PPT
advertisement
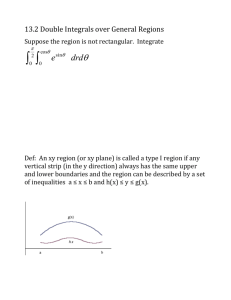
MAT 1236 Calculus III Section 15.3 Part II Double Integrals Over General Regions http://myhome.spu.edu/lauw HW&… WebAssign 15.3 II (7 problems, 51 min.) Quiz: 15.1-15.3 Preview Change the order of integration Properties (relation to section 6.1) Order of Integration If D is both type I & type II, then D b g2 ( x) f ( x, y )dydx a g1 ( x ) f ( x, y )dA h ( y ) d 2 f ( x, y )dxdy c h1 ( y ) Example 1 Evaluate 1 1 2 sin( y )dydx 0 x Example 1 1 1 2 sin( y )dydx 0 x The inner integral is impossible/difficult to evaluate Switch the order of integration Example 1 Sketch and state the region of integration and change the order of integration 1 1 2 sin( y )dydx 0 x Example 1 Sketch and state the region of integration and change the order of integration 1 1 2 sin( y )dydx 0 x Type I Example 1 Sketch and state the region of integration and change the order of integration y 1 1 1 2 sin( y )dydx 0 x yx Example 1 Sketch and state the region of integration and change the order of integration x 1 1 1 2 sin( y )dydx 0 x x0 1 1 Example 1 sin( y 2 )dydx 0 x 1 (1 cos1) 2 Summary Notice that the inner integral is difficult to evaluate Sketch the region Reverse the order of integration Evaluate the iterated integral Expectations You are expected to label your graph Transitional integral 1 1 2 2 sin( y ) dydx sin( y ) dA 0 x D 1 y sin( y 2 ) dxdy 0 0 You are expected to write down the two set descriptions of the domain D. Properties [ f ( x, y) g ( x, y)] dA f ( x, y) dA g ( x, y) dA D D cf ( x, y) dA c f ( x, y) dA D D and others…. D Property 1 dA area of D D z 1 A D Consistency How do we know our calculus “system” is consistent? (No conflicts, agree with each other) Consistency How do we know our calculus “system” is consistent? (No conflicts, agree with each other) Volume formula “implies” area formula via 1 dA area of D z 1 D A D Type I: Region Bounded Above/Below A( D ) 1dA y g2 ( x) D b g2 ( x ) 1dydx a g1 ( x ) D b y y g2( x ) dx yg ( x) 1 a a b b g 2 ( x) g1 ( x) dx a y g1 ( x) Type II: Region Bounded Left/Right x h1 ( y) A( D ) 1dA D d d h2 ( y ) 1dxdy c h1 ( y ) d D x x h ( y ) dy x h2 ( y ) 1 c d h2 ( x) h1 ( x ) dy c x h2 ( y) c