Guided Notes Planetary Science Part 1-3
advertisement

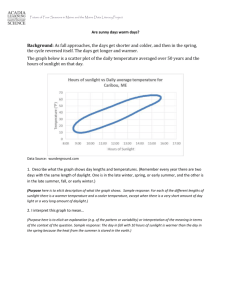
Planetary Science Notes Part 1 Name__________________________ Class______________ Date___________________________ I. Round Earth/Flat Earth A. Sailing Ships 1. The___________________is where the sky and Earth appear to meet. 2. Your____________________ is the straight path taken by light from an object to your eye. 3. Ships sailing out to see appear to _____________________on the horizon. 4. If the Earth were__________, you’d see the entire ship out on the horizon. B. Shadow Evidence 1. Eratosthenes found the circumference of the Earth using sticks, ______________, some geometry, and feet! 2. Light rays travel in ________________lines. 3. Because the Sun is so large and so far away, all rays of light hitting anywhere on Earth are ________________ to one another. 4. A pole only casts a ____________ when the sun shines on its ________, not on its top. 5. Poles on a _____________ surface cast shadows of different __________. 6. The shadows are longer at higher _________________. 7. ___________________ is when the sun is directly overhead in the sky (does not mean 12pm noon!) 8. Shadows in _________________ are longer than shadows in summer due to the changes in the ____________of the sun. II. Day and Night 1. Earth ___________, or spins on its axis in a ___________________ direction. (West to East) 2. Day and ___________ are a result of ____________________ 3. The _______ appears to move across the sky from _______ to _______ due to Earth’s ______________. 4. Shadows change during the day due to the changing position of the ________ in the sky. 5. The _______is a source of _________ that illuminates Earth during the day. 6. When light falls on a _____________ object, like a ___________, exactly _________ is in the light and half is in the dark. 7. The Earth ___________ on its __________ once every _______, giving the illusion of a _________ that rises and sets. 8. One complete _____________ of our planet describes one complete _________. One rotation of _________ is one day, or about _____ hours. III. Seasons 1. The earth ________________ (orbits) around the ________-about _____________ days--one ___________. 2. The ___________ axis --________ gives us _______________. 3. The angle of ______________ affects _______________--the more direct the __________ of sunlight the ___________ it is. The angle varies due to Earth's spherical shape. Ex. It is warmer at the _____________ because it gets more ____________ sunlight, and cooler at the poles because the sunlight is at an angle. 4. Earth's ______ affects not only the intensity of sunlight falling on earth, but also the number of ______________________. 5. The number of daylight __________ changes from ___________to season. 6. In the No. Hemisphere around _______________ is longest day of year. This is called the Summer_________________. 7. In the No. Hemisphere around _____________________ is the shortest day of the year. This is called the __________________Solstice. 8. The Vernal Equinox, or __________________ is around __________ 21 and _______________ Equinox, or Fall is around ___________ 21. Sunlight spreads ____________ across equator and there is about 12 hours of _________ and night across the globe. The amount of daylight varies due to refraction of light in the ____________________. 9. The Earth is actually a little ____________ to the sun in its orbit during __________. This is called ___________________. 10. The Earth is a little ____________ from the sun in _________________. This is called _________________.