AIM CSIT presentation
advertisement

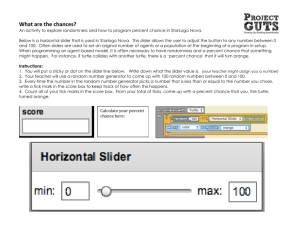
Computational Science: Middle Schoolers, Real World Problems, and Visualization TIE Conference 5 October 2007 Ruidoso, New Mexico Who are we? Celia Einhorn Betsy Frederick Irene Lee celia@pobox.com betsy.frederick@gmail.com lee@santafe.edu Supercomputing Challenge http://challenge.nm.org Growing Up Thinking Scientifically – Project GUTS http://projectguts.org Computational Science, Real World Problems and Visualization Introductions and Overview of The Challenge What is Computational Science? Population Growth Model – Paper Catchers Predator Prey Model – StarLogo 2.0, StarLogo TNG Virus Game and Infection Model Cool networking slides Word Walls, Concept Mapping and Cmap Fractals and Wolves and Sheep) and Blogging What is the Challenge? Formed in 1990, the Supercomputing Challenge is a statewide, school-year long competition set in a learning environment. Finalists, 2005 Who Are We? Secondary students work in teams on computational science problems. They are supported by teachers sponsors, mentors, and Challenge tutors. Expo, April 2007 The Challenge Year September – Registration, Project Proposals, Questions for Scientists October – Kickoff Workshops November – School Visits, Tutorials December – Interim Reports January – Peer Reviews February – First Project Evaluations March - Tour of Sandia National Labs April – Final Reports and Judging Expo of team projects Awards Day Celebration at LANL June-July – Summer Teacher Institute http://challenge.nm.org Challenge emphasis Students own interesting problems Mentors provide support, tutorials Computational science is emphasized Teamwork is encouraged Communication is oral, written, graphical Project planning for timelines, deadlines Community Teacher preparation and support Program Shifts Four years ago: Senator Bingaman urged us to include middle school students. We began a collaboration with MIT’s Adventures in Modeling: Exploring Complex, Dynamic Systems with StarLogo Program Shifts Summer 2007 Project GUTS Growing Up Thinking Scientifically NSF Academy for Young Scientists (NSFAYS) Informal, out of school program for middle school science, technology, engineering, and math (STEM). GUTS is an incubator for the Challenge. Program Shifts for Middle School Success Emphasis on “placed based” Month-long projects Data collection from multiple iterations Programming experiences Complex systems Epidemics, Traffic, Emergency egress, Pollution, Ecosystems. What is a complex system? Suppose you are studying traffic congestion. You could view it as a fluid dynamics problem and use mathematical equations to understand the underlying physics. You would probably use Java or MATLAB as your modeling tool. What is a complex system? Or you could look at it as a “complex system” composed of individual agents, drivers of cars in this case, that react to other drivers and to their environment. Here you might use StarLogo to model the problem. Some other examples Perhaps you are studying the spread of a disease or you’d like to understand bird flocking. Or the erosion in your neighborhood is a concern. Or you are figuring out escape routes from burning buildings or a large sporting stadium in case of an emergency. What else? Complex systems exhibit two properties 1) the system is composed of individual interacting agents who follow rules 2) the system exhibits emergent properties, that is, properties arising from the interaction of agents that can not be deduced simply by aggregating the properties of the individual agents. Tools and activities Offline activities Computer Software Programming StarLogo 2.0 and StarLogoTNG Vocabulary,language and relationships Blogs, word walls, concept mapping Project design, teamwork, timelines Paper Catchers – Population Growth Paper Catchers! Rules and patterns No limits. Restricted. Greatly restricted. Spread sheet, graph Rabbits and Grass A StarLogo Predator – Prey Model What are the sliders? How do they affect the model? What do the rules seem to be? What kind of curves are we seeing? Can you set the sliders to make the ecosystem steady? http://education.mit.edu/starlogo Fish and Plankton A StarLogo TNG Predator – Prey Model What are the sliders? How do they affect the model? What do the rules seem to be? What kind of curves are we seeing? Can you set the sliders to make the ecosystem steady? http://education.mit.edu/starlogo Participatory Simulations • Students become the “agents” in computermediated simulations of complex systems • Provide rich learning experiences where technology and social interaction are key • Use relatively simple and cheap technologies (Palms<$100) and Infrared peer-to-peer communication • Games include topics in economics, ecology, behaviour, mathematics, health