eisenhower in the white house chapter 31, sec. 1&2
advertisement
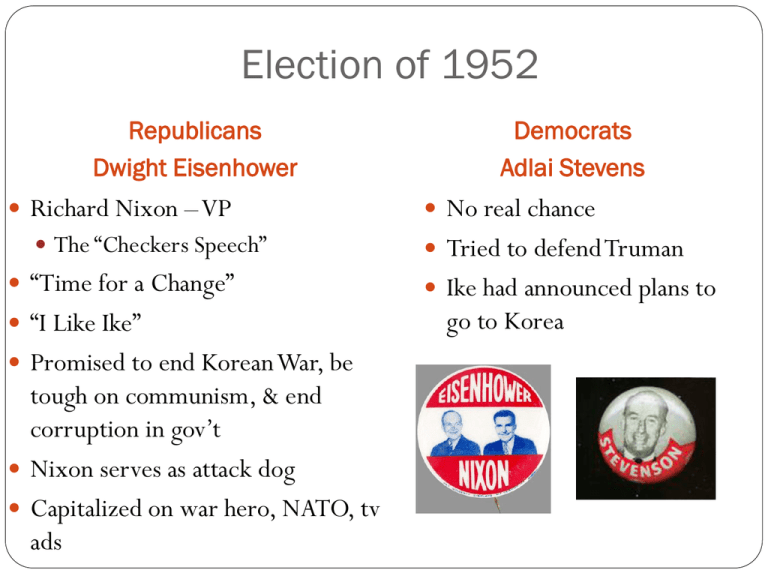
Election of 1952 Republicans Dwight Eisenhower Richard Nixon – VP The “Checkers Speech” “Time for a Change” “I Like Ike” Promised to end Korean War, be tough on communism, & end corruption in gov’t Nixon serves as attack dog Capitalized on war hero, NATO, tv ads Democrats Adlai Stevens No real chance Tried to defend Truman Ike had announced plans to go to Korea Eisenhower’s Style Very popular! Liked to work behind the scenes Relied heavily on his cabinet – became a true advisory board Administration became known as the “hidden hand presidency” Dynamic Conservatism: Small gov’t Modern Republicanism To slow the growth of the federal gov’t Cutting spending, reducing taxes, balancing budget Eisenhower’s administration…. Very middle of the road course Liberal with individuals; conservative with their money Eisenhower & the economy… 50s growth due to consumer credit/advertising Lowers Truman’s defense spending On business and labor…. Minimal business regulations Big business / many mergers Union growth slow; AFL-CIO merge; Teamsters corruption Eisenhower & the New Deal Programs… Debate was over how much larger they should become Social Security and unemployment increased During Eisenhower’s Presidency Operation “Wetback” A million illegal Mexican immigrants sent back Didn’t want to undercut program of legally imported farm workers begun in WWII In 1959: Alaska becomes 49th state Hawaii becomes 50th state Domestic Programs in Response to Cold War Interstate Highway System – why? Nuclear Arms Race: Hydrogen Bomb: US ‘52; Soviets ‘53 US Policy – Deterrence; conventional air power Soveits – long-range ICBMs NASA Established in response to Soviet success with Sputnik in ‘57 US Mercury I – ’58 Education – National Defense Education Act Math & science stress (STEM programs) AP Programs ; College Loans Ike’s Health & The 25th Amendment Ike’s health problems were an issue in the election of ‘56 Led to the 25th amendment on Presidential Disability 1. If P dies, resigns, retires = VP moves up 2. If VP office vacant = P appoints new VP 3. If P going to be unable to carry out duties, must tell Congress & VP becomes acting P 4. If P unable to inform Conress & is unable to carry out duties, VP & Cabinet go to Congress and have VP appointed as acting P CIVIL RIGHTS: Jim Crow still rules South Only 20% less were registered to vote Emmett Till, 1955 Jackie Robinson breaks color barrier in sports, 1947 Brown v. Bd. of Education, Topeka, KS, 1954 – Reverses Plessy v. Ferguson Thurgood Marshall (center) Ike: did not complete Truman’s integration of military & did not believe racial equality could be achieved by government action Ike’s biggest contribution: appointing C.J. Earl Warren THE LITTLE ROCK 9 Issue is forced integration of 9 black students into Little Rock’s Central High Gov. Faubus mobilized National Guard to prevent Little Rock 9 from entering the school / town mob Pres. Eisenhower federalizes National Guard/sends paratroopers to escort the 9 in – soldier bodyguards remain Ike sets up permanent Civil Rights Commission to investigate violations and authorizes injunctions to protect voting rights CRITICISMS OF IKE: Criticized for lack of attention to civil rights Civil Rights Bill of 1957 is mildest one possible Criticized for not doing enough