damage control systems and equipment
advertisement

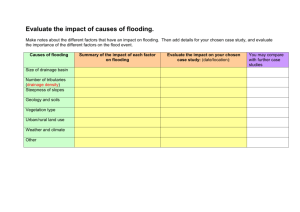
DAMAGE CONTROL SYSTEMS AND EQUIPMENT Learning Objectives • Know the procedures, objectives and priorities in combating the progressive deterioration from fire and underwater hull damage • Know the four classes of fire and the fire fighting agents, equipment, and procedures to extinguish each class • Know the use of equipment, materieals, and procedures for countering progressive flooding and structural deterioration Learning Objectives (cont.) • Know the principles of operation of the fire main system • Know the procedures for donning and proper operation of an Oxygen Breathing Apparatus (OBA), Emergency Egress Breathing Devise (EEBD), Supplementary Emergency Escape Devise (SEED), and Standard Navy Gas Mask MCU-2P Elements of fire tetrahedron • Fuel • Heat • Oxygen • Free radicals (Chemical reaction) Fuel • When a fire runs out of fuel it will stop. • Fuel can be removed naturally, as where the fire has consumed all the burnable fuel, or manually, by mechanically or chemically removing the fuel from the fire. • Examples: Paper, wood, oils/gas, wires, textiles/cloth, metal Heat • Temperature needed to exceed flash point: sparks, short circuit, matches, friction • Without sufficient heat, a fire cannot begin, and it cannot continue. • Heat can be removed by dousing some types of fire with water; the water turns to steam, taking the heat with it. DOES NOT WORK WITH ALL FIRES! Oxygen • Allows combustion to take place • Oxygen may be removed from a fire by smothering it with an aqueous foam, or some inert gas (e.g., carbon dioxide, Halon), dry chemicals, or enclosing it where the fire will quickly use up all of the available oxygen. Chemical Reaction • Free Radicals • Chemistry of Combustion − other specialized chemicals must be used to break the chain reaction of metallic combustion and stop the fire. − Lithium, Magnesium • What happens if you add water to these types of fires? Flare of Magnesium Powder w/ water Classes of Fire • Class A − Wood, paper, people − Leaves an ash − Fairly simple to fight and contain - by simply removing the heat or oxygen (or in some cases fuel), the fire triangle collapses and the fire dies out. • Class B − Combustible fuels, hydrocarbons, solvents − More difficult to combat – water may spread fire − Chemical retardant, carbon dioxide fire extinguisher, protein based foam • Class C − Electrical − Difficulties in combating • Water – electrical shock − Protein foam to remove oxygen − Turn off power supply ( Class A) • Class D − Metal fires • such as sodium, titanium, magnesium, potassium, uranium, lithium − Difficult to combat - Water and other common firefighting materials can excite metal fires and make them worse Firemain System • Receives water pumped from ocean • Types of systems: − − − − Single main – small ships Horizontal Loop Vertical Loop Composite versions • Primary purpose – FIRE FIGHTING • Other uses: flushing, auxiliary machinery cooling, water washdown Single Main • Extends longitudinally near the centerline of ship • Pumps discharge into risers then into main • Main supplies fireplugs & other services • Usually found on FF’s and DDG’s Horizontal Loop • 2 Single Mains on DC Deck • Minimizes damage • Cross-connected to form series of horizontal loops Vertical Loop • 2 Single Mains • Installed in oblique plane • Mains are cross-connected to form series of loops Composite • 2 or 3 service mains on DC deck • By-pass main installed at lower level near C/L • Cross-connects installed alternately between service mains & by-pass main Fire Station •Fireplug •Quick cleaning strainer •All-purpose nozzle •Vari-nozzle •Hoses Extinguishing Agents • Water − Firemain system − Sprinkler system • AFFF (Aqueous film-forming foam) − 94% water / 6% foam mix − Excludes oxygen from the surface of the fuel − Extremely corrosive Extinguishing Agents • Potassium bicarbonate (PKP) − Breaks combustion chain − Does not have cooling capability − May cause violent reaction in combustible metals − Non-toxic, however can cause breathing difficulty Extinguishing Agents • Halon 1301 system − − − − − Colorless, odorless gas when release Density ~ 5X that of air Decomposed on contact w/ heat Used in flooding systems At concentrations needed to extinguish fire, dizziness and reduced dexterity What type of extinguishing agent would you use? • Class A Fire − Water − Any • Class B Fire − − − − AFFF PKP Twin agent (AFFF/PKP) Halon 1301 Extinguishing agent for this fire? • Class C Fire − CO2 − Fog − PKP • Class D Fire − Solid stream, fog or jettison Flooding • Progressive Flooding − Partial flooding that can continue through small holes, cracks, loose rivets, etc − If continues, ship will lose buoyancy and list • Flooding Boundaries − Bulkheads and decks restricting partially flooded areas − If become completely flooded, boundaries may not hold and must be INSPECTED Dewatering Priorities • Effective allocation of resources − What if damage is too severe? • Stability − Loss of stability… • Flooding effect diagram Causes of Flooding • Damage inflicted from external sources − Mines, torpedoes, bombs, running aground etc. • Fire fighting efforts • Acute or chronic leakage • Broken firemain or other piping system Flood Control • P-250 pump − gas operated portable pump • Electric submersible pump − lighter than P-250 − submersible − can not be used for combustible liquids • Eductors − Increases rate of removal − Contaminated water Repair of Structural Damage • Shoring − Used to support ruptured decks, strengthen weakened bulkheads and decks, etc. • Types of shoring materials − Shore-portable beam − Wedge-triangular block − Strong back − Patches • Better to shore more than necessary than to risk structural failure Supplemental Air • Oxygen Breathing Apparatus (OBA) − Self contained O2 source − 1930s technology − Phase-out began in 2001 Supplemental Air • Self-Contained Breathing Apparatus (SCBA) − Provides air for breathing while firefighter is in a fire or other hazardous environment − Better range of motion Supplemental Air • Emergency Egress Breathing Device (EEBD) − Donning – 10 sec − Provides Oxygen 10-15 minutes − Operating Temp: 10°F – 149°F Supplemental Air • Supplementary Emergency Escape Device (SEED) − Worn on belt − 1.5 – 3 min of Oxygen − HEED (Helicopter) Gas Masks / CBR Attacks • Standard Navy Gas Mask MCU-2P − Replace canister after blood agent attack − Canister good for 30 days following all other chemical threat agents − Training canister labeled w/ white stripe (open for 60 days) Safety during DC operations • Electric shock hazard if water is used on class C fire • Exploding ordnance or fuels during fires • Splattering hot metal with class D fire • Being overcome by CO2 • Extremely cold temperatures with CO2 extinguishers • Heat Stress conditions • Smoke/Toxic fume inhalation QUESTIONS? • Wednesday, Nov 29 − Questions for panel • Friday, Dec 1 − Review • Monday, Dec 4 − Questions/Review • Wednesday, Dec 6 − Final Exam − Bring Books!!! MUST TURN IN BOOKS