Unit 5B: Two Dimensional Motion Review Note: review is due when

Unit 5B: Two Dimensional Motion Review
Note: review is due when the late bell rings on Thursday, 12/4 or Friday, 12/5 to earn 5 extra points of credit.
1. I have reviewed all of my notes, practice problems, and warm-ups. Yes ________ No ______
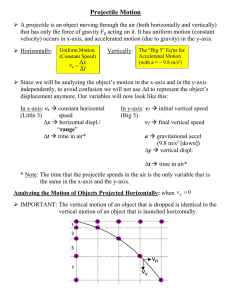
2. Label the variables, in the formulas below, and include the units.
V f
- V i
Δx = V i
* t + ½ at 2 a =
__ t
__
__
3. Describe the concepts below. __
__ a. Trajectory
__
__ b. Parabola
__
__ c. Range
__
__ d. Vertical distance
__
__ e. Horizontal distance
__
__
4.
List two examples of projectile motion.
__
__
__
5.
List two examples of linear motion.
6.
How are projectile motion and linear motion the same? How are they different?
7.
A projectile that is launched horizontally has a vertical and horizontal component. Explain what you know about an object’s horizontal velocity (initial and final) and it’s vertical velocity (initial and final).
8.
Draw a diagram of an object’s trajectory.
9.
Draw a diagram of a projectile being launched horizontally from a table 5 m high. The object lands 3 meters from the base of the table. Label the diagram with the terms height, range, horizontal distance, and vertical distance.
10.
If two identical objects are launched horizontally and dropped from the same height will they hit the ground at the same time? Support your answer.
11.
Circle all that apply to the following statement. Projectile motion is an example of
a) linear motion b) two dimensional motion
Use the graph below to answer question 12 and 13.
12.
What launch angles will result in a range of 10 meters?
13.
What launch angle is required for the projectile to travel 15 meters?
Use the words horizontal and vertical to fill in the sentence below.
14.
The ________________component of a projectile is constant/uniform and the _________________ component of a projectile is accelerated motion.
15.
Use your knowledge of projectile motion to quantify the horizontal and vertical initial velocity and acceleration.
16.
For each point on the trajectory draw and describe the objects horizontal and vertical velocities.
Use the following information to answer questions 17 thru 20. A student rolls a marble off of a 2 m tall table and it lands 3 m away. a t
Horizontal (X) Vertical (Y)
∆𝑥
V i
∆𝑦
V i a t
17.
Calculate the time the marble was in the air.
U: S:
E:
18.
Calculate the initial horizontal velocity .
U: S:
S:
S:
E:
19.
Calculate the final vertical velocity.
U: S: S:
E:
20.
What if the initial horizontal velocity changed to 1.5 m/s and time remained the same, what would the new range be?
U: S: S:
E: