Thyristor Structure and Specification
advertisement

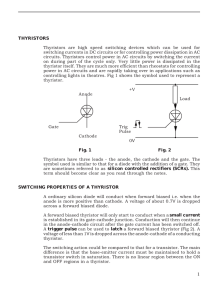
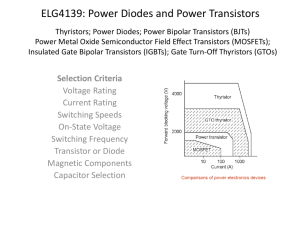
THYRISTOR STRUCTURE AND SPECIFICATION Eric Canniff Cody Johnson INTRODUCTION AND OUTLINE History Basic Characteristics Structure Specifications Applications HISTORY William Shockley proposed the concept of the Silicon Controlled Rectifier (SCR) in 1950 Engineers at Bell Labs supported this idea In 1956 Under the supervision of Gordon Hall, General Electric created an SCR Soon became a commercial product, due to the efforts of Frank W. Gutzwiller Predecessor was a gas filled tube device called a Thyratron BASIC CHARACTERISTICS Thyristor is composed of four alternate layers of N-type and P-type material TWO TRANSISTORS EQUIVALENT CIRCUIT I-V CHARACTERISTICS STRUCTURE BILATERAL STRUCTURE Allows for positive and negative voltages to pass TRIAC STRUCTURE MOS TURN-OFF THYRISTOR MOS GATED THYRISTOR V Groove Mos gated thyristor LIGHT TRIGGERED THYRISTOR (LTT) Have an optically sensitive region in the gate Used for protection of control circuit for HVDC Usually triggered by Infrared Light SPECIFICATIONS 50A Medium Power Thyristor APPLICATIONS DC transmission of power from Manitoba Hydro dams Heart of High-voltage direct current conversions now a days SUMMARY AND CONCLUSION Thyristor is a 4-layered alternating pn-material device Semiconductor Controlled Rectifier (SCR) Needs only a small gate pulse to stay on 4 Basic structures Mainly used in high voltage application REFERENCE SLIDE Neamen, Donald A. Semiconductor Physics and Devices. Fourth ed. New York: McGraw-Hill, 2012. 691-701. Print. Vishay, . Medium Power Thyristors. N.p., 19 Sept. 2008. Web. 27 Apr. 2013. <http://www.vishay.com/docs/93711/50ria.pdf>. Sentaurus Technology Template: Light-Triggered Thyristor. N.p., 2013. Web. 28 Apr. 2013. <http://www.synopsys.com/Tools/TCAD/Pages/thy ristor.aspx>. KEY CONCEPTS Structures Switching Characteristics Triggering Types Applications