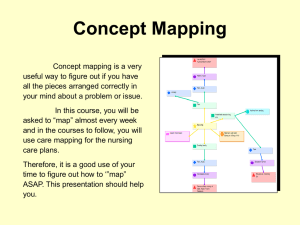
File
advertisement

Diagnosing Learning Outcomes 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Differentiate various types of nursing diagnoses. Identify the components of a nursing diagnosis. Compare nursing diagnoses, medical diagnoses, and collaborative problems. Identify basic steps in the diagnostic process. Describe various formats for writing nursing diagnoses. Learning Outcomes 6. 7. 8. 9. Describe the characteristics of a nursing diagnosis. List guidelines for writing a nursing diagnosis statement. Describe the evolution of the nursing diagnosis movement, including work currently in progress. List advantages of a taxonomy of nursing diagnoses. Nursing diagnosis identified and developed in 1973 because nursing role in the ambulatory nursing setting needed to be identified In 1977 the international recognition of the nursing diagnosis is occur In 1982 the name North America Nursing Diagnosis Association (NANDA) was accepted Purpose of it: to define, refine and promote a taxonomy of nursing diagnostic terminology of general use to professional nurses The Nursing Process Nursing Diagnosis (According to NANDA) define as: Clinical Judgment or conclusion about individual, family, or community response to actual or potential health problem standardized NANDA names for the diagnosis (diagnostic label or patient problem statement) Nursing diagnosis compose of diagnostic label and etiology NANDA – North American Nursing Diagnosis Association Identifies nursing functions Creates classification system Establishes diagnostic labels Types of Nursing Diagnoses Actual Diagnosis ◦ Problem presents at the time of the assessment ◦ Based on presence of associated signs and symptoms ◦ Ineffective breathing pattern Risk Diagnosis ◦ Problem does not exist Presence of risk factors indicate that the problem is likely to develop unless nursing intervene Risk for infection Types of Nursing Diagnoses Wellness Diagnosis ◦ Readiness for enhanced family coping Possible Diagnosis ◦ Evidence about a health problem incomplete or unclear ◦ Requires more data to either support or to refuse it Syndrome Diagnosis ◦ Associated with a cluster of other diagnoses Components of a Nursing Diagnosis Problem statement (diagnostic label) ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ Describes the client’s health problem or response Describe the client health status clearly and concisely Need to be specific Need qualifiers (words have been added to some NANDA label to give additional meaning) as: * Deficit: inadequate in amount, quality or degree, not sufficient * Impaired: weakened, damaged *Decreased: less in size, amount or degree * Ineffective: not producing the desired effect *compromised Components of a Nursing Diagnosis Etiology (related factors and risk factors) ◦ Identifies one or more probable causes of the health problem ◦ Possible causes should be differentiated because each may require different nursing intervention Components of a Nursing Diagnosis Defining characteristics ◦ Cluster of signs and symptoms indicating the presence of a particular diagnostic label (actual diagnoses) ◦ Factors that cause the client to be more vulnerable to the problem (risk diagnoses) Nursing and Medical Diagnosis, and Collaborative Problems Differences Based on ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ Description Orientation Responsibility for diagnosing Treatment orders Nursing focus Nursing actions Duration Classification system Medical vs. Nursing diagnosis Medical diagnosis Nursing diagnosis Identifies conditions the MD is licensed & qualified to treat Identifies situations the nurse is licensed & qualified to treat Medical vs. Nursing diagnosis Medical diagnosis Nursing diagnosis Identifies conditions the MD is licensed & qualified to treat Identifies situations the nurse is licensed & qualified to treat Focuses on illness, injury or disease processes Focuses on the clients responses to actual or potential health / life problems Medical vs. Nursing diagnosis Medical diagnosis Nursing diagnosis Remains constant until a cure is effected Changes as the clients response and/or the health problem changes Medical vs. Nursing diagnosis Medical diagnosis Nursing diagnosis Remains constant until a cure is effected Changes as the clients response and/or the health problem changes i.e. Breast cancer i.e. Knowledge deficit