The City of Copenhagen wishes to introduce Smart Parking
advertisement

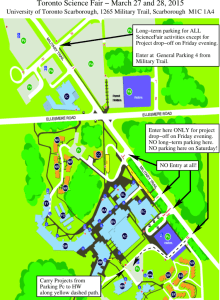
Smart Parking in Copenhagen: Invitation to dialogue The City of Copenhagen wishes to introduce Smart Parking solutions in the streets of Copenhagen to make better use of the existing parking space capacity by providing drivers in search of parking with timely information on e.g. the streets or areas near their final destination with the highest available capacity at any point in time. Background and purpose The City of Copenhagen is a leading Smart City winning several climate change and Smart City awards. As part of the Smart City programme the city is planning a large scale implementation of Smart Parking technologies in areas of the city with parking capacity challenges. The areas currently in scope are Inner City and Outer Østerbro with a total of around 4.700 street level parking spaces in scope for 2016-2017. Inner City 1 Outer Østerbro A number of Smart Parking technologies currently exist in the market including sensors embedded in the road, cameras mounted above parking spaces and radar solutions integrated in street lighting. Each of these solutions have both strong and weak points. As part of the risk mitigation for the large scale roll-out The City wants to test some of the solutions in order to identify the ones that best handle a number of key challenges related to Smart Parking in Copenhagen. These challenges are considered to be challenges that must be addressed before a larger implementation project can be initiated. The City of Copenhagen wishes to introduce Smart Parking solutions in the streets of Copenhagen to make better use of the existing parking space capacity by providing drivers in search of parking with timely information on e.g. the streets or areas near their final destination with the highest available capacity at any point in time. In other words the purpose is to better cater to the demand (drivers looking for available parking spaces) by making the current supply (currently available parking spaces) more visible or accessible to drivers. By guiding drivers more quickly to areas with more available parking spaces (current supply greater than current demand) the outcome is expected to be a better overall balance between supply and demand resulting in a more optimized use of the total parking capacity. This would in term mean a reduced need for investments related to increasing the parking capacity in the areas in scope (new on-street parking spaces or underground parking facilities). A number of additional benefits for The City, its residents, visitors and society in general have been identified. These include lowering the overall traffic volume resulting in fewer traffic jams, reducing air pollution (greenhouse gasses etc.), lowering fuel consumption and lowering the number of hours that drivers spend behind the wheel looking for a place to park. 2 Key challenges This section describes the key challenges for Smart Parking in Copenhagen. Each challenge is accompanied by a section in the Feedback Form where your response to each of the challenges is to be entered. Challenge 1: Parking bays are not always individually marked As shown below, not all parking bays in Copenhagen are individually marked (examples below are from Lange-Müllers Gade 24 (curbside parking) and Bryggervangen 70 (side-by-side parking)). Cars will not necessarily park within the same exact section of the total parking space each time as the space occupied will vary based on the size of the driver’s own car, the space available between already parked cars etc. These unmarked parking bays are seen throughout the city and represent a large portion of the total parking capacity in the city. Parking bays cannot be individually marked as part of this project as these unmarked parking areas are an integral part of Copenhagen’s on-street parking layout. Your task: Please provide information on how your product/technology can be implemented and will work under these conditions and how e.g. the accuracy of car detection is affected. Image © Google 3 Image © Google Challenge 2: Trees and other obstacles in the urban space Copenhagen is considered a green city with many roadside trees in the city center as shown below (example from Vejrøgade, Østerbro). Your task: Please provide information on how your product/technology is affected by obstacles in the urban space like roadside trees, signposts, bus shelters etc. Image © Google Challenge 3: Parking spaces on cobble/setts (not regular asphalt) Copenhagen is a historical city with older buildings and streets. A number of parking spaces are therefore placed on cobble and/or setts like shown below (example from Landemærket 8, Inner City). Your task: Please provide information on how your product/technology can be implemented in such a setting. 