AB, and O because it doesn’t have antibodies to clump cells. However it can only be giving to AB because all other blood types have antibodies that can cause clumping with the AB cell. • Use serums that contain these antibodies to test blood type Sex linked traits • Gender determined by XX or XY • Disorder/trait found on the “X” chromosome • seen more in men than women EX. (color blindness and hemophilia) • “Y” has to come from father • “XR or Xr” vs just “R or r” XR Y • Possible genotypes and phenotypes: XR XR = normal vision XR Xr = normal vision XR Xr Xr Xr = color blind XR Y = normal vision XRY XrY Xr Y = color blind XRXR XRXr Sex-influenced trait • Usually autosomal • Specific hormones influence trait/genotype EX. Baldness: testosterone influences BB Rh factor • people who are Rh+ have Rh antigens the red blood cell's surface • A person with Rh- blood has Rh antibodies in the blood plasma that react with the Rh+ blood antigens Testing Blood Type • Use anti-A serum and anti-B serum • If you use anti-A serum and it clumps then it has A antigens (proteins), if you use anti-B serum and it clumps then it has B antigens • No clumping = no antigens What blood type would this be? Homework • Read 237 -242 • Problems p 240 #1-6 • P 251 # 1, 4, 5, 6