Name: Period: _____ PUNNETT SQUARES – December 12, 2014
advertisement
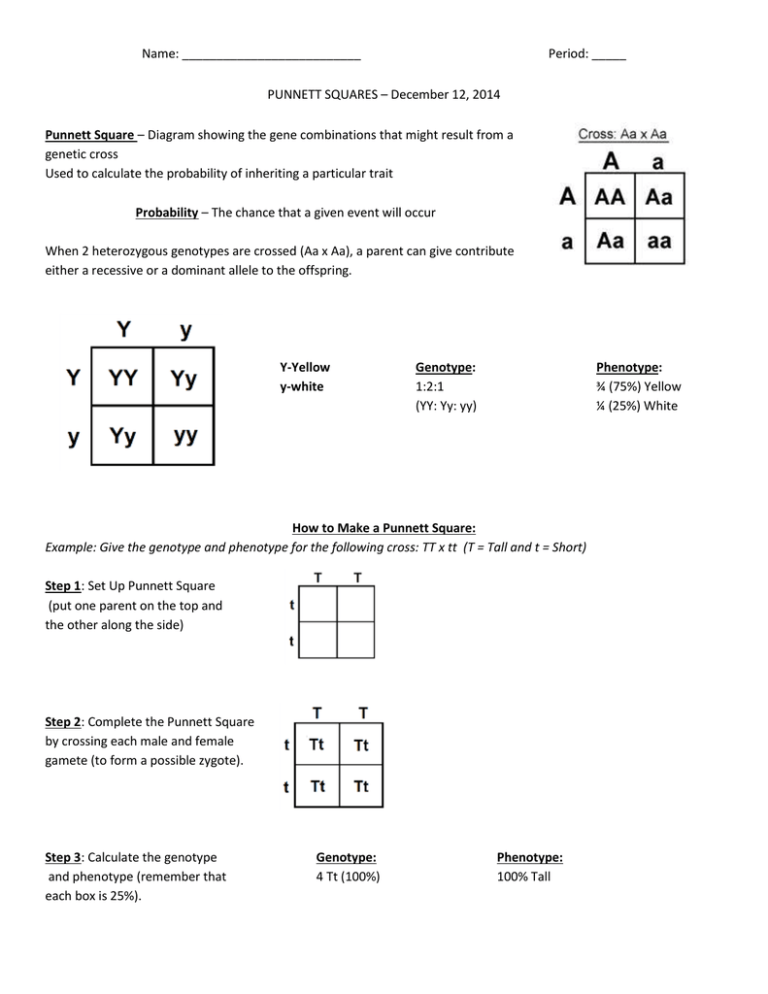
Name: __________________________ Period: _____ PUNNETT SQUARES – December 12, 2014 Punnett Square – Diagram showing the gene combinations that might result from a genetic cross Used to calculate the probability of inheriting a particular trait Probability – The chance that a given event will occur When 2 heterozygous genotypes are crossed (Aa x Aa), a parent can give contribute either a recessive or a dominant allele to the offspring. Y-Yellow y-white Genotype: 1:2:1 (YY: Yy: yy) Phenotype: ¾ (75%) Yellow ¼ (25%) White How to Make a Punnett Square: Example: Give the genotype and phenotype for the following cross: TT x tt (T = Tall and t = Short) Step 1: Set Up Punnett Square (put one parent on the top and the other along the side) Step 2: Complete the Punnett Square by crossing each male and female gamete (to form a possible zygote). Step 3: Calculate the genotype and phenotype (remember that each box is 25%). Genotype: 4 Tt (100%) Phenotype: 100% Tall 1) Give the genotype and phenotype for the following cross: Tt x tt What are the probabilities for each genotype? ____________________________________________ What are the probabilities for each phenotype? ___________________________________________ Some Terminology: P1 – Original parents F1 – First generation F2 – Second generation P1 X P1 = F1 F1 X F1 = F2 2) Complete the following Punnett Square showing a cross between Bb and Bb. B is the dominant allele for Black hair. b is the recessive allele for blonde hair. Genotypes and the probabilities for each: ___________________________ Phenotypes and the probabilities for each: __________________________