to protect natural resources IKE & FOREIGN POLICY KOREA: Armistice in Korea in ’53 after threat of nuclear weapons Also, Stalin died in ’53 & Khrushchev wants to end war also US losses – 54,000 Chinese & Korean losses – over a million NEW LOOK POLICY Sec. of State John Foster Dulles Containment is insufficient – promised “Massive Retaliation and Liberation” Need to prevent small wars from happening by threat of nuclear weapons “New Look” in defense policy – no large conventional army; buildup of nuclear deterrents instead Gives U.S. more “bang for the buck” “Brinkmanship” willingness to go to the brink of war to force the other side to back down Problems? Progress Through Science Atomic Anxieties: “Duck-and-Cover Generation” Atomic Testing: 1946-1962 U. S. exploded 217 nuclear weapons over the Pacific and in Nevada. SOVIET-AMERICAN VISITATIONS 1959 The Kitchen Debate VP Nixon & Soviet Premier Khrushchev Khrushchev attempts Disneyland, Sept. – turned away Meets with Ike at Camp David Wants West Berlin evacuated Agrees to summit meeting on disarmament with U.S. British, French in 1960 U-2 INCIDENT • U-2 spy plane • 1960 • Shot down by Soviet guided missile • Francis Gary Powers FOREIGN POLICY – LATIN AMERICA Why resentment toward U.S.? Guatemala? What happened to Nixon’s “goodwill tour” in Venezuela and Peru? CUBA: Castro takes over 1959; confiscates all U.S. property in Cuba U.S. cuts off imports of Cuban sugar Castro establishes ties with Soviets Anti-Castro Cubans (1 million + between 1960 & 2000) head to U.S. U.S. breaks off relations in Cuba in ’61 after Cuban Missile crisis & imposes trade embargo….still in effect Khrushchev threatens attack if U.S..? 1950s Society Changes in the workplace: Mechanization Led to many more “white collar” jobs than “blue collar” jobs – what’s the difference? Changes in wealth: Average income of American family tripled Home ownership up Materialism Rampant!– “keeping up with the Jones” Conformity Rules People more concerned with outward approval Well-Defined Gender Roles The ideal modern woman married, cooked and cared for her family, and kept herself busy by joining the local PTA and leading a troop of Campfire Girls. She entertained guests in her family’s suburban house and worked out on the trampoline to keep her size 12 figure. -- Life magazine, 1956 Marilyn Monroe The ideal 1950s man was the provider, protector, and the boss of the house. -- Life magazine, 1955 1956 William H. Whyte, Jr. The Organization Man A a middle-class, white suburban male is the ideal. A Changing Workplace Automation: 1947-1957 factory workers decreased by 4.3%, eliminating 1.5 million blue-collar jobs. By 1956 more white-collar than blue-collar jobs in the U. S. Computers Mark I (1944). First IBM mainframe computer (1951). Corporate Consolidation: By 1960 600 corporations (1/2% of all U. S. companies) accounted for 53% of total corporate income. WHY?? Cold War military buildup. 50’s SOCIETY THE AMERICAN DREAM: House in the ‘burbs TV in living room 2 cars in garage 50’s CONFORMITY •Suburbs, such as Levittown, NY flourish •1949 William Levitt produced 150 houses per week. •$7,990 or $60/month with no down payment. Suburban Living: The New “American Dream” k 1 story high k 12’x19’ living room k 2 bedrooms k tiled bathroom k garage k small backyard k front lawn By 1960 1/3 of the U. S. population in the suburbs.











