Voters and Voter Behavior
advertisement

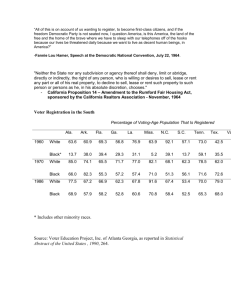
Voters and Voter Behavior Suffrage & Civil Rights 15th Amendment • Ratified in 1870 • Right to vote can’t be denied to any U.S. citizen b/c of one’s race, color or previous condition of servitude • Given the circumstances of U.S. in 1870, was this a law that could be easily enforceable? 15th Amendment • African-Americans generally were kept away from the polls in the South b/w 1870-1965 • Groups that disagreed w/the 15th Amendment used: – Violence – Subtle threats – Literacy tests – Poll taxes 15th Amendment • One tactic was gerrymandering – practice of drawing electoral district lines to limit voting strengths of a particular group/PP • http://www.govtrack.us/congress/findyourreps.xpd?sta te=AL • http://www.foxnews.com/interactive/politics/electionmap2010/#race=racesInPlay&pres=false&tab=senate&state =us-senate 15th Amendment • Results of gerrymandering in the South – Democrats dominated nearly every political office at every level, and most candidates were white • PP were considered to be “private associations”, which by law meant they could exclude anyone for no reason – Party primaries were only voted on by party members 15th Amendment • 1944 – Smith v. Allwright (Texas) – Outlawed exclusion of voters in primary voting – All political parties are public functions, thus cannot exclude particular people 15th Amendment • 1960 – Gomillion v. Lightfoot (Alabama) – AL legislature redrawn electoral district in Tuskegee, eliminating all blacks from the city limits – S.C. ruled that gerrymandering for racial purposes violated 15th Amendment Civil Rights Act of 1964 • Outlawed discrimination in job-related situations • Forbid any extra voter requirement used in an unfair/discriminatory manner • Allowed injunctions to enforce law – Court order that forces/limits performance of some act by a private individual/public official – Punishable by fine or imprisonment Civil Rights Act of 1964 • Outlawed discrimination in job-related situations • Forbid any extra voter requirement used in an unfair/discriminatory manner • Allowed injunctions to enforce law – Court order that forces/limits performance of some act by a private individual/public official – Punishable by fine or imprisonment Civil Rights Act of 1964 • SNCC started a voter registration drive for AfricanAmericans in Selma, AL • March 7, 1965 – 600 people began march from Selma to Montgomery • Law enforcement met group at Edmund Pettus Bridge – attacking group with billy clubs, tear gas, rubber tubes wrapped in wires Civil Rights Act of 1964 • SNCC started a voter registration drive for AfricanAmericans in Selma, AL • March 7, 1965 – 600 people began march from Selma to Montgomery • Law enforcement met group at Edmund Pettus Bridge – attacking group with billy clubs, tear gas, rubber tubes wrapped in wires Civil Rights Act of 1964 Civil Rights Act of 1964 Civil Rights Act of 1964 Voting Rights Act of 1965 • Applied to all elections held anywhere in the country • Originally only supposed to law for 5 years – Congress extended it 4 times – Most recent extension granted 25 years • Suspended literacy tests in any state/county where less than 1/2 electorate voted in 1964 elections Voting Rights Act of 1965 • Authorized attorney general appoint voting examiners to serve in any state/county • Any new election law, or change in pre-existing election laws, can go into effect w/o preclearance from the Dept. of Justice – Approval by DOJ Voting Rights Act of 1965 • Preclearance will not be given if 1 of the following is violated: – Location of polling places – Boundaries of electoral districts – Deadlines in election process – From ward to at-large elections – Qualifications of candidates must meet to run for office