Classification Study Guide
advertisement

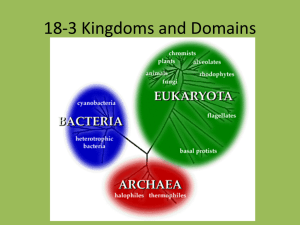
Classification Study Guide • 1. To what domain does the eubacteria kingdom belong? • Bacteria • 2. Bacteria are what type of cell? • Prokaryotes • 3. What type of cell does not contain a nucleus? • Prokaryotes • • • • • 4. Where do you find Eubacteria? Everywhere 5. Are all eubacteria harmful? No, some are helpful 6. To which domain does the Archeabacteria Kingdom belong? • Archaea • 7. How many cells do archeabacteria consist of? • one, unicelluar • 8. Where do you find archeabacteria? • In extreme environments such as hot springs and salt lakes • 9. What makes archeabacteria and eubacteria structurally different? • Their cell membranes are made of different substances • 10. What four kingdoms are found in the Eukarya Domain? • Plant, Animal, Fungi and Protists • 11. What type of cells are eukaryotes? • Cells with a defined nucleus • 12. What kingdom consists of unicellular and a few multi-cellular organisms? • Protists • 13. How are protists different from bacteria? • Protists are eukaryotic and bacteria are prokaryotic. • 14. In what habitat can you find protists? • Moist environments such as rivers, lakes, and ponds • 15. In what two ways are protists classified? • By movement and how they obtain nutrition • 16. What are the three types of protists? • plant like, animal like, and fungi like • 17. Are plant cells eukaryote or prokaryotes, explain. • Eukaryotes because all plant cells contain a nucleus. • 18. What kingdoms in the eukarya domain are solely made up of multi-cellular organisms? • Plant and Animal • 19. What is an autotroph and in which kingdom(s) do you find them? • Plant kingdom, they make their own food. • 20. What are the two major types of plants? • Vascular and non-vascular • 21. Where do you find non-vascular plants? Why? • Near water, because they do not contain the tissue needed to move water. • 22. What are three examples of non-vascular plants? • mosses, liverworts, and hornworts • 23. What characteristics make vascular plants able to grow tall? • The tube like structure insides the plant • 24. In which domain do you find the Kingdom Fungi? • Eukarya • 25. How are fungi different from plants? • They cannot make their own food • • • • 26. What is the habitat for fungi? Fungi live on dead or decaying matter 27. What are the three types of fungi? Yeast, mushrooms and mold • • • • • 28. What term is used to describe fungi? Decomposers 29. How do fungi absorb food? By absorbing in through hyphae 30. What are the tubes inside a mushroom called? • hyphae • 31. In which domain do you find the animal kingdom? • Eukarya • 32. What is the term used to describe organisms that cannot make their own food? • Consumers / Heterotrophs • 33. What type of cells do animals consist of? • Eukaryotic • 34. The animal kingdom is made up of what percentage of invertebrates? • 97% • 35. What invertebrates look like brightly colored flowers and live in colonies? (not the phylum, just the animal names) • Coral and Anemones • 36. What characteristics do arthropods share? • Arthropods have segmented bodies and exoskeletons • 37. What differences make up the two major classes of fish? • Skeletons, one class contains boney fish, the other cartilage fish • 38. What class or vertebrates have a “double life”? • Amphibian • • • • 39. Give an example of an amphibian Frog, Toad, Salamander, Caecilian 40. Which reptiles lack legs? Snakes • 41. What characteristics do mammals share? • All mammals have hair, mammary glands, breath air, contain a four chambered heart and are endotherms. • 42. What is the correct order of the levels of classification? • Domain, Kingdom, Phylum, Class, Order, Family, Genus, & Species. – Did King Phillip Come Over For Grape Soda? Students will choose one the following to answer on their test. • DISCUSSION QUESTION: What are the characteristics of invertebrates? Give three examples and describe them. • DISCUSSION QUESTION: Compare and contrast vascular and non-vascular plants (What are the differences and similarities between vascular and non-vascular plants?) • DISCUSSION QUESTION: What characteristics do Class Aves (birds) organisms share? Also, give an example of a specific avian.