Unit 9 Transitions: In Pursuit of Peace Content Specifications 7.9.1
advertisement

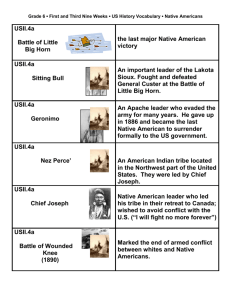
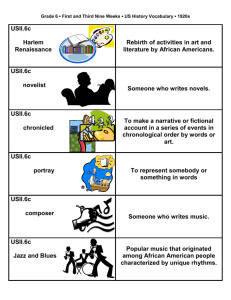
Unit 9 Transitions: In Pursuit of Peace Content Specifications 7.9.1 Describe the growth of the American economy after World War II. (USII.8b) conversion from war materials to consumer goods credit purchases changing role of women in the labor force passage of the GI Bill of Rights, education, housing, benefits labor unions became more powerful increased consumer spending workers gained wages and better working conditions 7.9.2 Describe the causes and effects of demographic changes in the United States in the years following World War II. (USII.8d, USII.9b) baby boom changing role of women air conditioning "migration” to the South suburbs television increased travel for business and pleasure greater access to information desegregation of the armed forces (Truman) GI Bill of Rights, access to college 7.9.3 Describe the international effects of World War II. (USII.8a) Soviet forces occupied Eastern and Central Europe partition of Germany into East and West Germany forced creation of Soviet “satellites” Nuremberg Trials establishment of the state of Israel in 1948 occupation of Japan by American forces formation of the United Nations 7.9.4 Identify the major political and governmental changes during the Cold War era. (USII.8a) communist victory in the People’s Republic of China—Mao Zedong democratic government in Japan division of Korea at the 38th parallel division of Vietnam at the 17th parallel 7.9.5 Describe the political and economic differences between the U.S. and the U.S.S.R during the Cold War period. (USII.8a) democratic vs. dictatorial governments individual ownership vs. state ownership free expression vs. state censorship capitalist vs. communist NATO vs. Warsaw Pact 7.9.6 Describe the characteristics of the Cold War. (USII.8c) competition between the United States and the Soviet Union war of words Soviet Union’s domination of Eastern Europe arms race espionage democracy vs. communism “iron curtain” 7.9.7 Describe the Truman administration’s responses to foreign policy challenges of the Cold War era. (USII.8c) Marshall Plan Truman Doctrine Berlin Blockade - Berlin Airlift containment policy Korean War (with U.N.) 7.9.8 Identify the causes and results of the Korean War. (USII.8c) invasion of South Korea by North Korea Chinese support of the North Koreans creation of a demilitarized zone continued division of North and South Korea along the 38th parallel stalemate 7.9.9 Describe the causes and effects of the anticommunist crusade of the early 1950s. (USII.1d) House Un-American Activities Committee blacklists, loyalty oaths McCarthyism 7.9.10 Describe the foreign and domestic issues during the Eisenhower administration. Sputnik greater investment in education domino theory peaceful coexistence interstate highway system (for ease of military movement if needed) Brown v. Board of Education Montgomery bus boycott (most of the details covered in the next unit) 7.9.11 Describe the foreign policy challenges and responses of the Kennedy administration during the Cold War era. Bay of Pigs invasion Cuban missile crisis - blockade of Cuba military advisors in Vietnam building of the Berlin Wall space program