Unit IV – Evolution, Change, and Diversity (15% of Public Exam)
advertisement

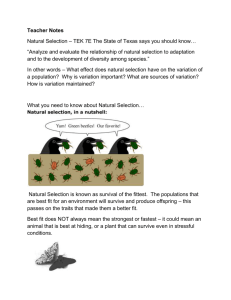
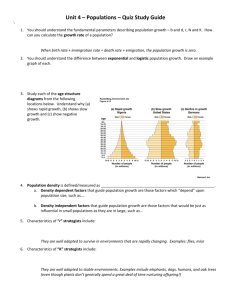
Unit IV – Evolution, Change, and Diversity (15% of Public Exam) Ch. 19 – Introducing Evolution (pp. 643 – 671) → what evolution is → natural and artificial selection → early ideas about evolution → evidence used to support evolution Ch. 20 – Mechanisms of Evolution (pp. 672-699) ( 1 Lab) → population genetics → various mechanisms of evolution → Hardy-Weinberg Principle Ch. 21 – Adaptation and Speciation (pp. 700-737) ( 1 STSE) → types of adaptations → theories on origin of life on Earth → how species form 19.1 Diversity of Life p. 643 → what is evolution? → natural selection → artificial selection What do you think Evolution is? Evolution • the relative change in the characteristics of populations that occur over successive generations • Read about it in you book (Section 19.1) Evolution • the relative change in the characteristics of populations that occur over successive generations • Read about it in you book (Section 19.1) Evolution • the relative change in the characteristics of populations that occur over successive generations Evolution • change in the • characteristics of populations that occur • over successive generations Adaptations in Evolution a particular: Structure (leaf, Leg Beak) –Physiology (digestion, metabolic rate) –behavior (nocturnal, arboreal) – that helps an organism survive and reproduce in a particular environment. What types of adaptations are these? Remember Adaptations in Evolution a particular Structure (leaf, Leg, Beak) or Physiology (digestion, metabolic rate) or behavior (nocturnal, arboreal) that helps an organism survive and reproduce in a particular environment. Variation in a Population • the form of a trait or significant deviation from the normal biological form, function, or structure. • Another word for Variation might be range • What is the variation or range in height among humans? • What is the variation or range in running speed? • What is the variation or range in intelligence? • All populations have variation (it easier to see in humans) Natural Selection Natural selection – process whereby the characteristics of a population of organisms change because individuals with certain inherited traits survive specific local environmental conditions. (Survival of the fittest) Individuals survive but populations change!! It is important to note that natural selection does not cause changes in individual organisms, rather entire populations of organisms over time. Natural Selection & Peppered Moths p. 644-645 Selective pressure environmental condition or conditions that select for certain characteristics of individuals and select against others. What was the selective pressure for the peppered Moth? Artificial Selection human selection of a particular trait Ex. Faster horses, disease-resistant plants, breeding of dogs