HISTORY OF LIFE Section 14
advertisement
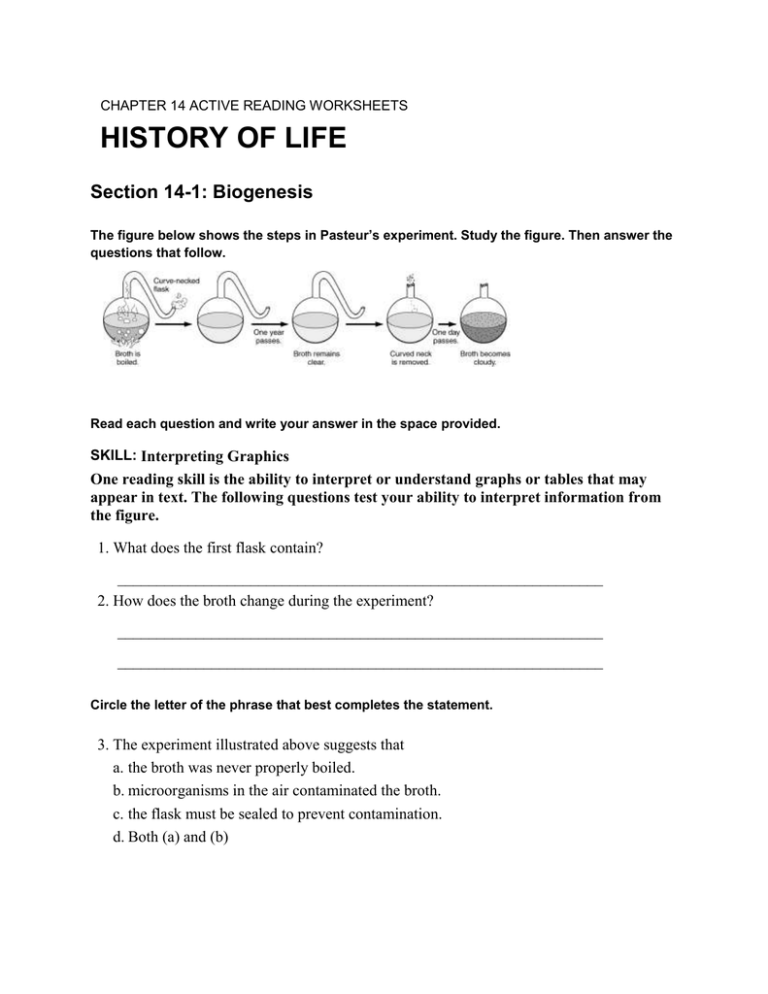
CHAPTER 14 ACTIVE READING WORKSHEETS HISTORY OF LIFE Section 14-1: Biogenesis The figure below shows the steps in Pasteur’s experiment. Study the figure. Then answer the questions that follow. Read each question and write your answer in the space provided. SKILL: Interpreting Graphics One reading skill is the ability to interpret or understand graphs or tables that may appear in text. The following questions test your ability to interpret information from the figure. 1. What does the first flask contain? ______________________________________________________________ 2. How does the broth change during the experiment? ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ Circle the letter of the phrase that best completes the statement. 3. The experiment illustrated above suggests that a. the broth was never properly boiled. b. microorganisms in the air contaminated the broth. c. the flask must be sealed to prevent contamination. d. Both (a) and (b) CHAPTER 14 ACTIVE READING WORKSHEETS HISTORY OF LIFE Section 14-2: Earth’s History Read the passage below, which covers topics from your textbook. Answer the questions that follow. Methods of establishing the age of materials include the technique known as radioactive dating. Recall that the atomic number of an element is the number of protons in the nucleus. All atoms of an element have the same atomic number, but their number of neutrons can vary. Atoms of the same element that differ in the number of neutrons they contain are called isotopes. Some isotopes have unstable nuclei, which tend to undergo radioactive decay; that is, their nuclei tend to release particles, radiant energy, or both. Such isotopes are called radioactive isotopes. Rates of decay of radioactive isotopes have been determined for many isotopes. The length of time it takes for one-half of any size sample of an isotope to decay is called its half-life. Read each question and write your answer in the space provided. SKILL: Identifying Main Ideas One reading skill is the ability to identify the main idea of a passage. Frequently a main idea is accompanied by supporting information that offers detailed facts about the main idea. 1. What is radioactive dating? ______________________________________________________________ 2. What causes an isotope to undergo radioactive decay? ______________________________________________________________ 3. What does half-life refer to? ______________________________________________________________ Circle the letter of the word or phrase that best completes the sentence. 4. Isotopes undergoing radioactive decay may release a. radiant energy. b. particles. c. carbon. d. Both (a) and (b) Skills Worksheet History of Life In the space provided, explain how the terms in each pair differ in meaning. 1. radioactive isotope, half-life ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ 2. biogenesis, spontaneous generation ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ 3. cyanobacteria, archaebacteria ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ 4. mass number, isotope ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ History of Life continued In the space provided, write the letter of the description that best matches the term or phrase. _____ 5. radiometric dating _____ 6. endosymbiosis _____ 7. biogenesis _____ 8. isotope _____ 9. half-life _____ 10. ribozyme _____ 11. ozone _____ 12. microsphere a. length of time it takes for one-half of a radioactive isotope to decay to a stable form b. substance in the atmosphere composed of three oxygen atoms that absorbs ultraviolet radiation c. RNA molecule that can act as a catalyst d. calculation of the age of an object by measuring the proportions of radioactive isotopes of certain elements e. spherical structures composed of protein molecules organized as a membrane f. the theory that mitochondria and chloroplasts evolved from symbiotic prokaryotes g. principle which states that all living things come from other living things h. atoms of an element that have different numbers of neutrons in the nucleus SECTION 14-1 REVIEW BIOGENESIS VOCABULARY REVIEW Define the following terms. 1. biogenesis _________________________________________________________ 2. spontaneous generation _______________________________________________ 3. vital force _________________________________________________________ MULTIPLE CHOICE Write the correct letter in the blank. ______ 1. One of the observations that led people to think that life could arise from nonliving things was that a. maggots turned into oval cases from which flies eventually emerged. b. fish appeared in ponds that had been dry the previous season. c. large fish developed from smaller fish, which hatched from fish eggs. d. fish grew larger by eating other living things, such as flies. ______ 2. The purpose of the netting in Redi’s experiment was to prevent a. maggots from leaving the jar. b. air from leaving the jar. c. adult flies from entering the jar. d. bacteria from entering