properties of capacitors
advertisement

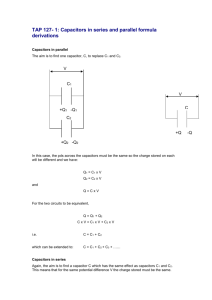
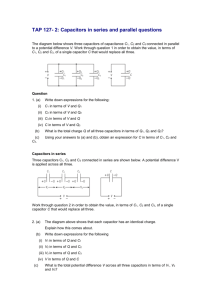
1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Proper understanding of the definition of capacitors. Identify the relationship between a resistor and a capacitor. Calculate capacitance in series and parallel circuit and in terms of same capacitance value. Classify capacitors according to materials and usage. Relate the topic to everyday living. A capacitor is a device that stores electrons. The basic capacitor is made up of two conductors separated by an insulator, or dielectric. Depending on how the capacitor is built, the dielectric can be made of paper, plastic, mica, ceramic, glass, a vacuum or any other such non conductive material. Capacitor electron storing ability (its capacitance) is measured in Farads. 1 Farad is actually a huge number of electrons (6, 280, 000, 000, 000, 000, 000 electrons to be exact), so we usually rate capacitors in microfarads (µF) and picofarads (pF). 1 µF is equal to 0.000001 F 1 pF is equal to 0.000000000001 F Capacitors comes in a variety of sizes, shapes, models, or if you so desire they can be manufactured by your specifications. Capacitors also come in a variety of materials, to name a few : Aluminum foil, Polypropylene, Polyester (Mylar), Polyesterene, Polycarbonate, Kraft Paper, Mica, Teflon, Epoxy, Oil-filled, Electrolyte, Tantalum, and the list goes on. Latest product (in reseach) is Nobium. The value of a capacitor can vary from a fraction of a picofarad to more than a million µF (µ means ´micro´). Voltage levels can range from a couple to a substantial couple hundred thousand volts. It can store electric charge even though the voltage source is already disconnected. It can discharge electrical voltages. An early classification is settled for capacitors. These were stablished and categorized into four namely (a)non-polarized , (b)polarized, (c) variable, and (d) trimmer. Non-polar capacitor is a type of capacitor that can be connected any way in a circuit. In other words, there is no positive or negative. Common types of non-polar capacitors are ceramic,mica and some electrolytic. There are two types of nonpolarized capacitors. The plastic foil that are non polarized by nature and electrolytic non polarized capacitors that are actually two capacitorsin series (back to back) so that the result is non polarized with half the capacitance. A capacitor stores electric charge. This type must be connected the correct way around. A capacitor stores electric charge. A capacitor is used with a resistor in a timing circuit. It can also be used as a filter, to block DC signals but pass AC signals. Polarized capacitors are the electrolytic type or tandalium type. They have large leakage current if the voltage is inverted. They are cheaper than equivalent non-polarized capacitors. They are sometimes physically smaller that non-polarized equivalents. They are meant for AC signals respectively. Electrolytic capacitors have a polarity unlike other capacitors. This is due to the fact that aluminum oxide layer is held in place by the electric field, and when reversebiased, it dissolves into the electrolyte. This allowsa short circuit between the electrolyte and the aluminum. Non-polarized capacitor has a big size with the smaller capacitance, and is used both in DC or AC circuits, low or high frequencies. Polarized capacitor has a small size with the large capacitance, and is used only in DC circuits or circuits related to DC current. Non-polarized capacitor has a very small leakage current, high frequency response of up to hundreds of GHz up to types. Polarized capacitor has a large leakage current low frequency response of only up to about tens of kHz at aluminum or 1MHz at tantalium caps. In general, they cannot replace each other!!! A variable capacitor is a capacitor whose capacitance can be varied. These are usually made up of one or more moving plates and one or more non moving plates separated by the dielectric. By moving the plates, we can vary the capacitance. A variable capacitor is used in a radio tuner. This type of variable capacitor (trimmer) is operated with a small screwdriver or similar tool. It is designed to be set when the circuit is made and then left without further adjustment. FIXED / NORMAL /NON-POLARIZED Ceramic capacitors – dip guard, monolithic (axial leads), monolithic (radial leads), disc, surface mount Film capacitors – polyester (axial leads), polyester (radial leads), polypropylene (axial leads), polypropylene (radial leads), polystyrene (axial leads) POLARIZED CAPACITORS Aluminum Electrolytic capacitors – axial leads, radial leads, computer grade, snap mount, twist lock, surface mount Tantalum capacitors – solid tantalum (axial leads), solid tantalum (radial leads), foil tantalum (axial leads),foil tantalum (radial leads), dipped tantalum, wet tantalum, surface mount VARIABLE CAPACITORS 1. Semiconductor diodes – rectifier, zener, LED 2. Bipolar Junction Transistors (BJT) – PNP, NPN 3. Integrated Circuit