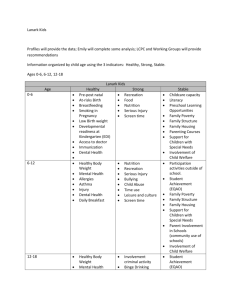
Federal Expenditures on Major Need
advertisement

EXPENDITURE PROGRAMS FOR THE POOR Chapter 13 A Quick Look at Welfare Spending • Means-tested • Cash versus in-kind assistance • Anti-poverty impact of non-means-tested programs Federal Expenditures on Major Need-Tested Programs (2009) Program Federal Expenditures ($) Health 319.3 Cash aid 129.6 Food assistance 77.5 Housing and development 59.9 Education 58.2 Social Services 44.3 Energy assistance Employment and training 10.3 8.6 Source: Spar [2011,p.9] 13-2 TANF • Aid to Families with Dependent Children (1935-96) • TANF-Temporary Assistance for Needy Families (1996?) – – – – No entitlement Time limits Work requirement Fixed $ Block grants to states • States have much flexibility and authority over structure of their welfare system – Benefit reduction rates 13-3 Work Incentives The Basic Trade-offs B = G – tE B = 0 if E = G/t Challenge: t – rate at which grant reduced when recipient How to provide an adequate income support program earns money while minimizing work disincentives? B – benefit received G – basic grant if not working 13-4 Income per month Analysis of Work Incentives D |Slope| = w c b 2w a 0 w Time endowment T Hours of leisure per month 13-5 Income per month Analysis of Work Incentives D |Slope| = w E1 G iii Income ii Leisure 0 i F Work T Hours of leisure per month 13-6 Income per month (= earnings + transfers) Analysis of Work Incentives D |Slope| = w |Slope| = 3/4w S Hours before TANF Q $100 0 F K T Hours of leisure per month Hours after TANF 13-7 Income per month (= earnings + transfers) Analysis of Work Incentives D Budget constraint with t = 100% 0 hours of work selected S R P1 P G $338 0 F T Hours of leisure per month 13-8 Income per month (= earnings + transfers) Analysis of Work Incentives D E2 P R Hours worked 0 M T Hours of leisure per month 13-9 Work Requirements When welfare recipient can’t choose work hours • Workfare: able-bodied individuals receive income-support only if they agree to participate in a work-related activity • TANF – Mandated work 13-10 TANF Characteristics • Time Limits – Lifetime – Per spell of welfare • Family Structure – Marriage – Childbearing – Empirical results as to whether TANF affected the structure of low-income families 13-11 National versus State Administration • Does State Administration create a Race to the Bottom? • State Administration allows state experimentation 13-12 Other Benefit Programs for the Poor Earned Income Tax Credit 2012 for a single parent with two children 13-13 Other Benefit Programs for the Poor Earned Income Tax Credit 13-14 Empirical Evidence: The Effect of the Earned Income Tax Credit on Labor Supply • Labor force participation • Work hours 13-15 Other Benefit Programs for the Poor • Supplemental Security Income: Federal program for aged, blind, disabled. – SSI vs. conventional welfare • Uniform minimum federal guarantee • Benefit levels • Work incentives • Medicaid – How Medicaid works – Work disincentives: Medicaid Notch 13-16 Income per year The Medicaid Notch M D R S Z N $1,000 0 X T Hours of leisure per year 13-17 Other Benefit Programs for the Poor Unemployment Insurance • Why does government insure against unemployment? – Adverse selection – Moral hazard • Benefits – Gross replacement rate • Financing – Experience rated • Effects on Unemployment 13-18 Other Benefit Programs for the Poor Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program • • • • SNAP as an in-kind transfer Direct cost paid by federal government Administered by the states Participation rates 13-19 Other Benefit Programs for the Poor Housing Assistance • How housing assistance works • Housing subsidies – Section 8 certificates – Voucher programs • Impact on stock of housing • Public housing and economic self-sufficiency of inhabitants 13-20 Other Benefit Programs for the Poor Programs to Enhance Earnings • Education – Head Start • Employment and Training 13-21 New Ideas • Replace current hodgepodge with single cash assistance program • Are benefit levels high enough? • Faith-based social services might address the hypothesized (by some) “spiritual” and “moral” roots of poverty 13-22 Chapter 13 Summary • Means-tested programs transfer income and services such as housing, health insurance, food, education, and job training, to people whose resources fall below a certain level • Economic research surrounds how well these programs achieve the dual goals of providing adequate assistance and minimizing work disincentive 13-23