09
Pure Competition in the Long
Run
McGraw-Hill/Irwin
Copyright © 2012 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
The Long Run in Pure Competition
• In the long run:
• Firms can expand or contract
capacity
• Firms enter and exit the industry
LO1
9-2
Profit Maximization in the Long Run
• Easy entry and exit
• The only long run adjustment we
•
•
LO2
consider
Identical costs
• All firms in the industry have identical
costs
Constant-cost industry
• Entry and exit do not affect resource
prices
9-3
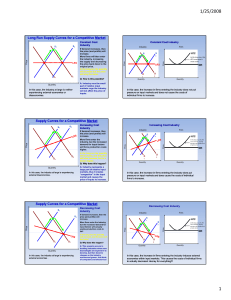
Long-Run Equilibrium
• Entry eliminates profits
• Firms enter
• Supply increases
• Price falls
• Exit eliminates losses
• Firms exit
• Supply decreases
• Price rises
LO3
9-4
Entry Eliminates Economic Profits
P
P
S1
MC
ATC
$60
50
MR
40
S2
$60
50
D2
40
D1
0
100
(a)
Single Firm
LO3
q
0
80,000 90,000 100,000
Q
(b)
Industry
9-5
Exit Eliminates Losses
P
P
S3
MC
ATC
$60
S1
$60
50
50
MR
D1
40
40
D3
0
100
(a)
Single Firm
LO3
q
0
80,000
90,000
100,000 Q
(b)
Industry
9-6
•
•
•
LO4
Long Run Supply
Constant cost industry
• Entry/exit does not affect LR ATC
• Constant resource price
• Special case
Increasing cost industry
• Most industries
• LR ATC increases with expansion
• Specialized resources
Decreasing cost industry
9-7
LR Supply: Constant-Cost Industry
P
P1
P2 $50
Z3
Z1
Z2
S
P3
D1
D3
0
LO4
Q3
90,000
Q1
100,000
D2
Q2
110,000
Q
9-8
LR Supply: Increasing-Cost Industry
P
S
P2 $55
Y2
P1 $50
Y1
P3 $40
Y3
D2
D1
D3
0
LO4
Q3
90,000
Q1
100,000
Q2
110,000
Q
9-9
LR Supply: Decreasing-Cost Industry
P
P3 $55
X3
X1
P1 $50
X2
P2 $40
D3
S
D2
D1
0
LO4
Q3
90,000
Q1
100,000
Q2
110,000
Q
9-10
Pure Competition and Efficiency
• In the long run, efficiency is achieved
• Productive efficiency
• Producing where P = min. ATC
• Allocative efficiency
• Producing where P = MC
LO5
9-11
Pure Competition and Efficiency
Single Firm
Market
P=MC=Minimum
ATC (Normal Profit) MC
Consumer
Surplus
S
Price
Price
ATC
P
MR P
Producer
Surplus
D
0
LO5
Qf
Quantity
0
Qe
Quantity
9-12
Dynamic Adjustments
• Purely competitive markets will
•
LO6
automatically adjust to:
• Changes in consumer tastes
• Resource supplies
• Technology
Recall the “Invisible Hand”
9-13
Technological Advance: Competition
• Entrepreneurs would like to increase
profits beyond just a normal profit
• Decrease costs by innovating
• New product development
LO6
9-14
Creative Destruction
• Competition and innovation may lead
to “creative destruction”
• Creation of new products and
methods destroys the old products
and methods
LO6
9-15
Efficiency Gains from Entry
• Patent protected prescription drugs earn
•
substantial economic profits for the
pharmaceutical company.
Generic drugs become available as the
patent expires on the existing drug.
• Results in a 30-40% reduction price
• Greater consumer surplus and
efficiency
9-16
Efficiency Gains from Entry
a
S
P1
b
c
d
f
P2
D
Q1
Q2
9-17