Powerlessness Grieving, anticipatory Body image disturbance Individual coping, ineffective Diangosis Nursing diagnosis Medical diagnosis Breathing patterns, ineffective Activity intolerance Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease Cerebrovascular accident Pain Appendectomy Body image disturbance Amputation Body temperature, risk for altered Strep throat Collaborative Problems Involve human response mainly to Physiologic complications of disease, tests, treatments Oriented to pathophysiology Nurse and physician diagnose Physician orders definitive treatment Independent nursing action for monitoring and preventing Dependent nursing actions for treatment Present when disease/situation present No classification system Diagnostic process Steps in Diagnostic Process Analyzing Data ◦ Compare data against standards and norms (identifying significant cues) ◦ Cluster cues (generate hypothesis) ◦ Identify gaps and inconsistencies Compare Data: Cues considered significant if it does any of the following: 1. Point to +ve or –ve change in patient health status 2. Varies from norms of client population 3. Indicate development delay Cues and Inferences Cues = signs and symptoms Cues Inference = what you think, a judgement about the cues Inference Swollen finger Reddened Painful Broken finger Cluster Cues: - - - Clustering: process of determining the relatedness of facts and determine whether any pattern present Beginning of synthesis Involve making inferences about data Identify gaps and inconsistencies: It should include final check up to ensure that data complete and correct Source of conflict: measurement error, unreliable report Data can be found in nursing assessment, patient history Identifying health problems, risks, and strengths: - Determine problems risks - Determine strength Formulating diagnostic statements Writing Nursing Diagnoses Basic Two-Part Statement ◦ Problem (P) ◦ Etiology (E) Writing Nursing Diagnoses Basic Three-Part Statement (PES format) ◦ Problem (P) ◦ Etiology (E) ◦ Signs and symptoms (S) Problem Related to Etiology As manifested by S&S Situational low self-esteem r/t Feeling of rejection by husband a.m.b a.e.b Hypersensitivity to criticism; stated ‘I don’t know if I can manage by myself’ and reject positive feedback Noncompliance (diabetic diet) related to unresolved anger about diagnosis as manifested by S- ‘I forgot to take my pills’ ‘I can’t live without sugar in my food’ O- weight 98kg (gain of 4.5kg) blood pressure 190/100 mmHg Writing Nursing Diagnoses One-Part Statement ◦ Wellness (e.g. readiness for enhanced parenting) ◦ Syndrome: a diagnosis that is associated with a cluster of other diagnoses: Risk for Disuse syndrome (experienced by long-term bedridden. Clusters of diagnoses associated with this syndrome include: Impaired physical mobility Risk for impaired tissue perfusion Risk for activity intolerance Risk for constipation Risk for infection Risk for injury…….etc Example of Nursing Dx Ineffective therapeutic regimen management R/T difficulty maintaining lifestyle changes and lack of knowledge AEB B/P= 160/90, dietary sodium restrictions not being observed, and client statements of “ I don’t watch my salt” “It’s hard to do and I just don’t get it”. Guidelines for Writing a Diagnostic Statement State in terms of a problem, not a need. Word the statement so that it is legally advisable. Use nonjudgmental statements. Make sure that both elements of the statement do not say the same thing. Be sure that cause and effect are correctly stated. Word the diagnosis specifically and precisely Use nursing terminology rather than medical terminology to describe the client’s response and probable cause of client’s response INEFFECTIVE BREATHING PATTERNS DEFINITION Ineffective Breathing Patterns: State in which a person experiences an actual or potential loss of adequate ventilation related to an altered breathing pattern DEFINING CHARACTERISTICS Major (Must Be Present, One or More) Changes in respiratory rate or pattern (from baseline) Changes in pulse (rate, rhythm, quality) Minor (May Be Present) Orthopnea Tachypnea, hyperpnea, hyperventilation Dysrhythmic respirations. Splinted/guarded respirations Diagnosis (P) Related to r/t (E) As evidenced by Ineffective Breathing Patterns Immobility and chest pain Secondary to abdominal surgery (S) in respiratory rate from 12 to 22 pulse rate 88 to 104 and irregular