Compare Y2 Maths objectives to framework
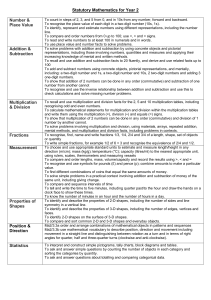
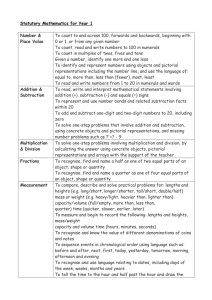
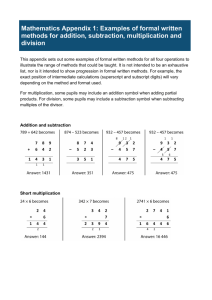
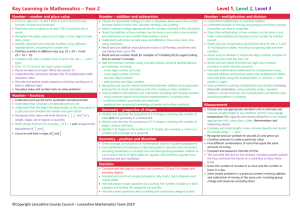
advertisement

Y2 Maths Test Performance Descriptor Analysis National Curriculum Objective (NAHT KPIs in bold) 2.1a count in steps of 2, 3, and 5 from 0, and in 10s from any number, forward and backward 2.1b recognise the place value of each digit in a two-digit number (10s, 1s) 2.1c identify, represent and estimate numbers using different representations, including the number line 2.1d compare and order numbers from 0 up to 100; use <, > and = signs 2.1e read and write numbers to at least 100 in numerals and in words 2.1f 2.2ai use place value and number facts to solve problems. solve problems with addition and subtraction: using concrete objects and pictorial representations, including those involving numbers, quantities and measures solve problems with addition and subtraction applying their increasing knowledge of mental and written methods recall and use addition and subtraction facts to 20 fluently, and derive and use related facts up to 100 add and subtract numbers using concrete objects, pictorial representations, and mentally, including: a two-digit number and 1s, a two-digit number and 10s, 2 two-digit numbers, adding 3 one-digit numbers show that addition of 2 numbers can be done in any order (commutative) and subtraction of one number from another cannot 2.2aii 2.2b 2.2c 2.2d 2.2e recognise and use the inverse relationship between addition and subtraction and use this to check calculations and solve missing number problems. Test Frameworks Performance Descriptor Statement count in multiples of 2, 5 and 10 to 100, forwards and backwards count forwards in multiples of 3 to 30 count in steps of 10, to 100, forward and backward (e.g. 97, 87 use place value in whole numbers up to 100 to compare and order numbers identify, represent and estimate numbers within a structured environment (e.g. estimate 33 on a number line labelled in multiples of ten) use place value in whole numbers up to 100 to compare and order numbers, using less than (<), equals (=) and greater than (>) signs correctly read and write numbers to at least 100 in numerals, and make recognisable attempts to write numbers to 100 in words use place value and number facts to solve problems (e.g. 60 – = 20) solve simple 2-step problems with addition and subtraction solve simple 2-step problems with addition and subtraction use addition and subtraction facts add and subtract numbers using concrete objects and pictorial representations, including: a two-digit number and ones; a two-digit number and tens; two two-digit numbers; three one-digit numbers know that addition and multiplication of two small numbers can be done in any order (commutative) and subtraction of one number from another cannot use inverse operations to solve missing number problems for addition and subtraction 2.3a recall and use multiplication and division facts for the 2, 5 and 10 multiplication tables, including recognising odd and even numbers 2.3b calculate mathematical statements for multiplication and division within the multiplication tables and write them using the multiplication (×), division (÷) and equals (=) signs show that multiplication of 2 numbers can be done in any order know that addition and multiplication of two small numbers can be (commutative) and division of 1 number by another cannot done in any order (commutative) and subtraction of one number from another cannot solve problems involving multiplication and division, using materials, solve problems involving multiplication and division arrays, repeated addition, mental methods, and multiplication and division facts, including problems in contexts. recognise, find, name and write fractions 1/3, 1/4, 2/4 and 3/4 of a recognise and find half of a set of objects or a quantity (e.g. find 1 length, shape, set of objects or quantity 2 of 18 pencils) and begin to find 1/3 or ¼ or ¾ of a small set of objects recognise, find and name fractions, ½ 1/3, ¼, 2/4, and ¾ of a shape write simple fractions, for example 1/2 of 6 = 3 and recognise the recognise the equivalence of two quarters and one half in practical equivalence of 2/4 and 1/2. contexts choose and use appropriate standard units to estimate and measure choose and use appropriate standard units to measure length / height length/height in any direction (m/cm); mass (kg/g); temperature (°C); in any direction (m / cm); mass (kg / g); temperature (°C); capacity (litres capacity (litres/ml) to the nearest appropriate unit, using rulers, scales, / ml) to the nearest appropriate unit thermometers and measuring vessels compare and order lengths, mass, volume/capacity and record the compare and order lengths, mass, volume / capacity results using >, < and = recognise and use symbols for pounds (£) and pence (p); combine recognise and use symbols for pounds (£) and pence (p); combine amounts to make a particular value amounts to make a particular value find different combinations of coins that equal the same amounts of find different combinations of coins to equal the sameamounts of money money solve simple problems in a practical context involving addition and solve problems in a practical context involving addition and subtraction subtraction of money of the same unit, including giving change of money of the same unit, including giving change compare and sequence intervals of time 2.3c 2.3d 2.4a 2.4b 3.1a 3.1b 3.1c 3.1d 3.1e 3.1f recall and use multiplication and division facts for the 10 multiplication table using the appropriate signs (×, ÷ and =) recall and use multiplication facts for the 2 and 5 multiplication tables and begin to recall and use division facts for the 2 and 5 multiplication tables using appropriate signs recognise odd and even numbers 3.1g tell and write the time to five minutes, including quarter past/to the hour and draw the hands on a clock face to show these times. 3.1h know the number of minutes in an hour and the number of hours in a day identify and describe the properties of 2-D shapes, including the number of sides and line symmetry in a vertical line identify and describe the properties of 3-D shapes, including the number of edges, vertices and faces identify 2-D shapes on the surface of 3-D shapes compare and sort common 2-D and 3-D shapes and everyday objects. order and arrange combinations of mathematical objects in patterns and sequences use mathematical vocabulary to describe position, direction and movement including movement in a straight line and distinguishing between rotation as a turn and in terms of right angles for quarter, half and three-quarter turns (clockwise and anti-clockwise). interpret and construct simple pictograms, tally charts, block diagrams and tables ask and answer simple questions by counting the number of objects in each category and sorting the categories by quantity ask and answer questions about totalling and comparing categorical data. 3.2a 3.2b 3.2c 3.2d 3.3a 3.3b 4.1a 4.1b 4.1c recognise, tell and write the times: o’clock, half past and quarter past and quarter to the hour; draw hands on a clock face to show half past and o’clock times begin to tell and write the time to five minutes, including quarter past / to the hour and draw hands on a clock face to show these times compare and sort common 2-D shapes and everyday objects, identifying and describing their properties compare and sort common 3-D shapes and everyday objects, identifying and describing their properties identify 2-D shapes on the surface of 3-D shapes and images of them order and arrange combinations of mathematical objects in patterns use mathematical vocabulary to describe position, direction (e.g. left and right) and movement including movement in a straight line and distinguish between rotation as a turn, and in terms of right angles for quarter and half turns interpret simple pictograms, tally charts, block diagrams and simple tables answer questions by counting the number of objects in each category and sorting the categories by quantity answer questions about totalling and begin to compare simple categorical data