fraction computation 2012
advertisement

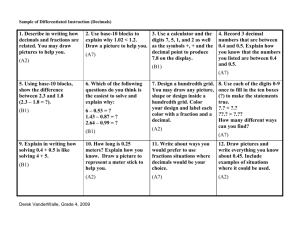
Welcome! Quiz 3 • Please use the explicit trade model for these division problems by drawing a picture of base ten blocks and include written explanations for each step. 1. 153/2 2. 315/5 Book Shares Solve: Use words, pictures and numbers to answer the problem. Be sure you can explain why your answer is correct. • 3/4 x 8 • 4 x 2/3 Solve: Use words, pictures and numbers to answer the problem. Be sure you can explain why your answer is correct. • 2/3 x 3/4 Solve: Use words, pictures and numbers to answer the problem. Be sure you can explain why your answer is correct. • 1/2 x 3/4 Use words, pictures and numbers to answer the problem. Be sure you can explain why your answer is correct. • There were 3¾ gallons of lemonade in the cooler for the class picnic. During the picnic, the students drank ⅔ of this lemonade. How many gallons did they drink? Use words, pictures and numbers to answer the problem. Be sure you can explain why your answer is correct. • Carlos and his father were sharing a large pizza. Carlos’ father ate ⅓ of the pizza and Carlos ate ¾ of the rest. How much of the whole pizza did Carlos eat? Use words, pictures and numbers to answer the problem. Be sure you can explain why your answer is correct. • Someone ate 1/10 of the cake, leaving only 9/10. If you eat 2/3 of the cake that is left, how much of a whole cake will you have eaten? Use words, pictures and numbers to answer the problem. Be sure you can explain why your answer is correct. • Gloria used 2 1/2 tubes of blue paint to paint the sky in her picture. Each tube holds 4/5 ounce of paint. How many ounces of blue paint did Gloria use? Decimals/Percents Big Ideas 1. Decimal numbers are another way of writing fractions. 2. The base-ten place-value system extends infinitely in both directions. 3. The decimal point is a convention to indicate units position. 4. Percents are hundredths and another way to express fractions and decimals. 5. Addition and subtraction with decimals are a simple extension of whole numbers. 6. Multiplication and division of two numbers will produce the same digits, regardless of the positions of the decimal points. Copyright © Allyn and Bacon 2010 Connecting Fractions and Decimals • Base-ten fractions — base-ten fraction models — multiple names and formats • Extending the place-value system — a two-way relationship — the role of the decimal point — the decimal with measurement and monetary units • Fraction–decimal connection Copyright © Allyn and Bacon 2010 Introducing Percents • Models and terminology • Realistic percent problems • Teaching percents 1. Limit the percents to familiar fractions 2. Do not suggest any rules or procedures 3. Use terms part, whole, and percent 4. Require students to use models or drawings 5. Encourage mental computation • Estimation Copyright © Allyn and Bacon 2010 Where Does the Decimal Point Go? • 23.408 + 3.6 + 124.052 + 7.75 = 1 5 8 8 1 0 0 Where Does the Decimal Point Go? • 714.6 − 35.0112 = 6 7 9 5 8 8 8 Where Does the Decimal Point Go? • 7.8 × 24.35 = 1 8 9 9 3 Where Does the Decimal Point Go? • 8.432 × 5.75 = 4 8 4 8 4 Where Does the Decimal Point Go? • 3.326 × 0.32 × 31.5 = 3 3 5 2 6 0 8 Where Does the Decimal Point Go? • 306.15 ÷ 75.4 = 4 0 6 0 3 4 4 8 Problem of the week • Ann and Sue bought identical boxes of stationery. Ann used hers to write 1-sheet letters, and Sue used hers to write 3-sheet letters. Ann used all the envelopes and had 50 sheets of paper left, while Sue used all of the sheets of paper and had 50 envelopes left. How many sheets of paper and how many envelopes were in the box to begin with?