the jar. ______ 3. In the experimental group in Spallanzani’s experiment, the a. broth remained clear. b. flask contained no broth. c. broth was not boiled. d. flask was not sealed. ______ 4. Spallanzani’s opponents disagreed with his conclusion that microorganisms from the air contaminated the boiled meat broth. They argued that Spallanzani a. heated the flasks too long, killing the microorganisms in the broth. b. heated the flasks too long, destroying the “vital force” in the air inside the flasks. c. waited too long before he sealed the flasks after heating them. d. accidentally contaminated the broth when he sealed the flasks. ______ 5. In Pasteur’s experiment, the function of the curved neck on the flask was to prevent a. air from entering the body of the flask. b. air from leaving the body of the flask. c. solid particles from entering the body of the flask. d. broth from spilling out of the flask. SHORT ANSWER Answer the questions in the space provided. 1. What observations made in the 1600s and 1700s led some people to believe that there was a “vital force” in the air? _______________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ 2. Why did Spallanzani boil the broth in his experiment? ______________________ _______________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ 3. How did Pasteur’s experiment differ from Spallanzani’s experiment? _______________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ 4. How did Pasteur’s experiment answer the objections raised by supporters of the “vital force” hypothesis? ________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ 5. Critical Thinking How might the believers in spontaneous generation have disputed Redi’s onclusion if Redi had not used a control group? ___________________________ _______________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ STRUCTURES AND FUNCTIONS The diagrams below illustrate steps in the control and experimental groups of Spallanzani’s experiment. In the spaces provided, list the steps in each group in their proper order. A step may be used in more than one group. SECTIO N 14-2 REVIE W EARTH’S HISTORY VOCABULARY REVIEW Explain the relationship between the terms in each of the following pairs of terms. 1. radioactive isotope, radioactive dating __________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ 2. radioactive decay, half-life ____________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ 3. microsphere, coacervate ______________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ MULTIPLE CHOICE Write the correct letter in the blank. ______ 1. The age of Earth is estimated to be a. about 700,000 years. b. about 50 million years. c. about 400 million years. d. more than 4 billion years. ______ 2. Sulfur has an atomic number of 16. Therefore, the isotope sulfur-35 has a. 19 protons and 16 neutrons. c. 16 protons and 19 neutrons. b. 35 protons and 16 neutrons. d. 16 protons and 35 neutrons. ______ 3. When performing radioactive dating, scientists measure the a. number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of a radioactive isotope. b. amount of a particular radioactive isotope contained in a material. c. age of a living organism that is exposed to radioactive isotopes. d. rate at which the mass of an object decreases over time. ______ 4. Carbon-14 dating is useful for estimating the age of a. relatively young organic material.c. Earth. b. old rocks. d. the solar system. ______ 5. Researchers using the technique of Miller and Urey have been able to produce a. amino acids and nucleotides. c. ATP and mitochondria. b. proteins and DNA. d. cell membranes and simple cells. SHORT ANSWER Answer the questions in the space provided. 1. Explain how the half-life of a radioactive isotope affects the usefulness of that isotope in dating specific types of rocks. __________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ 2. Why do some scientists think that areas protected from the atmosphere might have favored the production of organic compounds on early Earth? ______________________ _______________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ 3. Why was the discovery of microspheres and coacervates an important contribution to the understanding of how life might have originated on Earth? ___________________ _______________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ 4. Critical Thinking Does radioactive dating with isotopes of uranium and thorium provide an estimate of the beginning, middle, or end of the period of Earth’s formation? Explain your answer. _______________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ STRUCTURES AND FUNCTIONS Use the figure to answer the following question. The graph below represents the radioactive decay of an isotope. If the half-life of thorium230 is 75,000 years, how old is a rock that contains only 1/16th of its original thorium-230? Show your calculations in the space below.
![tutorial #14 [nuclear physics and radioactivity] .quiz](http://s3.studylib.net/store/data/008407305_1-1884988a9e5162a6b7a2b0d0cf8c83c5-300x300.png)





