Unit 2 I - Public Schools of Robeson County
advertisement

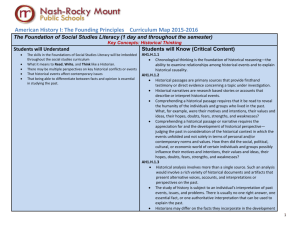
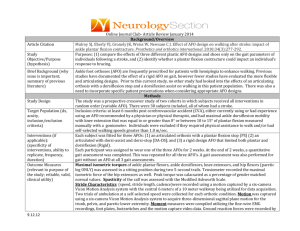
Public Schools of Robeson County AH1 Unit 2 AMERICAN HISTORY 1 INSTRUCTIONAL ALIGNMENT Essential Standard: AH1.H.1 Apply the four interconnected dimensions of historical thinking to United States History Essential Standards in order to understand the creation and development of the United States over time AH1.H.2 Analyze key political ,economic and social turning points in United States History using historical thinking AH1.H.4 Analyze how conflict and compromise have shaped politics, economics and culture in the United States AH1.H.3 Understand the factors that led to the exploration, settlement, movement and expansion and their impact on the United States development over time. AH1.H.5 Understand how tensions between freedom, equality and power have shaped the political, economic and social development of the United States. AH1.H.7 Understand the impact of war on American politics, economics, society and culture. AH1.H.6 Understand how and why the role of the United States in the world has changed over time. AH1.H.8 Analyze the relationship between progress, crisis and the “American Dream” within the United States Clarifying Objective(s): Essential Question(s): AH1.H.1.1 (Use Chronological thinking) 1. Why did English policy after the French and Indian War lead to a colonial AH1.H.1.2 (Use Historical Comprehension) rebellion? AH1.H.1.3 (Use Historical Analysis and Interpretation) 2. What role did the development of an American identity and the desire for selfAH1.H.1.4 (Historical Research) government play in the growing tensions between the colonies and England? AH1.H.2.1: Analyze key political, economic and social turning points from 3. How did the “power of the pen” influence the political atmosphere in the colonies colonization through Reconstruction in terms of causes and effects prior to the American Revolution? AH1.H.2.2: Evaluate key turning points from colonization through 4. What role did cultural differences and location play in the divisions of people, Reconstruction in terms of their lasting impact. colonial and indigenous, during the American Revolution? AH1.H.3.2 Explain how environmental, cultural and economic factors influenced the patterns of migration and settlement within the U.S. before the Civil War AH1.H.4.1 Analyze the political issues and conflicts that impacted the United States through reconstruction and the compromises that resulted. AH1.H.4.2 Analyze the economic issues and conflicts that impacted the United States through Reconstruction and the compromises that resulted AH1.H.4.4 Analyze the cultural conflicts that impacted the United States through Reconstruction and the compromises that resulted AH1.H.5.1 Summarize how the philosophical, ideological and/or religious views on freedom and equality contributed to the development of American political and economic systems through Reconstruction AH1.H.6.1 Explain how national, economic and political interests helped Public Schools of Robeson County set the direction of United States foreign policy from independence through Reconstruction AH1.H.7.1 Explain the impact of wars on American politics through Reconstruction AH1.H.7.2 Explain the impact of wars on the American economy through Reconstruction AH1.H.7.3 Explain the impact of wars on American society and culture through Reconstruction AH1.H.8.2 Explain how opportunity and mobility impacted various groups within American society through Reconstruction Pacing Guide: 10 Day Unit of Study Establishing an American identity and American Revolution Major Concepts conflict, war, international affairs, freedom, war, American dream AH1 Instructional Task Define current vocabulary Essential Vocabulary Pre: Instructional Resources Text Resources: Discuss concepts for the unit of study. Revolution Enlightenment and Enlightenment philosophies Self-government Prentice Hall, United States History, 2008 Examine and explain the impact of economic, political and social policies on the American Revolution and the aftermath. Analyze reasons for and impact of American Revolution Compare and contrast tactics and motives of European nations vying for empire. Formulate ideas that explain the impact of the Current: Albany Plan of Union Bacon’s Rebellion Boston Massacre Boston Tea Party Connecticut Plan/ Great Compromise Declaratory Act English Bill of Rights French and Indian War Fundamental Orders of Connecticut “Declaration of Independence” p. 21-25 “Liberty or Death” p. 1041 “Common Sense” p. 1042 “Free and Independent States” p. 1043 “Virginia Statute for Religious Freedom” p. 1043 Articles of Confederation “The Northwest Ordinance” p. 1044 Digital Resources: Excerpts from Paine’s Common Sense http://xroads.virginia.edu/~Hyper2 /CDFinal/Paine/cover.html Sample Assessment Prompts Explain why colonists objected to writs of assistance and viceadmiralty courts. Explain what the British meant by virtual representation and why the American colonists rejected the concept. Between 1689 and 1763 Britain and France and their respective allies fought four wars for supremacy in Europe and control of India and North America. Discuss the impact of those wars on America and relations between Britain and her thirteen colonies. Public Schools of Robeson County separation from the mother country on the American Dream. Explain the transformation of American economics, society, and politics and determine the limits of the transformation. AH1 House of Burgesses Indentured servants Intolerable Acts/Coercive Acts John Locke Jonathan Edwards Joint-stock Companies Northwest Ordinance of 1787 Proclamation of 1763 Quartering Act Social Contract theory Sons of Liberty Stamp Act Stamp Act Congress Sugar Act Tea Act Townshend Acts Treaty of Paris, 1763 and Treaty of Paris, 1783 Articles of Confederation Whiskey Rebellion The Declaration of Independence http://www.archives.gov/national_a rchives_experience/charters.html John Dickinson’s Letters from a Farmer 1767-68 http://www.earlyamerica.com/early america/bookmarks/farmer/ Edmund Burke - Speech on Conciliation with America, March 22, 1775. http://www.earlyamerica.com/early america/firsts/cartoon/snake.html PBS Video – “Liberty! The American Revolution” The Revolutionary Era, Documents of Destiny, Goldhil Home Videos Chronicle of the Revolution & The Road to Revolution http://pbs.org/liberty/ Curriculum Pathways Resources (available at: www.sasinschool.com) Becoming “Enlightened”: Introductory: Generating a Group Quiz from Primary Source Documents, Web Lesson 594 Federalism Civic participation The Influence of John Locke, Web Lesson 616 Public Schools of Robeson County AH1 The Stamp Act, InterActivity 30 These documents can be found at the web site for the Avalon Project at Yale Law School • English Bill of Rights • Thomas Paine, Common Sense • Declaration of Independence • DeToqueville’ Democracy in America • English Petition of Rights • Patrick Henry’s speeches • Jefferson’s writings on law • John Lockes’ Treatises • Magna Carta • Mayflower Compact • Montesquieu’s Spirit of the Law • Pledge of Allegiance • Rousseau’s Social Contract • Maryland Toleration Act • Virginia Declaration of Rights, Literary Connections: Primary Source Documents: “Common Sense” Declaration of Independence” “Federalist Papers” etc. “1776” David McCullough "Benedict Arnold: Patriot and Traitor” Willard Sterne Randall “The Americanization of Benjamin Franklin” Gordon S. Wood Public Schools of Robeson County AH1 “Liberty’s Exiles: American Loyalists in the Revolutionary World” Maya Jasanoff