Professional Life Cycle Mine, Your's, and SLA's
advertisement

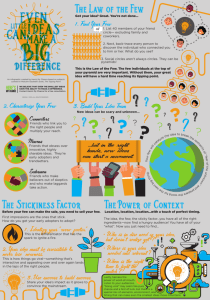
Tipping Points and Competencies: Our Profession and our Association Ethel M. Salonen, MSLS June 9, 2003 SLA Annual Conference Professional Competencies for the Digital Age: Cybrarian, Librarian, or Information Specialist Agenda • • • • • • • Tipping Point – What is it? Examples Tipping Point – What does it mean? SLA 2003 Competencies Document – June How the two relate Conclusions Bibliography Ethel M. Salonen 2 What is a “Tipping Point?” – “A tipping point is that moment in an epidemic when it reaches a critical mass; it’s the point on the curve when the epidemic starts to take off.” – “Ideas and products and messages and behaviors spread just like viruses do.” – “Three characteristics – contagiousness, the fact that little causes can have big effects, and that change happens not gradually but at one dramatic moment.” – “The moment of critical mass, the threshold, the boiling point. “ – “Why is it that some ideas or behavior or products start epidemics and others don’t?” • Gladwell, Malcolm. The Tipping Point: How Little Things Can Make a Big Difference. Little, Brown and Company, January 2002, 301pages. Ethel M. Salonen 3 Some examples • • • • • • Hush Puppies – East Village of Manhattan Paul Revere’s Ride to Lexington, MA Sesame Street William Bratton Internet Web based platforms Ethel M. Salonen 4 Three rules of the Tipping Point • The Law of the Few • connectors – know lots of people, special gift for bringing people together, information specialists, social glue • maven – one who accumulates knowledge, connects people to the marketplace and has the inside scoop on the marketplace, data banks • salespeople – skills to persuade us when we are unconvinced of what we are hearing, energetic, enthusiastic, charming Ethel M. Salonen 5 Three rules of the Tipping Point (cont.) • The Stickiness Factor • the content of the message must be so memorable that it can create change and spur someone to action • can be small and trivial • The Power of Context • epidemics are sensitive to the conditions and circumstances of the times and places in which they occur • epidemics can be reversed, tipped, by tinkering with the smallest details of the immediate environment • minor changes in our external environment can have a dramatic effect on how we behave and who we are Ethel M. Salonen 6 Professional Competencies • Relates to the practitioner’s knowledge of information resources, access, technology and management, and the ability to use this knowledge as a basis for providing the highest quality information services. • There are 4 major competencies, each augmented with specific skills • Draft: Competencies for Information Professionals of the 21st Century, Revised: June 2003 Ethel M. Salonen 7 Professional Competencies (cont.) • Four competencies – Managing information organizations • alignment, assessment and communication, effective processes, strategic planning, team leader, marketing skills, product development, copyright and intellectual property issues – Managing information resources • product life cycle, collection management, content management, policy development Ethel M. Salonen 8 Professional Competencies (cont.) • Four competencies – Managing information services • client driven information services, client driven market research, research information products, metrics management, value based services – Applying information tools and Technologies • tool driven solutions, information organization management, privacy, current awareness services Ethel M. Salonen 9 Personal Competencies • Represent a set of attitudes, skills and values that enable practitioners to work effectively and contribute positively to their organizations, clients and profession. These competencies range from being strong communicators, to demonstrating the value-add of their contributions, to remaining flexible and positive in an ever changing environment. Ethel M. Salonen 10 Personal Competencies (cont.) • • • • • • Seeks our challenges and new opportunities Sees the big picture Effective communicator Creates partnerships and alliances Mutual respect and trust Team approach Ethel M. Salonen 11 Personal Competencies (cont.) • • • • • • • • Knows how to prioritize Career planning skills Innovative and creative thinker Networking skills Work/Life balance skills Adaptable to change Positive and flexible Celebrates achievements for others and self Ethel M. Salonen 12 Tipping Point and Competencies • We are connectors – KM, workflow tools • We are mavens – information specialists • We are salespeople – selling intranet services • The vote on the proposed name change – Law of the Few, Stickiness, Power of context Ethel M. Salonen 13 Conclusions • Tipping Point – Starting epidemics requires concentrating resources on a few key areas. The Law of the Few says that Connectors, Mavens, and Salespeople are responsible for starting word-of-mouth epidemics, which means that if you are interested in starting a word-of mouth epidemic, your resources ought to be solely concentrated on those three groups. • SLA’s Tipping Point – Whatever decision is made at the June 2003 Annual Business Meeting • Professional Tipping point – How each of use uses these skills to bring effective change to our organizations. Ethel M. Salonen 14 Bibliograhpy • Cross, Rob and Larry Prusak. “The People Who Make organizations Go—or Stop.” The Harvard Business Review, June 2002, P. 104 • Gladwell, Malcolm. The Tipping Point: How Little Things Can Make a Big Difference. ittle Brown and Company, January 2002, 301 pages. • Kim, W. Chan and Renee Mauborgne. “Tipping Point Leadership.” The Harvard Business Review, June 2003, P. 60 Ethel M. Salonen 15 Questions • Thank you! Ethel M. Salonen Manager, External Content Information Resources Millennium Pharmaceuticals 75 Sidney Street Cambridge, MA 02139 Voice: 617-444-1297 Email: salonen@mpi.com Ethel M. Salonen 16