sciences and the science of networks. Virus! …an interactive computer simulation of the spread of an infectious disease through a population. • StarLogo TNG Infection Model Like the Rabbits and Grass Model, in this example students can experiment with different initial conditions to make observations about phenomena. Networks as complex systems Networking is used more and more to study complex topics across broad areas of interest. What is a network? What are some characteristics of networks? Some examples of networks…..TB Some examples of networks…Les Miserables Network of Rivers Some examples of networks…Relationships neuronal morphologies in the auditory cortex "Texture of the Nervous System of Man and the Vertebrates" by Santiago Ramón y Cajal. Word Walls, Concept Mapping, Blogging Language is an important part of middle school curricula. Word walls Concept map – Cmap Blogs Fractals, Sheep and Wolves, Cogno’s Challenge Fractal Foundation Fractal activities, lesson plans and download Xaos, the free fractal zoomer http://www.fractalfoundation.org/ Wolves and Sheep Cogno’s Weekly Challenges Resources NECC – Atlanta- June 25, 2007 Links for Computational Science: Middle Schoolers, Real World Problems, and Visualization NM Supercomputing Challenge is an established school-year long project in which teams of secondary students design and implement computational science projects of their own choosing. The mission of the Supercomputing Challenge is to improve students' understanding and use of technology by developing their skills in scientific inquiry, modeling, computing, communication, and teamwork. http://challenge.nm.org Betsy Frederick, Supercomputing Challenge Program betsy.frederick@gmail.com Project GUTS gives students the opportunity to conduct scientific research right in their own school and around their neighborhood. Students will learn to use technology to explore realworld problems and analyze them with scientific tools. Later, they will have a chance to share their experiences and findings to advise local decision makers and inform fellow students. http://www.projectguts.org Irene Lee, Project Guts, Santa Fe Institute lee@santafe.edu StarLogo and TNG (The Next Generation) StarLogo is a programmable modeling environment for exploring the workings of decentralized systems -- systems that are organized without an organizer, coordinated without a coordinator. With StarLogo, you can model (and gain insights into) many real-life phenomena, such as bird flocks, traffic jams, ant colonies, and market economies. http://education.mit.edu/starlogo/ StarLogo – Irene Lee, Santa Fe Institutel ee@santafe.edu TNG - Hal Scheintaub, The Governor’s Academy, MIT hscheintaub@gda.org Resources, continued Participatory Simulations use Palm OS handheld computers to embed people inside of simulations. Interactions between players in the game are mediated by peer to peer beaming These simulations have been used with students (from fourth grade through graduate school) and teachers (in science, math, technology, and social sciences). Most PDA simulations have a related StarLogo activity. http://education.mit.edu/pda/pda@education.mit.edu Research Tips from Oregon School Library Information System share citation maker links along with Research Process, Search Strategies, Gathering & Organizing Information, Beyond Surfing, Evaluating Information, Citing Sources, Presenting Results and Online Tools. http://www.oslis.org/secondary/index.php Cmap Excellent free concept modeling software. http://cmap.ihmc.us/ Fractal Foundation Fractal activities, lesson plans and download Xaos, the free fractal zoomer http://www.fractalfoundation.org/ Triazzle PuzzleMosaic puzzles for problem solving, geometry and team buildingwww.triazzle.com/ NETS Standards Addressed: grades 6-8 and 9-12 Emphasis on Collaboration and Simulations • Use content-specific tools, software, and simulations to support learning and research. (3,5) • Apply productivity tools... to support group collaboration, and learning throughout the curriculum. (3,6) • Collaborate with peers, experts, and others using telecommunications and collaborative tools to investigate curriculum related problems.... (4,5) • Select and use appropriate tools and technology resources to accomplish a variety of tasks and solve problems. (5,6) • Select and apply technology tools for research, information analysis, problem-solving, and decision-making in content learning. (4,5) • Investigate and apply expert systems, intelligent agents, and simulations in real-world situations. (3,5,6) • Collaborate with peers, experts, and others to contribute to a contentrelated knowledge base by using technology to compile, synthesize, produce, and disseminate information, models, and other creative works. (4,5,6)