4 Image © Google Challenge 4: Weather conditions, winter maintenance and flooded streets Copenhagen is located in the oceanic climate zone with unstable conditions throughout the year resulting in an average daytime high in July at around 20 degrees and average temperatures around the freezing point during winter. Due to the unstable weather conditions Copenhagen is often hit by heavy snowfall during the winter resulting in heavy use of road salt, snow plows and -sweepers in the streets. Furthermore, Copenhagen is occasionally hit by cloudbursts resulting in flooded streets. Typical winter conditions in Copenhagen. Image © City of Copenhagen 5 Occasional flooding in Copenhagen. Image © flickr/Lisa Risager CC BY-SA 2.0 Your task: Please provide information on how your product/technology is affected by weather conditions in general (below freezing temperatures, sun, rain and wind as well as snow and fallen leaves in the streets) and how it is affected by e.g. piles of snow and the use of salt and snow plows/sweepers. Challenge 5: Power and networking requirements Electricity is available in or near lighting poles or in relation to the wired lighting fixtures which is used throughout the city but cannot be expected to be extended to reach each parking bay. Your task: Please provide information on power requirements (mains and battery) for your product/technology including for the network equipment required for communicating with endpoints/nodes. Please provide a brief overview on the networking protocols used and any needs for wired network connections. Challenge 6: Aesthetics Copenhagen is a historical city with an emphasis on keeping parts of the city authentic. This means that Smart City technology solutions cannot disrupt the overall look-and-feel of the city. In other words the Smart Parking technologies are to be unobtrusive and seamlessly blend into the surroundings in a given street or area. Your task: Please provide information on the physical appearance, color and size of your product/technology and how it can be adapted to match its surroundings. Challenge 7: Apps/services and end-user adoption A key to success is providing end users (drivers) with timely and easily accessible information on how to find an available parking space. Another key to success is providing municipal employees with accurate insights into the data created by your product/technology. 6 Your task: Please provide information on how your product/technology is able to deliver information to end users (drivers) as described above and how a large user base can be established. Please also provide information on the analytics capabilities of your product/technology. Challenge 8: Open Data and open business models Copenhagen is a strong proponent of Open Data as Open Data is seen as being crucial in creating innovative digital solutions, open business models and integrating products and services across markets and use cases. As part hereof the City of Copenhagen will need to have full ownership of the data created using the implemented Smart Parking technologies. Your task: Please provide information on how 3rd party applications can make use of the data created by your product/technology e.g. through APIs - and the conditions under which this can be done. Instructions for replying ● ● ● ● ● ● ● Please fill in the Feedback Form on key challenges by providing a short description on how your company and parking technology/solution is able to handle each of the challenges listed. You will have the chance to elaborate during the subsequent dialogue meetings. Feel free to attach or refer to any additional documentation about your services, products or technologies that are of relevance to your technology/solution or the challenges listed. Feel free to mention any implementation projects you’ve done for cities with similar challenges. Please provide us with name, telephone number and email address of your primary contact person. Please state if you are available for face-to-face meetings in Copenhagen on either January 29th or February 1st - or if you prefer joining a video/Skype call. Please return your response to Project Manager Pia Preibisch Behrens by e-mail (zj3s@tmf.kk.dk) in Word or PDF format. Please make sure that your response is returned to us no later than January 22nd 2016. The process following your reply Please notice that your timely reply does not necessarily guarantee you an invitation to the subsequent dialogue meetings: We reserve the right to choose any solution providers for continued dialogue but we aim to include as many solution providers and technologies as possible. 7 Dialogue meetings will be held in the form of one-on-one meetings between the City of Copenhagen and each of the solution providers on January 29th and February 1st 2016. For solution providers from outside Denmark the dialogue meetings can be held in the form of a video conference/Skype call. The City of Frederiksberg will also attend the dialogue meetings. The City of Frederiksberg is planning a test of smart parking solutions. For further information about the process at Frederiksberg, please contact Head of GIS and Smart City, City of Frederiksberg by e-mail (haha09@frederiksberg.dk). The process for testing and subsequently implementing the technologies/solutions chosen as result of the dialogue meetings is not in place yet. Your feedback to us during the dialogue meetings will be vital in ensuring a good project design. 8 Feedback Form: Key challenges to be addressed Challenge 1: Parking bays are not always individually marked [Please provide a short description on how you aim to handle this challenge] Challenge 2: Trees and other obstacles in the urban space [Please provide a short description on how you aim to handle this challenge] Challenge 3: Parking spaces on cobble/setts (not regular asphalt) [Please provide a short description on how you aim to handle this challenge] Challenge 4: Weather conditions, winter maintenance and flooded streets [Please provide a short description on how you aim to handle this challenge] Challenge 5: Power and networking requirements [Please provide a short description on how you aim to handle this challenge] Challenge 6: Aesthetics [Please provide a short description on how you aim to handle this challenge] Challenge 7: Apps/services and end-user adoption [Please provide a short description on how you aim to handle this challenge] Challenge 8: Open Data and open business models [Please provide a short description on how you aim to handle this challenge] 9