What is Ethics?
advertisement

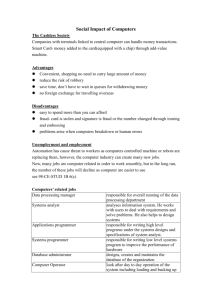
Computer and Society Introduction to: • World Wide Web • Wild Card • Security/Privacy • Computer Crimes • Viruses • Ethics • Etiquette/ Netiquette • Email Edited By A. Moore 02/12 Information retrieved from 2008 Exploring Business Technologies & Business Computer Technology—BE 6400, and Digital Literacy curriculum. Lesson Objectives After completing this lesson you will be able to: • • • • • Understand the world wide web and the use of the wild card symbol. Identify the common measures used to protect your computer and your data. Discuss security, confidentiality, and ethical issues as related to computer usage. Identify computer viruses. Understand computer ethics, etiquette, and netiquette. World Wide Web • WWW - collection of data that is accessible from the Internet. • Web browser - software that allows you to retrieve resources from the web. – Internet Explorer, Mozilla Firefox, Google Chrome • Search engine – allows users to search for information on the WWW. – Google, Alta Vista, Excite Wild Card Searching • The * symbol, called an asterisk, is considered a wildcard character. • Used if you don’t know the spelling of a word – Example: N*Ryan to search for Nolan Ryan • Used to search plurals or variations of words. What is Computer Security & Privacy? • Damages your computer or the data on it is a computer threat. • When your computer is connected to a network, the computer becomes more vulnerable to computer threats. Video 5 Worst Photos Post Online Security Measures Maintain & enforce security measures such as: • Passwords • Firewalls – Limits data that passes through the Internet and protects data from damage by unauthorized users. • Antivirus software Other Terms • Scams - attractive offers through e-mail messages or chat room communication. • Online predators - individuals who contacts Internet users online. Involve others into inappropriate and unethical relationships. Computer Privacy • Computer privacy - keeping personal files, data, and e-mail messages, away from anyone without permission • Computer Security – protecting a computer system from accidental or intentional loss and tampering (Ex: user name and password). Computer Laws • Copyright - Law protecting the original work of an artist or author (software, text, paintings, photographs, books, songs, video/movies). Computer Crimes Criminal act committed through the use of a computer. • Hacker - Using the computer to misuse or tamper with the programs and data stored on the computer. • Computer hacking - Invading someone else’s computer, for personal gain or the satisfaction of invasion. • Computer fraud - Manipulating a computer or its data for dishonest profit. • Theft of computer time - Using a company’s computer for personal use. Computer Crimes (con’t.) • Plagiarism - Taking ideas or words that are not yours and claiming it as yours (research papers). • Data diddling - Changing data before or while entering in the computer. • Piracy - Violation of copyright law. Illegally copying and reselling as your original. Identity Theft Hacker steals your personal information to assume your identity. Viruses http://www.commoncraft.com/video/computer-viruses-and-threats • Viruses – software written to cause malfunctioning of a computer or damage the stored data. • Worms – uses computer networks and duplicates copies of itself in the computer's memory and causes the computer to crash. • E-mail viruses – travels as an e-mail attachment by automatically mailing itself to the address book. Viruses con’t. • Trojan horse - does something harmful while appearing to do something useful (trick disguised as a game). • Logic bomb – virus takes affect at an event (deleting an email, closing a pop-up window) • Time bomb – virus takes affect at a certain date or time (Friday 13th). • Hoax – virus that tricks you into thinking you have a virus. Spyware •Spyware – program installed on your computer without your knowledge. Secretly sends out information about your Web browsing habits or other personal details to another computer through the network. EXE • Called executable files, make things happen. • EXE files are necessary for running your applications. • EXE files can be dangerous files and damage your computer system and your security. • Do not open EXE files than you received as an e-mail. What is Ethics? • Moral principles or values • Distinguishing between right and wrong Technology Ethics Ethics - moral principles by which people conduct themselves. – Not play computer games during work hours. – Not check personal e-mail. – Not use the Internet for personal use such as shopping online. Acceptable Use Policy (AUP) • Policy a user must agree to follow in order to be provided access (login - user name & password) to a network or to the Internet. E-mail Etiquette • Etiquette - Use good manners when writing email messages. • Use correct spelling and punctuation. • Keep your message short. • DO NOT USE ALL CAPS! It looks like you are yelling. Netiquette - Good internet behavior Electronic Mail • Electronic form of postal mail. • Email consists of three parts: • The user name of the individual • The @ symbol • The user’s domain name (name of the computer that handles your mail) Example: rsmith@yahoo.com Body Header Parts of an E-Mail Message Are You Paying Attention? • Take out a blank sheet of paper. • Write your first name, last name, class and date in the right corner. • Label this assignment “Computer Society” • Number it 1-5. 1) You receive an e-mail message from an unknown e-mail address. The message requests you to share your credit card details to receive a discount on some music CDs. What will you do with this message? A. Reply to the message to provide your credit card details. B. Encrypt the message. C. Scan the message for viruses. D. Delete the message. 2) Lina is unable to access the e-mail account that her Internet service provider (ISP) provides. She realizes that someone has hacked into her account. What action will she take to remedy this issue? A. B. C. D. Protect her computer from surges and spikes Use Microsoft® Windows® Update Install spyware Report the incident to her ISP 3) Ken decides to download the latest song from his favorite band from a publicly available Web site and share it with his friends. What is Ken doing? A. B. C. D. Breaching copyright Breaching security Slandering the singer Violating privacy 4) While reading a novel, you realize that the author has copied material from another author. How will you categorize this violation? A. B. C. D. Phishing Plagiarism Libel Slander 5) Gloria uses the Internet frequently for online purchasing. To protect her system from virus attacks, she installs an antivirus program. However, within a few days, she gets a virus alert on her system. Which of the following measures will she implement to prevent this virus in the future? A. B. C. D. Update and run virus scans daily. Update the Internet browser. Check Windows Update. Use a strong password.